Insulation for the walls of a wooden house outside for siding - choosing the best option
In this article we will analyze which insulation is best for the walls of a wooden house outside for siding. Due to the peculiarities of wooden houses, the number of options for thermal insulation materials for them is limited - not every insulation can be used for their external insulation.

What properties should a heater for a wooden house have
Houses made of timber look neat, they are beautiful even without external decoration. But if the homeowner is faced with the task of reducing heat loss, making the building heat efficient, then it is necessary to insulate the frame outside. This issue is especially relevant in the Russian climate. A heater that is suitable for solving this problem should have the following properties:
- Be vapor permeable. This indicator at the insulator should not be less than that of the beam from which the house is built.
- It’s good to keep warm.
- Do not absorb moisture, since when wet, the thermal insulation properties of the insulation deteriorate.
- Be non-combustible.
With all the abundance of thermal insulation materials on the construction market, only a few types are suitable for warming wooden houses. The insulation, which is used for thermal insulation of wooden houses, has special requirements. The material should have such properties that, in all technical parameters, a wooden house meets the building standards adopted in the Russian Federation - SNiP 31-02-2001.
Thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity coefficient shows how much thermal energy a material can transmit over a certain period of time. The lower this figure for the insulation, the better, since the heat loss of the building will be lower. Thermal conductivity standards for insulation for wooden houses are regulated by SNiP 23-02-2003. The insulation should be selected taking into account the thermal conductivity, and the thickness of the insulation layer depends on the region in which the house is being built.
Vapor permeability
Wood is a vapor-permeable building material. This means that with a temperature difference in the street and in the house, a pressure differential is created, as a result of which the wet vapor moves through the walls from the inside out. To ensure the exit of moisture from building structures, the insulation used must have the same vapor permeability properties as wood.
In this case, all the moisture from the house will go outside, providing a natural drying of building structures. If you install an unpermeable material along the contour of a wooden house, then water will accumulate in the timber or logs, causing them to rot faster.
Fire safety
Fire resistance is one of the most important parameters when choosing materials for insulation and wall decoration of a wooden house. The log house itself is made of combustible material, so everything possible is done in construction to reduce the possibility of fire of wooden structures.
In normative documentation, it is customary to classify building materials according to the degree of combustibility into several types: from non-combustible (NG) to flammable ones with a burning class from G1 to G4. Insulation for siding for houses made of timber or logs should be non-combustible NG. According to this parameter, basalt wool is suitable - made of rock, it can withstand heat up to 1000 degrees Celsius.
Insulation shrinkage
The heat-insulating material must be form-stable - to maintain its shape throughout the life of the building, not sit down. Otherwise, between the individual elements of the insulation layer (plates, mats, rolls), gaps appear through which the heat leaves. As a result, the amount of heat loss increases, the efficiency of the building's insulation decreases.
Water absorption
When absorbing wet vapors from the environment, any insulation loses its heat-preserving properties. Water conducts heat better than air, freezes when the temperature drops below zero, turning the heat insulator into a piece of ice. So that the heat-saving properties of the walls do not decrease during operation, it is necessary to conduct external insulation with a heater with a low coefficient of water absorption.
The water absorption of the material is indicated as a percentage - this is the amount of water that it absorbs when completely immersed. The lower the water absorption coefficient, the better.
All technical parameters of the insulation material are indicated by the manufacturers on the packaging.
Which heaters are best suited for the walls of a wooden house
The main requirement for the insulation for the walls of a wooden house outside is the vapor permeability of the material. This parameter is measured in mg / (m * h * Pa). The vapor permeability of the heat insulator used for the external insulation of a wooden house should not be lower than that of the tree of which the building is built.
Coniferous wood, spruce, pine, larch, cedar, whose vapor permeability is about 0.32 mg / (m * h * Pa), is most often used in timber house-building.
To compare the coefficients of the vapor transmission capacity of different materials, the table below:
| Insulation | The coefficient of vapor permeability, in mg / (m * h * Pa) |
|---|---|
| Expanded polystyrene extruded (EPS) | 0,013 |
| Expanded polystyrene foam | 0,05 |
| Polyurethane foam | 0,05 |
| PVC foam | 0,23 |
| Ecowool | 0,32 |
| Mineral wool with a density of 200 kg / cubic m | 0,49 |
| Mineral wool with a density of 50 kg / cubic m | 0,6 |
The table shows that, in terms of vapor permeability, only mineral wool and ecowool are suitable for thermal insulation of the walls of a wooden house. They have more vapor permeability than wood, or the same. All other heat-insulating materials of synthetic origin (polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam, etc.) cannot be used for insulation of buildings made of wood.
Any vapor-proof building materials that do not absorb moisture will lead to excessive accumulation of wet vapors in wooden structures. This will cause rapid decay of the tree, will lead to complete destruction of the log house. As a result, the house will become unusable in 2-3 years after commissioning.
Therefore, wooden buildings are insulated only with vapor-permeable insulation: mineral wool, ecowool. For siding, it is more convenient to mount hard slabs of stone wool, the technical parameters of which also outperform competitors.
Mineral wool insulation
The mineral wool insulation group includes several varieties of fibrous materials that differ in the composition of their constituent components:
- Basalt mineral wool. It is made of stone rocks of volcanic origin.
- Glass wool. It is made from the same components as glass, only after melting and solidification of the mass the smallest fine fibers are formed.
- Slaggy. Made from waste from the coke industry.
Stone wool is used for thermal insulation of private houses more often. It is used for external insulation of facades for plaster, for siding, in mounted ventilation facades. Glass wool is less used material. It shrinks very much, therefore it is more suitable for insulation of closed horizontal surfaces - ceiling, floor floors. Today, everyone refused to use cheap and non-ecological slag in residential housing construction.
Basalt (stone) cotton wool
Basalt mineral wool is made in industrial conditions from rocks of volcanic origin.The stone is melted to form a pulp into which a synthetic binder is added. The term "basaltic" is used as a general term for all types of stone-fiber insulation, although different rocks can be included in the composition - diabase, porphyrite, dolomite, limestone, and basalt. In addition to stone fiber obtained by the method of melting, the composition of mineral wool includes a polymer binder.
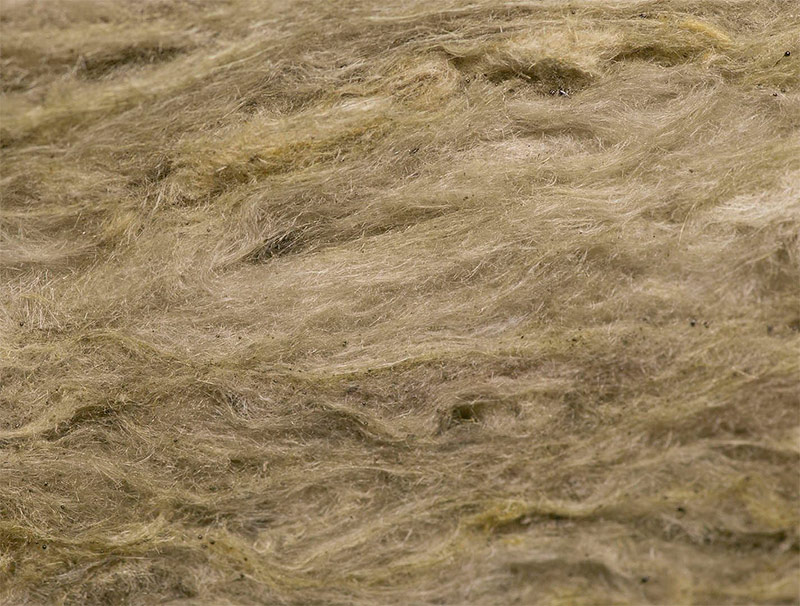

