Arbolite blocks - disadvantages, advantages and characteristics
Arbolite in most sources is described as a material with wonderful properties. Advertising articles extol arbolite blocks, material deficiencies are modestly silent. But miracles do not happen, there are also disadvantages. In order to maximize the use of positive qualities and neutralize the negative, it is worthwhile to thoroughly understand the properties of arbolite, its characteristics and application features.

Content:
- Composition and production of arbolite blocks
- Arbolite density
- Strength of Arbolite Blocks
- Thermal conductivity of wood concrete
- Moisture absorption
- Frost resistance
- Material shrinkage
- Fire resistance of wood concrete blocks
- Soundproofing
- Vapor permeability
- Disadvantages of Arbolite Blocks
- Advantages of arbolite blocks
Composition and production of arbolite blocks
We start our material with the composition and production process. The thing is that the presence or absence of certain material defects depends on the quality of the performance of certain processes. And this is very important. Arbolit is positioned as one of the varieties of coarse-grained lightweight concrete. It uses wood chips as a filler. Wood chips are bonded into a monolithic structure with cement paste.
The material is used in construction in several ways:
- large-format masonry blocks;
- hollow blocks;
- heat insulating plates;
- mixtures for pouring walling in place.
Masonry blocks have found the widest application and the term "arbolit" is understood, first of all, as they. The most common size of arbolite blocks is 500 × 300 × 200 mm. But in recent times, manufacturers have begun to expand their product lines and offer arbolite in other sizes.
The manufacturing technology of the blocks is relatively simple, but as elsewhere, there are subtleties. The quality of future products depends on compliance with several important manufacturing issues. If the manufacturer uses the term "arbolite" in the name of his product, he must comply with the requirements of the regulatory documentation for such products, these are:
- 1. GOST 19222-84 "Arbolite and products from it. General specifications."
- 2. SN 549-82 "Instructions for the design, manufacture and use of structures and products from wood concrete."
The composition of arbolite blocks
For the manufacture of wood concrete blocks used:
- Wood chips;
- Chemical additives;
- Water;
- Cement.
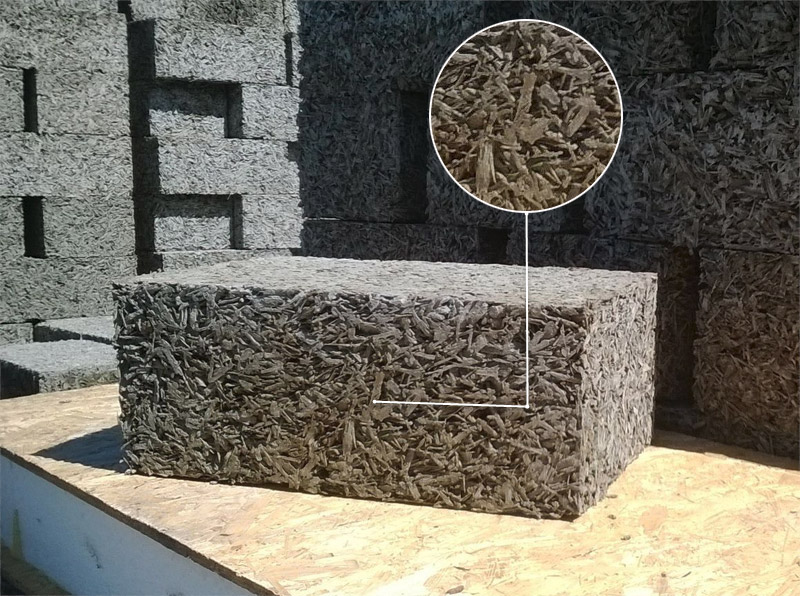

#1. Wood chips. The final strength is highly dependent on the size of the chips. In order to produce exactly arbolite, the properties of which are strictly normalized, chips should be used for production. Its sizes are regulated. GOST recommends a maximum particle size of 40 × 10 × 5 mm (length / width / thickness).
The best performance for blocks with chip sizes from the intervals:
- length - up to 25 mm;
- width - 5..10 mm;
- thickness - 3..5 mm.
Sawdust, shavings, thyrs, bonfire, straw and everything else that they try to mix with cement for the production of wood concrete is not suitable for its manufacture. Only clean wood chips without bark, leaves, soil and other undesirable impurities. It is believed that adding up to 10% of the bark or 5% of the foliage does not seriously affect the characteristics of arbolit. But it is better when these impurities are absent.
Often the production of wood concrete blocks, organized at sawmills and other wood processing enterprises. For them, arbolite is not a core business. As a result, unscrupulous manufacturers, in order to increase the profitability of production, add what is available, in addition to the chips themselves. Hence the unpredictable quality of the products.

