Foam concrete blocks - their advantages, disadvantages, selection criteria and tips for use
This material weighs very little, but it is very durable and excellent in keeping heat. And he has the ability to easily remove excess moisture, passing it through his pores. We are talking about foam concrete, which is far from familiar to everyone. Because of this, many people think that it is not at all suitable for building houses. However, the foam concrete blocks characteristics are such that they are quite capable of replacing bricks or cinder blocks. But you need to work with them a little differently. And how - read on.

Foam concrete blocks: types, brands and basic parameters
There are 4 varieties of foam produced in a non-autoclave method.
1. Materials of grades from D150 to D400 are called heat-insulating. Their density varies from 150 to 400 kilograms per cubic meter. Grades below D400 are not rated by strength class. And for the D400, this parameter ranges from B0.5 to B0.75. This corresponds to a tensile strength of 9 kilograms per cm.3. The frost resistance of the listed grades of foam concrete is not subject to standardization.
2. Materials of grades from D500 to D900 are called structural and thermal insulation. They have a density of 500 to 900 kilograms per cubic meter. The strength of the D500 brand is 13 kilograms per square centimeter. Its class is not standardized, as well as frost resistance. Strength classes for other brands:
- D600 - from B1 to B2 (strength 16 kilograms per square centimeter);
- D700 - from B1.5 to B2.5 (strength 24 kilograms per square centimeter),
- D800 - from B2 to B3.5 (strength 27 kilograms per square centimeter),
- D900 - from B2.5 to B5 (strength 35 kilograms per square centimeter).
The coefficient of frost resistance F in increasing order of the brand: 15-35, 15-50, 15-75, 15-75.
3. Materials of grades from D1000 to D1200 (structural) have a density of 1000 to 1200 kilograms per cubic meter. According to the strength class, the parameters are as follows:
- D1000 - from B5 to B7.5 (strength 50 kilograms per square centimeter),
- D1100 - from B7.5 to B10 (strength 64 kilograms per square centimeter),
- D1200 - from B10 to B12.5 (strength 90 kilograms per square centimeter).
The coefficient of frost resistance F is the same for any of the brands: its value is 15-50.
4. Materials of grades from D1300 to D1600 are called structurally porous. Their density varies from 1300 to 1600 kilograms per cubic meter. They are produced in small batches, therefore, the characteristics of the foam blocks of these brands do not have designations in GOST.
The specific strength indicator depends on the temperature and humidity at which the foam concrete was produced, as well as its filler and the brand of cement used. Dividing the number of foam concrete brands by 20, you can get an approximate indicator of strength (though slightly underestimated). Take, for example, D1600 foam concrete. We get (with a decent margin) tensile strength of 90 kilograms per cm2. However, the stock in this case will only benefit.
Consider the thermal conductivity of various grades of dry foam, the filler of which is sand. The unit is watts per meter per degree Celsius. And also under the same conditions, the vapor permeability coefficients of these foam concrete brands are also comparable. The unit is kilogram per meter-hour-Pascal.
| Grades of foam concrete blocks | Thermal conductivity, (W * m *0FROM) | The coefficient of vapor permeability, (Kg * m hour * Pa) |
|---|---|---|
| D300 | 0,08 | 0,26 |
| D400 | 0,1 | 0,23 |
| D500 | 0,12 | 0,2 |
| D600 | 0,14 | 0,17 |
| D700 | 0,18 | 0,15 |
| D800 | 0,21 | 0,14 |
| D900 | 0,24 | 0,12 |
| D1000 | 0,29 | 0,11 |
| D1100 | 0,34 | 0,1 |
| D1200 | 0,38 | 0,1 |
As for the dimensions, the brands D600 and D800 have dimensions of 20 by 30 by 60 centimeters. D600 is also produced in the amount of 10 by 30 by 60 centimeters.
Comparative characteristics of foam concrete and other building materials
| Parameters | Ceramic brick | Ceramic block | Silicate brick | Gas block | Foam block |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sizes, cm | 25/12/6,5 | 38/25/24 | 25/12/6,5 | 20/30/60 | 20/30/60 |
| Wall weight, kg / m2 | 1200 - 1800 | 600 - 800 | 1450 - 2000 | 100- 900 | 100 - 900 |
| Density, kg / m3 | 1500 - 1750 | 700 - 900 | 1700 - 1950 | 300 - 1200 | 300 - 1200 |
| Water absorption,% | 12 | 12 - 14 | 16 | 20 | 14 |
| Thermal conductivity, W / M * K | 0,4 - 0,7 | 0,1 - 0,2 | 0,8 - 1,1 | 0,1 - 0,4 | 0,1 - 0,4 |
| Frost resistance cycle | 25 | 50 | 25 | 35 | 35 |
| The limit of compressive strength, MPa | 2,5 - 25 | - | 5 - 30 | 0,5 - 25 | 0,25 - 12,5 |
| Consumption, pcs / m3 | 400 - 500 | 34 - 45 | 400 - 500 | 21 - 27 | 21 - 27 |
| Price, $ / m3 | 63 - 112 | 62 - 90 | 17 - 90 | 60 - 94 | 49 - 68 |
What is good and what is bad foam concrete
Both on television, in the press, and on the Internet, there is debate about which foam concrete is better - autoclaved or non-autoclaved. Manufacturers of both types of material angrily denounce each other's products, and consumers can only speculate on which of the materials is best suited for construction. But in fact, both gas silicate and foam concrete blocks are very close in properties, and both materials have disadvantages. Next, we consider in detail the characteristics of foam concrete, trying to give this material an objective assessment. Moreover, in all respects we will compare it with gas silicate.
