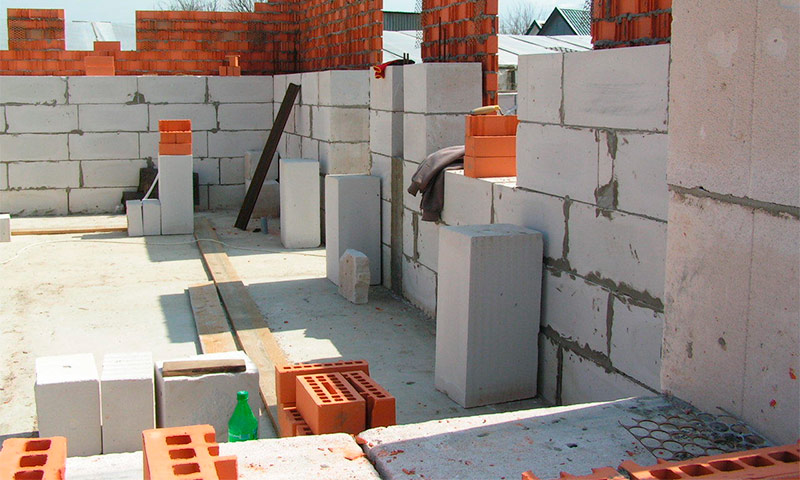
What blocks are better to use for building a house
Modern building technologies as a wall material increasingly offer blocks of various materials instead of bricks. They differ in size, properties and price. Each type of block has its own sphere of preferred application, but all of them are capable of replacing bricks, both in residential and industrial construction.
In order to choose the right blocks, which in each case will show only their positive characteristics, it is necessary to compare them by the main parameters. Physico-chemical properties of materials determine their behavior in the wall under load and in many respects affect the microclimate in the house.
The article will consider the main types of blocks that are used in private and industrial construction: aerated concrete; foam concrete; ceramic; arbolite; expanded clay concrete.
The analysis will concern not only the properties of a particular block, but also their interaction with other types of building materials, the complexity of preparatory and finishing works, the need to strengthen the structure, and the life of the unit. An attempt to determine which blocks are best for building a house will be based only on objective data, without a bias in advertising of one kind or another.

Content:
What blocks are used for building walls of the house and their brief description
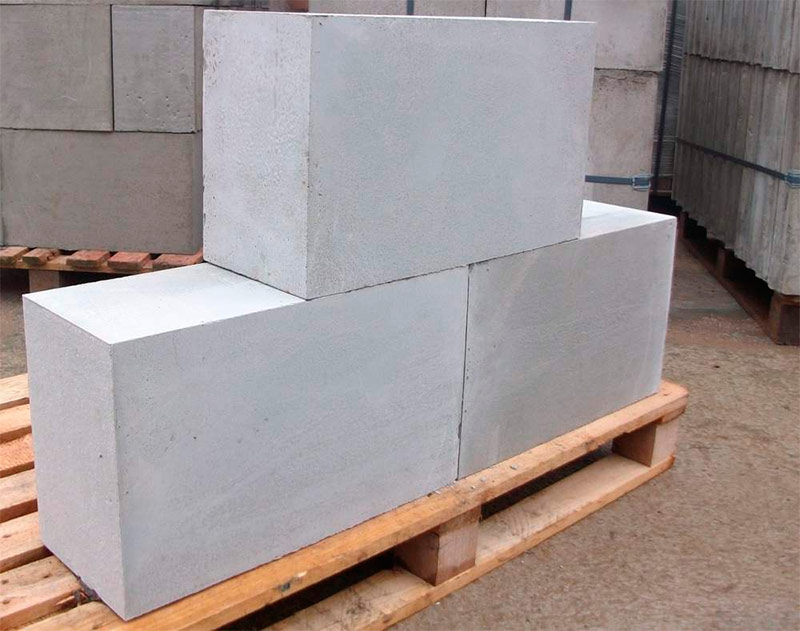
Aerated concrete blocks
One of the most common types of cellular concrete. It differs in closed pores, as a result of which it absorbs moisture very weakly. In the production of blocks, natural materials are used - lime, Portland cement, water and quartz sand. Aluminum powder is used as a blowing agent.
After mixing the components in a certain proportion, the raw materials are placed in molds and loaded into autoclaves, where they are exposed to high-pressure water vapor. There they harden over a period of time and acquire their main properties - dimensional accuracy, low weight, and high enough density.
In addition to autoclave hardening, blocks can be made from the same material by natural drying in the open air. In their parameters, they are significantly inferior to the first.
By purpose, the blocks are divided into:
- heat insulating;
- structural and heat insulating;
- constructional.
Their differences are in compressive strength, thermal conductivity and density.
The dimensions of the blocks are 600x200-300x80-400 mm (LxWxH). The shape of the blocks may be different. For the construction of load-bearing walls, blocks with a groove / crest surface relief are used. Partitions and secondary walls are built from ordinary rectangular blocks with smooth edges. U-shaped are used for mounting armopoyas and lintels above door or window openings.