Specialized enterprises install productive roll crushers calibrated to the desired chip size.
For the final consumer, the type of wood from which the raw materials are produced does not matter much, but technologists must take this into account for the correct dosage of mineralizers and the choice of degree of compaction. So, larch wood chips require a double amount of additives relative to other conifers. More often than others, pine, spruce, and less often hardwood are used for the production of wood chips.
#2. Chemical additives. The wood filler contains sugars that prevent the adhesion of cement paste to the surface of wood particles.
To solve this problem, 2 main strategies are used:
- 1. Drying of wood raw materials before use in production for several months.
- 2. Mineralization of the surface of the chips in a solution of chemical components.
The best results are achieved with an integrated approach to solving the problem. Reducing the sugar content and mineralization of raw materials allows us to solve other important tasks:
- increasing the biological resistance of the material;
- reduction in water permeability during operation of the finished product.
To solve all these problems, the following components can be used in the production of arbolite: calcium chloride (GOST 450–77), water glass (GOST 13078–67), silicate block (GOST 13079–67), alumina sulfate (GOST 5155–74) , lime (GOST 9179–77).
#3. Water. Arbolite blocks whose characteristics correspond to the given ones can be obtained by following a certain order of technological operations. Water with the addition of mineralizers is prepared in advance. Consumption of components is taken in the following ratios:
| Additive | CaCl2 | Al2 (SO4)3 | Al2(SO4)3+ Ca (OH)2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumption per 1m3 wood concrete, kg | 12 | 12 | 8+4 |
Chips are poured into the forced action mixer. Conventional gravity concrete mixers do not provide sufficient homogenization. Water with a dissolved mineralizer is mixed and evenly distributed over the surface of the chips. Mixing takes place over 20 seconds. At the next stage, cement is added. Mixing with cement lasts 3 minutes.
#4.Cement. Sufficient material strength for use in construction is achieved only when cement with a grade of at least 400 is used. Cement has the property of quickly losing the grade during storage. Even at the factory outlet, cement often does not meet the declared characteristics. Therefore, it is better when, arbolitic blocks, the technical characteristics of which must meet the requirements for structural materials, are made of 500th cement.
Block forming
Molding must be completed within the next 15 minutes after mixing. Depending on the degree of mechanization of subsequent processes, the following molding methods are distinguished:
- manual molding without vibration;
- manual molding with vibration;
- production on a vibrating machine;
- production on a vibrating machine with a load.
Mechanization of processes allows to obtain higher in quality and parameter-stable arbolite blocks. In this case, the dimensions, geometry and density are saved from product to product.
The curing of the product in the formwork is used in handicraft production, when the removal of the formwork immediately after molding is prevented by a too liquid consistency of the solution. In general, molds are removed without exposure.