Advantages of non-autoclave foam blocks
The ability to retain heat is high. Compared with brick, this material has a thermal conductivity coefficient less than three times. In fact, gas silicate blocks are not far behind in this. The thermal conductivity index of them is at the same level as that of foam blocks.
Weight is light. Compared with expanded clay, it is two and a half times less. Gas silicate weighs about the same. Therefore, blocks from both autoclave and non-autoclave foam concrete are easier to load, transport and assemble than traditional building materials. And from them you can build houses without equipping them with a heavy foundation, which will affect the speed and ease of installation. Naturally, we are talking about low-rise buildings - in high-rise buildings, the foundation must be solid.
Durability is sufficient. Of the foam concrete blocks of grades from D900 and higher, it is completely possible to put load-bearing walls of three-story (no higher) houses.

If you also mount a reinforced concrete supporting frame, then you can build a building of any number of storeys.
As for gas silicate blocks, they are even stronger.
Resistance to frost is excellent. Due to the porous structure, both foam concrete and gas silicate have enough space inside for water, which expands when it freezes. Therefore, when a wall freezes, its damage will not occur both outside and inside.
Fire resistance is good. This applies to foam concrete blocks, and gas silicate. About four hours, no less, they are capable of being exposed to open fire and very high temperature.
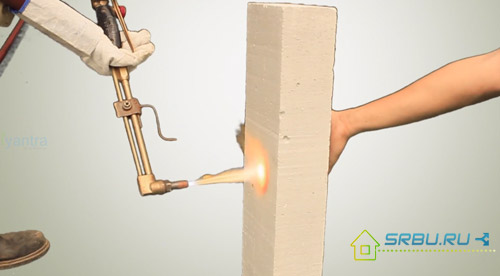
This is easy to verify: aim the gas burner on a wall made of foam concrete, and then observe for several hours. The result will please - unlike ordinary concrete, there will be neither splitting of the surface, nor explosions.
Environmental friendliness and biostability - on top. This material is not subject to decay and does not deteriorate from time to time. He does not emit harmful substances hazardous to health. By the way, when compared with gas silicate, the latter is less safe in this regard. Indeed, in the autoclave, when foaming, the smallest pieces of aluminum and lime enter into a chemical reaction, resulting in hydrogen. It will stand out (in small quantities) later, during the installation of blocks, and during operation of the house. But for the production of foam concrete, foaming agents (synthetic or protein) are used, which do not contain hazardous gases. Yes, and the pores of this material are tight - they are the same in structure as the foam.
Suitability for monolithic construction is utter. Foam concrete blocks can be made on the spot - just put the installation. To create the necessary pressure with a compressor and to supply the material obtained through a special hose to where it is necessary during the construction process.Monolithic construction has its own specifics, and for it, foam concrete can only be insulation or additional material.
So, for example, it is possible to make a brick wall half a brick thick either inside or outside. Then (not end-to-end) they put a moisture-proof drywall partition. Foam concrete is poured into the resulting gap for thermal insulation. This will take a little time, and will cost less than installing a traditional heat insulator.
Ease of processing - very impressive. Foam concrete is very easy to cut, drill and hammer. No special tools are required, and physical efforts are practically not necessary. Moreover, due to the lightness of the material, you can easily transfer the blocks to the place of processing and vice versa.
The price is quite low. Compared to other building materials, foam concrete blocks significantly benefit in value. As a rule, a comparison is made, recounting the volume of material on a brick. If we take into account the fact that the foundation is needed inexpensive (lightweight), then the construction will turn out to be very economical. In some cases, this is a determining factor.
Moisture resistance is not bad. Sealed closed cells contribute to this. But gas silicate blocks having channels inside, passing from one edge of the material to the other, are afraid of water. After all, she impregnates them quickly enough, passing through these channels.

The closed structure of the cells does not allow water to penetrate the entire thickness of the block and if it is put on the surface of the water, it will float.
Disadvantages of foam concrete blocks
Shrinkage due to the high moisture content is a significant minus. Moreover, it can be from one to three millimeters per meter of the wall being erected. This happens if in the process of water production add more than necessary, or not wait until 28 days have passed. It takes so much time for the blocks to solidify well. In this case, they should in no case get water. Unfortunately, some dishonest manufacturers do not comply with the technology. But gas silicate is devoid of this drawback - it is not subject to shrinkage. Therefore, such precautions should not be taken when working with it.