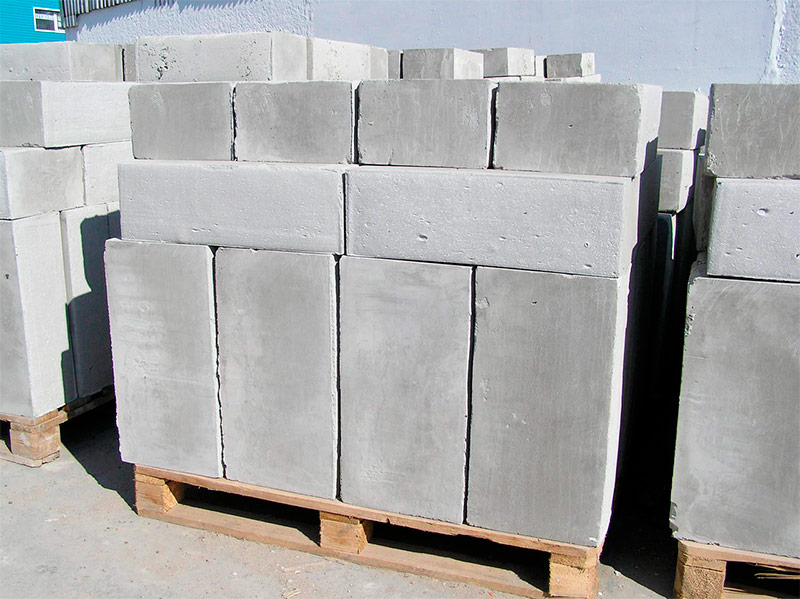
Foam concrete blocks
A kind of cellular concrete. It is made from sand, cement and water with the addition of blowing agents. In the form of loose foam, the raw material is poured into molds for finished blocks or in large formwork structures. After solidification within 10 to 12 hours, collapsible molds open and foam blocks are removed for further hardening.
If the blocks are manufactured using cutting technology, then the massive block is kept in formwork for several hours (4-10), then it is removed and the workpiece is cut into smaller blocks of appropriate sizes with special steel strings, chain or band saws.
In its density of frost resistance, foam concrete can be compared with aerated concrete, but it is inferior in strength and accuracy of forms. By their properties, they are suitable for the construction of houses no higher than three floors.But in monolithic reinforced concrete construction, foam concrete is very popular because of its lightness to fill the openings between the supporting parts of the frame.

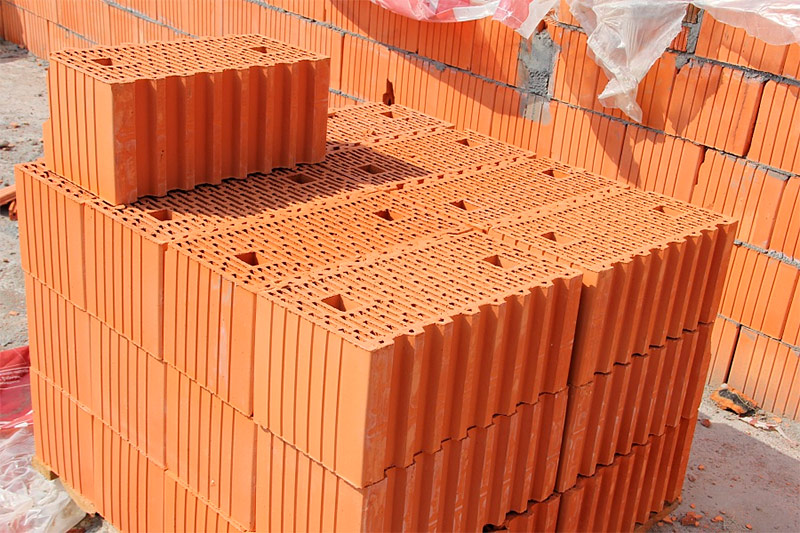
Ceramic blocks
Made from the same material as normal. brick - clay and water. Billets are fired in furnaces and get the specified hardness. But with a much larger size than a conventional brick, blocks are almost twice as light. This is determined not only by the fact that through the voids are provided in the block, but also by the fact that during the preparation of raw materials the clay is mixed with sawdust or other combustible material. In the firing process, impurities burn out and the material becomes porous, and, therefore, lighter.
The standard dimensions of the ceramic block are 250 - 510x250-380x219 mm. Large sizes allow laying twice or even three times faster than brick. Lighter walls can save on the foundation, and the porous structure - on the insulation.
From ceramic blocks, houses of any number of storeys are built. Here, the material is used for external and internal load-bearing walls, partitions, filling openings.