Raw blocks remain on a removable bottom-pallet or directly on the floor of the workshop.
Arbolite blocks, the composition of which is the same, can receive different characteristics depending on the method and degree of compaction. The main purpose of pressing a mixture into a mold is not to increase its density. The main task is the creation of a structure evenly distributed over the volume of wood chips from an arbitrarily oriented, completely covered with cement dough.
Vibration during compaction is very metered. Excessive vibrations cause the cement paste to settle on the bottom of the mold. It is important to maintain its uniform distribution over the volume with full cover of the filler grains. Even in high density wood concrete, wood chips do not float in a solution of cement with water. Cement dough works like an adhesive covering the filler grains.Only the concentration of wood chips in the volume and the thickness of the cement stone covering it changes.
The blocks are sealed at values sufficient for the mutual reorientation of the filler grains and increase the area of their contact. Compression and deformation of the chips themselves does not occur. This ensures the preservation of the block size after removal of the sealing force.
The need for accurate dosing of all components and compliance with technology
The accuracy of the dosage of the components is regulated by GOST. Tolerances cannot exceed a few percent. In conditions of lack of water, hydration of the entire volume of cement does not occur. Its excess is undesirable for several reasons:
- Exceeding the water-cement ratio reduces strength.
- Excess ductility prevents the wet block from being taken out of the mold immediately after molding.
- The storage time of the block on the pallet is increased until the initial setting.
The concentration of mineralizers for wood chips going into arbolite is important for the strength and durability of the material. The dosages of the components given in the standards are calculated for a certain caliber of the aggregate and its humidity at the level of 25%. The optimal dosage is selected empirically based on tests of finished samples.
For the hydration process, the temperature of the water solution with mineralizers is important. It should not be less than 15 ° C. To set the required temperature in the cold season, the water is heated or kept in a heated room. Chemical heating of water is also possible when used as a mineralizer CaCl2.
Arbolite density
According to the purpose, the material is conditionally divided into 2 types:
- heat insulating;
- constructional.
The determining factor is the density of the product. It is believed that blocks with a density of up to 500 kg / m3 not suitable for use as part of supporting structures. But they can be used for thermal insulation during the construction of external walls in buildings where the load from the roof or floors is perceived by columns or other elements.
Typical values for structural blocks are density values from 550 to 700 kg / m3. But you can buy products with a density of up to 850 kg / m3. Too high values indicate good load-bearing capacity of the elements, but inferior to the lighter in thermal insulation qualities. The density of the material is measured at a steady mass when the unit stops losing moisture.
Walls made of cast arbolite can have a density of about 300 kg / m3, but in bearing capacity they are not inferior to those made of stones with a density of 550 kg / m3.
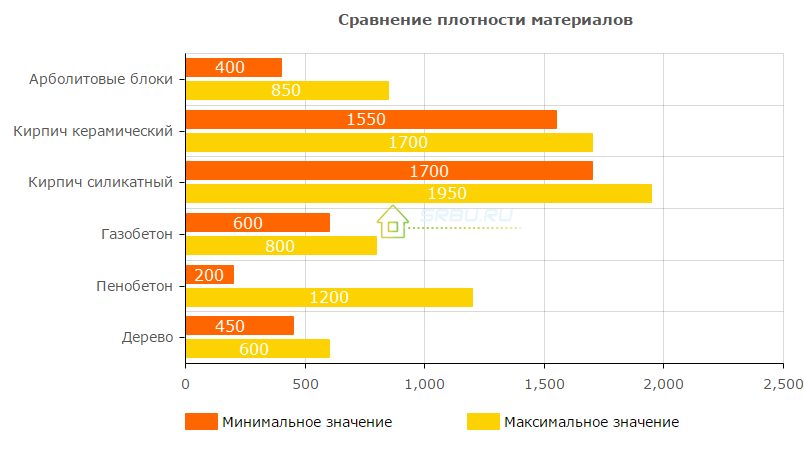
Strength of Arbolite Blocks
The bearing capacity of the blocks is characterized by their compressive strength. According to the test results, products can be assigned a brand and a class for compressive strength. In general, they are related to the density of materials.
| Density, kg / m3 | Mark | Class |
|---|---|---|
| 400 - 500 | M 5 | At 0.35 |
| 450 - 500 | M 10 | At 0.75 |
| 500 | M 15 | At 1.0 |
| 500 - 650 | - | At 1.5 |
| 500 - 700 | M 25 | In 2.0 |
| 600 - 750 | M 35 | At 2.5 |
| 700 - 850 | M 50 | At 3.5 |
As in the case of products from heavy concrete, the brand is the average value according to the results of testing a batch of samples. The class characterizes the guaranteed strength, 95% of the samples must correspond in class.
For real tests with a good sample, the relationship between brand and class through conversion factors is not correct. In this case, the gap between the brand and the class can tell about the culture of production in the enterprise. The smaller the gap, the higher the organization of production. In domestic practice, the manufacture of arbolite blocks is taken into account using the coefficients of variation. For products of the 1st quality category, a value of 18% is allowed, for the highest - 15%.
In masonry, the small size of the products makes the concept of classiness meaningless. When buying large masonry stones, which are arbolite blocks, it is worth giving preference to products with an assigned class.
For the construction of load-bearing walls of one-story buildings up to 3 m high, it is allowed to use blocks of class B 1.0. For higher walls, elements of class B 1.5 are needed. For 2 - 3-story buildings use blocks of classes B 2.0 and B 2.5.