The ability to absorb moisture in the material is available. It is not very large (much smaller than that of gas silicate blocks), but it forces the use of additional finish. In particular, you can apply the technology of a ventilated facade, plaster the walls or cover them with a special water repellent designed for concrete. This product is available in the form of an emulsion.
Foam concrete can easily chip, especially on the edges. It is necessary to load this material carefully, in no case without piling it into the body. In principle, the lightness of the material allows it to be carefully transferred without any damage.
Walls made of foam concrete will not hold either nails or ordinary dowels - they just fall out. It is necessary to use a special dowel for foam concrete with a nozzle made of ABC plastic. There is a thread on this nozzle. First, a metric screw should be screwed into this nozzle. A screw designed for wood is also suitable. Having drilled a hole in the wall and having thoroughly cleaned it, it is necessary to screw the nozzle with a screw inside very carefully. This design holds quite reliably.
Manufacturers who do not comply with the technology and the ratio of the necessary components, which do not allow foam concrete to mature, contribute to the appearance of negative reviews about this material. They are pushed by the thirst for quick profit. But reliable foam concrete companies that monitor the quality of their products produce materials that satisfy the most demanding developer. Laboratory tests confirm this - the technical characteristics of the foam block manufactured by such a company fully comply with all standards.
Choosing foam concrete correctly - selection criteria
1. First of all, see who exactly makes these foam blocks. Ask for a certificate, check delivery conditions and product compliance with GOSTs.If the manufacturer openly provides maximum information, it means that he has nothing to hide, and he has the material of the proper quality. By the way, this is what large companies do, reliable and well-established. A good foam block manufacturer usually has a production area of at least 180 square meters, on which stands a unit for cutting blocks. Moreover, the production room must be heated and have a roof.
2. Price matters too. On average, for the D800 brand, it is about $ 80 per cubic meter. If the material is much cheaper, it is worth considering - this may affect the quality.
And one more thing: if the manufacturer convincingly declares that his foam concrete of the D600 brand is structural, as it is made using “secret” technology, do not believe it. No special recipes, no subtleties of technology will not be able to turn one brand into another. You cannot even lay out a small one-story house with such blocks - this brand of material cannot be used for load-bearing walls.
3. Carefully inspect the blocks - they should not be pure and bright white. This will not allow technology. Normally, foam concrete should be grayish, slightly lighter or darker, and non-uniform surface color is not allowed.
4. Check how tight the foam cells are. If they are interconnected, moisture will easily penetrate into the material. Chop one block and see if its structure is the same on the outside and inside. The cells must be round, no chips or cracks are allowed.
5. To put walls without problems, the blocks must be strictly rectangular - check this. Putting two foam blocks on top of one another, try to sway them, see if there are any gaps. Moreover, examine all four sides of the blocks - this is important, since a flaw can only be on one side. And in the future, this can take you a lot of time, and spoil your nerves.
6. Having bought fresh material, do not immediately use it for walling. After all, foam concrete blocks will acquire the necessary strength and other technical characteristics only 28 days after manufacture. Therefore, the most appropriate solution is to withstand the foam concrete purchased for two or three weeks. At the same time, it should be either well covered from moisture, or be indoors. This will help you avoid troubles if you were sold the same underexposed material.

An example of improperly organized storage of foam blocks, they are not covered by anything from above and it is already clear that moisture was sodden from the moist earth.
Tips for using foam blocks
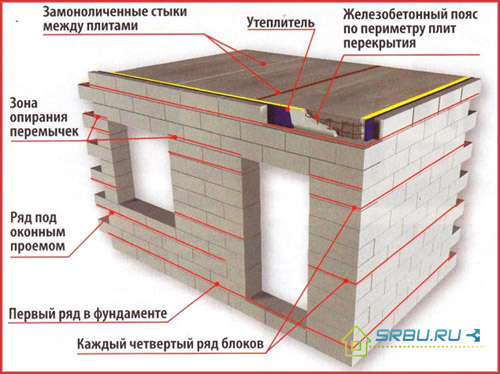
This infographic shows the features and nuances of performing masonry from foam blocks.
Tip 1. Since foam concrete blocks are easily damaged on the edges, try to unload them carefully. It is better to put them not on a standard solution (although this is possible for them), but on a special glue with a cement base. Its layer (only 2 or 3 millimeters) will turn out much thinner than a layer of ordinary cement mortar, and cold bridges will not appear. But the thick seams between the blocks will inevitably release some of the heat out.
Tip 2. Walls made of foam concrete, without fail, need cladding. Do not believe the manufacturers claiming the opposite - they shamelessly lie. Rains, snow, winds and hurricanes will gradually destroy foam concrete if it is not protected by anything. The facing material may well be plaster (both conventional and mineral), as well as the material used for ventilated facades. As for the plaster, you will need to lay a mesh under it, fixing it to the wall of foam concrete.
Tip 3. When facing foam blocks with brick, be sure to leave an air gap - because these materials have different permeabilities to air. With their tight fit, water vapor will not be able to break through the brick lining. They will bounce off of it, go back through the foam concrete and return to the house. Do not allow this.
Video. House of foam concrete blocks