Arbolite blocks
Another type of blocks, relatively little known to non-specialists in the construction business. In its technical essence, arbolite is a coarse-grained concrete in which such seemingly incompatible materials as wood and cement are combined. In production, wood chips are mixed with a cement-sand mixture, diluted to a semi-liquid state, and poured into molds.
From this light and durable material are made:
- heat insulating plates;
- mixtures for pouring into the formwork in place;
- masonry blocks;
- large-format mounting blocks.
For the construction of buildings, blocks of the standard 500 × 300 × 200 mm are used, but other sizes can also be found on sale - they are regulated by GOST 19222-84, but many manufacturers produce blocks according to the technical specifications developed at the enterprise itself. But well-known factories seek to produce material in a standard size, or a multiple of it - this facilitates and speeds up the process of walling.
For the production of blocks, wood chips with a size of 40 × 10 × 5 mm (maximum) are used. Some unscrupulous manufacturers, along with wood chips, and even instead use bark, shavings, straw. But such blocks do not meet the requirements for arbolit and can be used only for the construction of utility structures.
In addition to the main raw materials, various chemical additives are used in arbolite, which increase the strength and water resistance of products. These additives neutralize compounds present in the tree that prevent the cement from sticking to the chips. As a result of chemical treatment, a tree receives a level of adhesion to cement no worse than gravel or gravel.
Of the additives most commonly used are:
- liquid glass;
- calcium chloride;
- alumina sulfate;
- slaked lime.
In an industrial production method, the mixture is poured into molds and pressed by a vibration method. With the exact dosage of the components and the correct choice of the vibration mode, the blocks are homogeneous in density throughout the volume. According to this parameter, two types of wood concrete are produced - structural, with a density of 500 to 850 kg / m3 and thermal insulation, unsuitable for load-bearing structures. Its density is in the range of 300 - 500 kg / m3.