The compressive strength of wood concrete is typical for cellular concrete. An important difference is the bending strength of the blocks, which ranges from 0.7 to 1.0 MPa. The elastic modulus of the elements can reach up to 2300 MPa. Such values make arbolite special among cellular concrete. If for foam concrete and aerated concrete there is a high probability of cracking, then for arbolite this problem is not worth it.
Thermal conductivity of wood concrete
Thermal conductivity for wood concrete is one of the key parameters.
It grows with an increase in its density in the following progression:
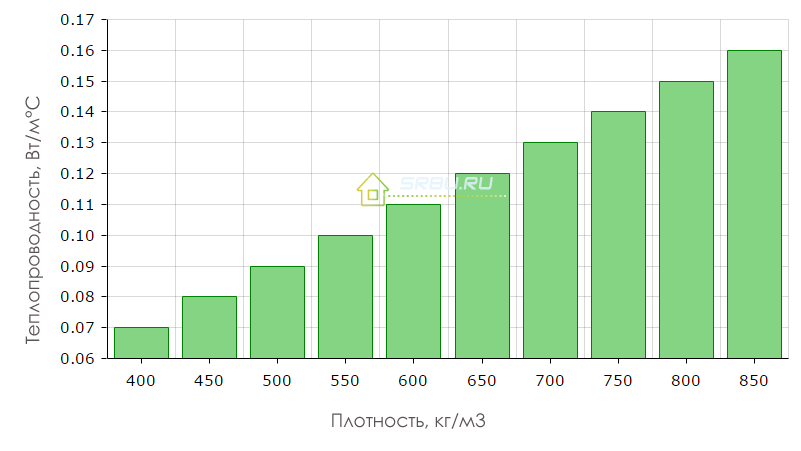
Recommended by GOST, the thickness of the enclosing structures made of wood concrete in temperate latitudes is 38 cm. But walls of this thickness are rarely erected. In practice, for the walls of residential buildings, blocks of 500 × 300 × 200 mm are laid flat in a row. Together with internal and external decoration, this is enough to maintain a comfortable temperature in the rooms without problems with condensation.
Additional thermal insulation is often carried out using warm plaster systems with a thickness of 1.5-2 cm with the addition of perlite. For not heated or periodically heated rooms (baths), laying of blocks on the edge is often used.
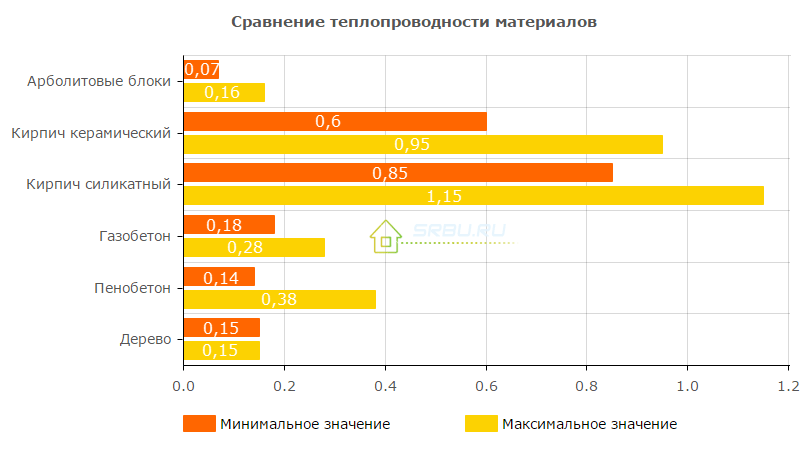
Moisture absorption of wood concrete
The characteristics of arbolite indicate the amount of water absorption up to 85% for heat-insulating blocks and up to 75% for structural. These values need to be understood. The block structure consists of disparate wood chips glued together with a cement stone. They are oriented relative to each other randomly.
Water poured onto the surface of the block flows freely through it. Naturally, when dipping, water is able to displace a large amount of air contained inside the unit. If the unit is pulled out of water, water flows out and the cement stone dries quickly.
Arbolite blocks located in the natural environment, for example, in the wall of a house, do not actually accumulate moisture from the surrounding air. This is due to the very low sorption moisture of the material, since mineralized wood chips and cement are non-hygroscopic and slightly wettable materials. This is what caused the popularity of the use of material for the construction of baths.
If you pour water on an unfinished wall made of wood concrete from the outside, there is a chance to see it inside. Therefore, the material is not used without facade decoration. For wood concrete, finishing with stucco mortars or the installation of suspended facade systems is recommended.
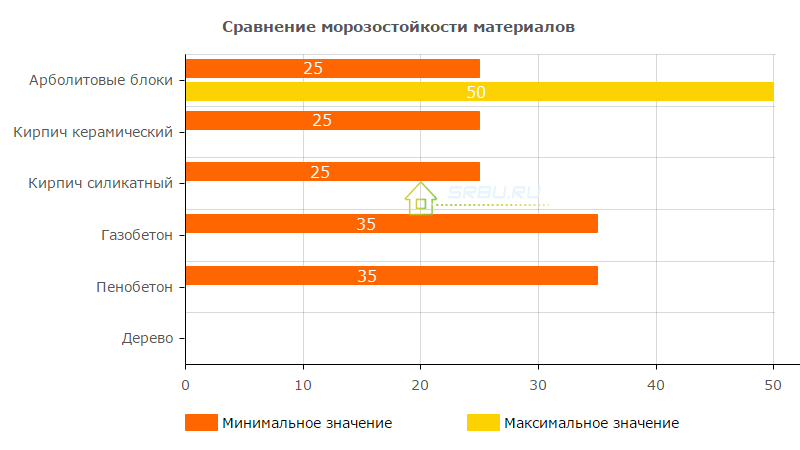
Frost resistance
The gradual destruction of products during freezing and thawing occurs as a result of the expansion of freezing water in voids. The more water they contain, the fewer cycles of freezing - thawing is able to withstand the material without destruction.
Low sorption moisture absorption gives arbolite good resistance to freezing. The minimum value is F25 and reaches F50. Protection of wood concrete from direct exposure to moisture, improves the real frost resistance of the material in the structure. In addition, there are real examples of the operation of buildings made of wood concrete for 7-10 years without damage to the walls. And we are talking about walls, which are not protected from the effects of external environmental factors.
Material shrinkage
It is believed that arbolite is completely not prone to shrinkage. But small shrinkage processes are still present in the first months. Basically, they stop even at the stage of maturation of the block in production. An uncritical reduction in block size (by 0.4 - 0.8%) is possible after laying the blocks in the structure.
Some reduction in the height of the blocks can occur under the weight of overlying elements, ceilings and roof structures. To prevent problems with the finish is not recommended to perform plastering in the first 4 months after completion of the main complex of works.
Fire resistance of wood concrete blocks
In terms of fire resistance, arbolite blocks have the following parameters:
- combustibility group - G1, i.e. it is a low-combustible material;
- flammability group - B1, flame-retardant material;
- smoke-generating ability - D1, low smoke-forming material.
Soundproofing
In noise absorption, arbolite blocks are superior to materials such as brick and wood. The noise absorption coefficient of arbolite blocks is 0.17 - 0.6 in the acoustic range from 135 to 2000 Hz.
Vapor permeability
Arbolit is a breathable material; its vapor permeability is up to 35%. That is why in houses built from this material there is no dampness, and the microclimate is comfortable both in the cold and in the warm season.
Disadvantages of Arbolite Blocks
No matter how good the arbolite is, the disadvantages of the material are still worth knowing and taking into account.
Several dubious moments are capable of shaking the resolve of the builder:
- 1. The abundance in the market of blocks of "garage" quality.

