Pros and cons of building from aerated concrete blocks
Aerated concrete manufacturers, on numerous sales sites, claim that there is no better building material. At no less massive construction forums they say the opposite, it is impossible to live comfortably in houses made of aerated concrete. The purpose of this article is to reveal the truth. What are the pros and cons of aerated concrete blocks, in which specific technological processes for construction, their use is optimal, and in which there is an alternative. How not to overpay for material and work, and not repent of what was done later.

Content:
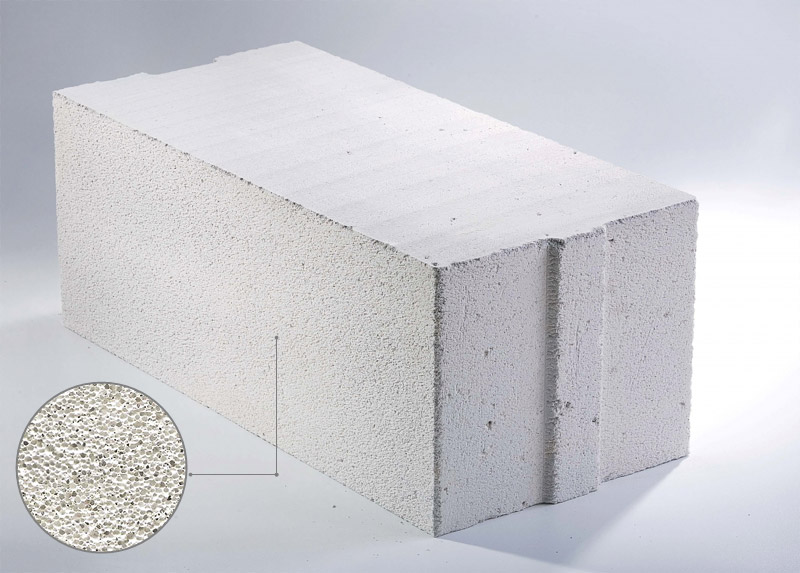
What are aerated concrete blocks and how are they made
Before we look directly at the pros and cons of aerated concrete, let's decide and see what material we are dealing with.
There are several ways to make aerated concrete products. In the factory, autoclave and hydration methods are used. However, the initial stages of the process are identical for all types.
1. Cleaning and preparing molds for pouring
There are two types of forms:
- collapsible - the design consists of a pallet, sides and several jumpers that can be removed to fill elements of a larger volume;
- cap - are a monolithic design. Mainly used in large-scale production.
2. Preparation of the composition
Many recipes are used, depending on their use, the final technical characteristics of the products vary.
The usual mixture consists of:
- cement, grades no less than M400 - 500 (50-70%);
- filler - sifted sand of fine fractions (20-40%);
- aluminum powder or paste (0.04-0.09%);
- lime (up to 5%);
- water (up to 0.8%).
3. Fill
The prepared mixture is poured into molds preheated to 400C, and carefully leveled.
4. Drying.
Here the significant differences begin, affecting the quality of the resulting blocks.
- When placed in an autoclave, hardening occurs at elevated pressure up to 12 bar, humidity and temperature up to 2000C. Such products are the most durable and high quality. Can be used for masonry bearing walls.
- With hydration hardening, the forms are placed in a special box with heating and high humidity. Such aerated concrete is used for insulation.
- In handicraft production, the molds are simply wrapped for several hours before being removed for further drying in an unsuitable room. Such blocks are better to never use anywhere.

Brands and types of aerated concrete blocks
First of all, aerated concrete blocks are divided into brands. Brand is actually the density of the product.
| Mark | Strength MPa | Thermal conductivity W / (М2х0С) | Application (Characteristics) |
|---|---|---|---|
| D350 | 0,7-1,0 | 0,08-0,09 | Very fragile material, used as insulation. |
| D400 | 1-1,5 | 0,1-0,11 | It is used as a heater to fill openings and erect piers. |
| D500 | 2-3 | 0,12-0,13 | Bearing walls in low-rise construction. |
| D600 | 2,5-4,5 | 0,14-0,15 | Load-bearing walls with ventilated facades |
There are special products created according to a special recipe with the addition of chemically active modifiers, which have increased heat resistance or sound insulation. Such blocks are used for cladding or erection of specialized structures.
Also, products are divided according to the type of binder: lime-gypsum and cement. And by the type of fillers: slag, ash, sand, using ferroalloy waste and secondary products. The use of all these materials is regulated by GOST. These materials affect the basic strength and thermal insulation characteristics of the final product insignificantly.
Sizes of aerated concrete blocks
The small specific gravity of the material allows the manufacture of products of enlarged dimensions. The most popular technological form is a box with grooves and ridges at the ends.
At the same time, the height and length of the element remain standard 250x625mm, and the width varies between 100-400mm. There are elements of other shapes and sizes, for insulation or device reinforced jumpers.
Pluses of aerated concrete blocks
+ 1. Thermal insulation level