Expanded clay blocks
Expanded clay wall blocks are made by vibration casting into finished molds. The raw materials are cement, expanded clay and sand or dolomite. The classic block, made according to GOST 6133-99, contains up to 50% expanded clay and about 50% cement. Such blocks are used for the construction of walls and partitions, filling openings of frame structures.
The dimensions of the blocks are 390x190x185 mm or 390x190x90 mm, which allows the construction to be carried out very quickly. The cavities inside the blocks perform the functions of stiffeners, reduce weight and increase heat-saving properties. One of the walls, perpendicular to the direction of the cavities, is continuous, which allows to reduce the flow rate of the solution, laying blocks in the wall with holes down.
Depending on the fillers and the expanded clay / cement proportion, the standard block can weigh from 9 to 21 kg, density - from 500 to 1800 kg / m3. Blocks are used in the bearing walls of houses up to 3 floors only with the installation of an armored belt and reinforced concrete strapping. But the main scope of application is partitions, filling frames, fences, fences, outbuildings.
Comparison of blocks used for walling
All types of wall blocks can be used in construction, observing certain restrictions inherent in one or another of their types. In order to make the picture of which blocks it is better to build a house more clear, you need to not only talk about each type separately, but also make a comparative analysis of them in terms of the main parameters.
The most significant characteristics are as follows:
- Strength;
- Environmental friendliness;
- Fire safety;
- Frost resistance;
- Thermal conductivity and the degree of need for insulation;
- Steam and air permeability;
- Shrinkage;
- The need for reinforcing masonry;
- Requirements for the type of foundation;
- Type of ceilings and the need for an armored belt;
- The need for exterior decoration materials;
- Cost of blocks;
- The cost of masonry.
Basic data on building materials are given in the table:
| Block view | Density, kg / m3 | Mass in the wall | Water absorption,% | Thermal conductivity, t / M * k | Frost resistance | Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Gas block |
300 - 1200 | 100 - 900 | 20 - 25 | 0,1 - 0,4 | 35 | 0,5 - 25 |
Foam block |
300 - 1200 | 100 - 900 | 10 - 16 | 0,1 - 0,4 | 35 | 0,25 - 12,5 |
Expanded clay block |
300 - 1500 | 900 - 1000 | 50 | 0,15 - 0,45 | 25 - 75 | 50- 150 |
Arbolite blocks |
500 - 900 | 300 - 700 | 75 - 85 | 0,2 - 0,3 | 25 | 20 - 50 |
Ceramic block |
700 - 900 | 600 - 800 | 12 - 15 | 0,1 - 0,2 | 50 | 2,5 - 25 |
Strength
Strength refers to the ability to withstand external physical effects of compression. The main indicator is the brand. It shows the ultimate load in kg / cm2that the material can withstand before the start of destruction. For example, M-175 shows that the load is 175 kg / cm2 may cause damage to the material. For comparison, the brand of brick in high-rise buildings should be at least M150, in single-story buildings - M100. Of the blocks, claydite-concrete have the greatest strength. The only problem is that these blocks are often produced in artisanal conditions and because of the economy, not all manufacturers can provide the indicated strength.
Frost resistance
Frost resistance of the MPC is indicated by a figure that shows the number of cycles of complete freezing and thawing of the material that it can withstand before the destruction of the internal structure. As a rule, the material does not completely freeze in the wall even in harsh winters, so the indicator can be considered relative. The level of Mrz 35 is quite acceptable for middle latitudes. Most types of blocks correspond to this indicator.
Density
Density - weight per unit volume of the material, measured in kg / m3. The parameter is important in that the wall pressure on the foundation depends on it, and, therefore, the need for a less or more heavy foundation. As a material for the construction of load-bearing walls, it is best to use blocks with a density above 800 kg / m3 . On the one hand, the higher the density, the better the strength of the material and the walls erected from it. But density has a downside. The higher it is, the greater the thermal conductivity of the material, which means that more funds will be needed to warm the house.
Thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity - shows how fast the heat flux is transmitted through the thickness of the material. The higher the thermal conductivity, the less heat it can save in the house and the thicker the thermal insulation must be installed on the walls. The warmest materials are aerated concrete and foam concrete. Almost all types of blocks have both thermal insulation and structural, and structural versions. The scope of each variety is different.
Moisture absorption
This parameter shows the ability of the material to absorb some moisture. When compared with brick, then this indicator for all types of blocks is not at the highest level. That is why walls built from all types of blocks need external decoration with facade materials.
But, even comparing the data in the table, to make a final conclusion about what types of blocks are better for building a house, it is necessary to take into account such an important parameter as the cost of the whole process.In this case, it is necessary to take into account such significant items of expenditure as the costs of the foundation, insulation, reinforcement, and exterior decoration. Sometimes cheaper blocks turn out to be much more expensive with full costing of their purchase and installation costs and additional operations.
Shrinkage
To determine which blocks it is better to build a house from, you can study all the technological processes of their installation and the phenomena that occur in the wall after construction. For example, attention is rarely paid to such an important thing as shrinkage. Among all these materials, the most susceptible to such a rather unpleasant, but predicted phenomenon of aerated concrete walls and foam blocks.
Expanded clay and ceramic blocks, which in this parameter are equal to ordinary brick, do not shrink. Arbolite has a very low shrinkage, but only if it is really high quality. This parameter is determined by the properties of the material, but if the masonry technology is violated, then shrinkage can be expected from any material, up to the appearance of cracks on the walls.
Type of foundation
By the type of foundation required for the construction of a low-rise building, all blocks require continuous monolithic strip foundations of medium depth. This is one of the most economical foundations, taking into account the cost of its installation in relation to strength and durability.
If you build walls from foam blocks and wood concrete up to 40 cm thick, then you can make a grillage foundation on screw piles. But this type of foundation should take into account the type of exterior decoration. If it will be made of face brick, then the foundation, nevertheless, must be made tape or pour a solid concrete slab.
Masonry reinforcement
When laying walls, mesh reinforcement is performed using all types of blocks; under the ceiling, the armo-belt is poured along the entire perimeter, standard factory jumpers or cast concrete are placed above the window and door openings.

Erection speed
Building from blocks compared to brick is faster, even taking into account the time spent on additional operations in the form of masonry reinforcement.
Exterior finish
One of the most expensive operations. Almost all known options are used here - from the “wet” facade with insulation, to the ventilated and cladding with brick, siding, lining. Gas blocks and foam blocks, when installing an external finish, require a ventilation space - high vapor permeability of materials requires removal of excess moisture from the wall.
Expanded clay and ceramic blocks are best in harmony with brick facades and plaster, they are most consistent with these materials both in physicochemical characteristics and in application technology.
Construction cost
To determine which blocks are best for building a house, you can simply calculate the costs of the entire construction cycle. If for 100% we take the cost of masonry from ordinary solid brick, then the cost of one meter of cubic blocks with external decoration with homogeneous materials will be:

Gas block
96%

Foam block
93%

Expanded clay
83%

Arbolite
80%

Ceramic block
80%
Obviously, the use of blocks is beneficial in any case - in addition to winning money, they give a double advantage in construction time, which also results in significant cost savings.