Their strength, heat transfer resistance is unknown even to the manufacturer. There are difficulties with the acquisition of factory wood concrete in the regions. Above, we wrote about the most important moments in the production of arbolite blocks. As you understand, it is simply not possible to perform certain tasks in artisanal conditions.
- 2. Insufficient geometry accuracy.

The geometry accuracy of arbolite blocks is inferior to that of other light-concrete masonry stones (foam concrete, aerated concrete). This is especially true for industries with a large share of manual labor. Deviations in the size and relative position of the surfaces make it necessary to increase the thickness of the joints up to 10 - 15 mm. And this entails the freezing of masonry at the seams, cost overruns and a decrease in the speed of masonry work.
Manufacturers recommend using warm perlite solutions for masonry, but their preparation is more expensive. Recently, to improve the geometry of the blocks begin to apply surface milling.
- 3. The need for protection against direct exposure to moisture.

In theory, an unprotected masonry can be permeable to large wind pressures, but no real confirmation of this phenomenon has been obtained. Applying plaster coatings to the surface solves permeability problems.
- 4. The high cost of arbolite blocks.

This is due to insufficient automation of production processes, the degree of technology development and modest production volumes. As a result, the prime cost of foam concrete and aerated concrete blocks is 1.5 times lower.
- 5. The presence of restrictions in the choice of finishing materials.

For proper operation, it is important to combine only “breathable” finishes with wood concrete masonry.
Advantages of arbolite blocks
Those who decide to build on arbolite technology should be inspired by its many advantages:
+ 1. The environmental friendliness of the material.

Even its mineralizers do not emit harmful substances into the atmosphere.
+ 2. The highest vapor permeability.

+ 3. The lightness of the material.

The lightness of the material and its elasticity do not require a powerful and rigid foundation. An added bonus is earthquake resistance.
+ 4. Ease of processing.

+ 5. Easy mounting hardware.

You can drive nails into the arbolite and screw the screws into it, like in a tree.
+ 6. Low thermal conductivity.

Excellent heat transfer resistance with sufficient strength for low-rise construction allows you to do without additional insulation and get a single-layer wall structure.
+ 7. Low sound permeability.

+ 8. Refusal of reinforcement.

The ability to abandon the reinforcement of masonry and the device of monolithic belts on small objects.
+ 9. Biological resistance.

+ 10. Incombustibility.