The main indicator that sales managers emphasize is the incredible level of thermal insulation of the material. Aerated concrete wall will have a lower cost than a brick structure with comparable thermal insulation properties.
+ 2. High precision and large sizes

High accuracy and large block sizes allow you to build walls with minimal deviations and high speed. Accordingly, the cost of exterior decoration is reduced. The use of elements with grooves prevents the formation of cracks in the masonry.
+ 3. The possibility of refusing to use a cement composition for masonry

The use of a special adhesive instead of the usual cement mixture minimizes the effect of cold bridges. This reduces heat loss from 25% to 8-10%. The amount of glue used is significantly less, up to 5 times, compared with cement mortar.
+ 4. Good vapor and air permeability

The coefficient of vapor and air permeability is similar to wood structures. It is argued that the air circulation and humidity level in such a house will be regulated in a natural way, creating an optimal microclimate.
+ 5. Fire Resistance
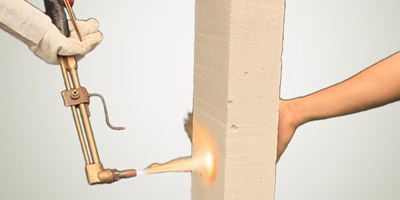
High level of resistance to fire and other aggressive environmental influences.
+ 6. Light weight

The light weight of the elements allows you to create light walls for which you do not need a heavy-duty foundation, which also reduces the cost of construction.
+ 7. Easy workability

Aerated concrete blocks are easily sawn, drilled and amenable to any manual processing.
+ 8. Ecological cleanliness

Aerated concrete blocks are environmentally friendly building material. In this regard, he is better than brick but worse than a tree.
+ 9. It has biological resistance

Aerated concrete blocks are resistant to damage by various microorganisms, rodents and insects. Although a small green coating on it can still form, but only in the case of constant moisture.
+ 10. Frost resistance

Aerated concrete blocks have a good level of frost resistance, which is F-50, i.e., 50 freeze-thaw cycles.
Cons of aerated concrete blocks
Let's analyze the points, is it really true, the information provided by sellers.
- 1. Required wall thickness

Many manufacturers regulate a sufficient wall thickness of 380mm. But sellers forget to mention that such a thickness is sufficient under ideal operating conditions and absolutely dry building material. According to SNiP 23-01-99 "Construction Climatology", the thermal resistance of the outer wall for the middle strip of Russia is a factor of 3.15. From another source of Construction Norms and Regulations II-3-79 * "Construction Heat Engineering" we find out that the humidity level of aerated concrete blocks varies from a minimum of 5% to a maximum of 12%. For a product of the D500 brand, this will be 0.17 W / (M2x0C). As a result, we obtain That the minimum wall thickness for the Moscow region should be 535 mm.
We take into account the cold bridges, which give an additional 10% reduction in protection - 588 mm. The presence of technologically necessary jumpers and reinforced belts for strengthening window openings, which give another 10 to 30%, and we get a wall 65 cm thick.
- 2. High hygroscopicity

One of the most significant disadvantages of aerated concrete blocks is their high hygroscopicity. The amount of moisture in the total mass can reach 35%. This practically negates the insulating qualities of the material. In addition, the elements swell, which leads to linear deformations, cracking and delamination.It is recommended to perform a systematic, every 2 years, surface treatment with special water-repellent impregnations, which leads to a significant increase in operating costs.
- 3. The appearance of cracks, with improper installation of the foundation

As the messages on numerous construction forums say, there is a problem of cracking the walls, both along the masonry lines, and directly the blocks themselves. Practice shows that microcracks appear already for 2-4 years of operation, up to 20% of blocks can be affected by them. This is due to the fact that large building elements are very sensitive to shrinkage of the foundation, thus, plus aerated concrete turned into a minus. The glue used to fasten the blocks cannot ensure the solidity of the structure, as happens with heavier masonry. The conclusion follows from this - to save on the foundation will not work.
- 4. Problems with the interior decoration

Another minus of aerated concrete is manifested in the interior decoration. Manufacturers recommend the use of gypsum-based plaster, and it really has a high level of adhesion to aerated concrete surface. But with sharp thermal differences at such a wall cracks immediately form, repeating the masonry contours. These places need to be strengthened with a mounting grid, which further increases the cost of finishing work.
Summary
Aerated concrete blocks are a high-tech material. Its production and installation requires a high level of knowledge and strict adherence to process technology.
1. The feasibility of using aerated concrete blocks as the main structural material for the construction of the building is under great question, however, with the strict observance of the entire technology is possible.
2. The use of elements from aerated concrete for high-speed construction of internal lintels, in principle, is welcome.
3. As a heat-insulating material, aerated concrete slabs do not have a decisive advantage over traditional polystyrene foam or mineral wool, neither in price nor in the laying technology, and even slightly inferior in terms of heat-insulating properties.