Fibers of stone wool.
The thermal insulation effect is achieved due to the large amount of air between the fibers, which is considered an excellent heat insulator. At the same time, stone wool has chemical and biological resistance, is not hygroscopic, environmentally friendly, extremely resistant to temperature deformations, and is able to withstand, without melting, temperatures up to 1000 ° C.
High-quality stone wool retains its geometric dimensions throughout the entire life cycle and is not subject to shrinkage. Due to this, bridges of cold are not formed. In addition, thanks to hydrophobic additives, moisture is difficult to penetrate into the insulation, which positively affects the thermal insulation properties. In this case, moisture in the form of steam that has got inside the insulation can easily evaporate.
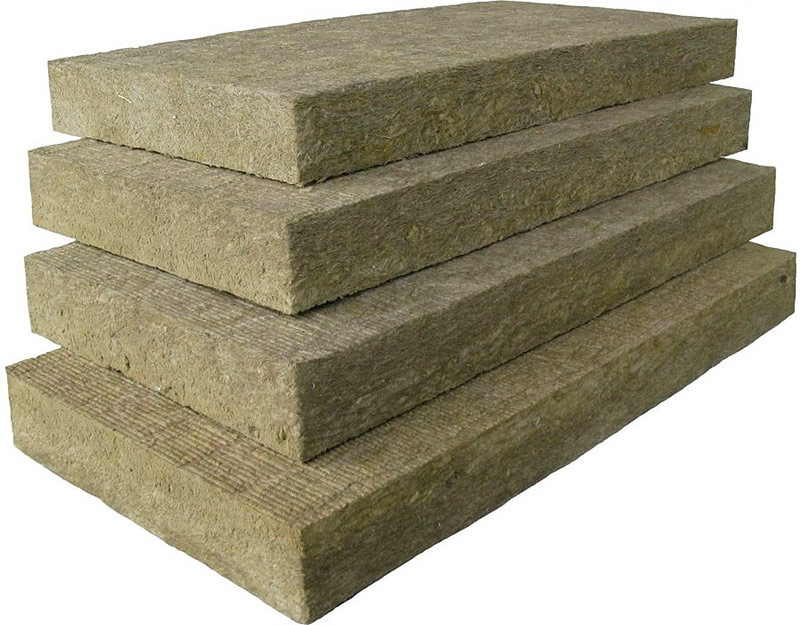

Slabs of stone wool.
Glass wool
The components for the production of glass wool are the same materials from which glass is made - quartz sand, borax. Light material has a loose structure and low density - only 20 kg / sq. m, available in soft rolls. Due to the short length of the glass fiber, glass wool “crumbles”. Inhaling it is unsafe, and if it comes into contact with the skin, small glass fibers cause itching and irritation. Therefore, this material is used less often, they prefer a more environmentally friendly and easy to install basalt cotton wool.
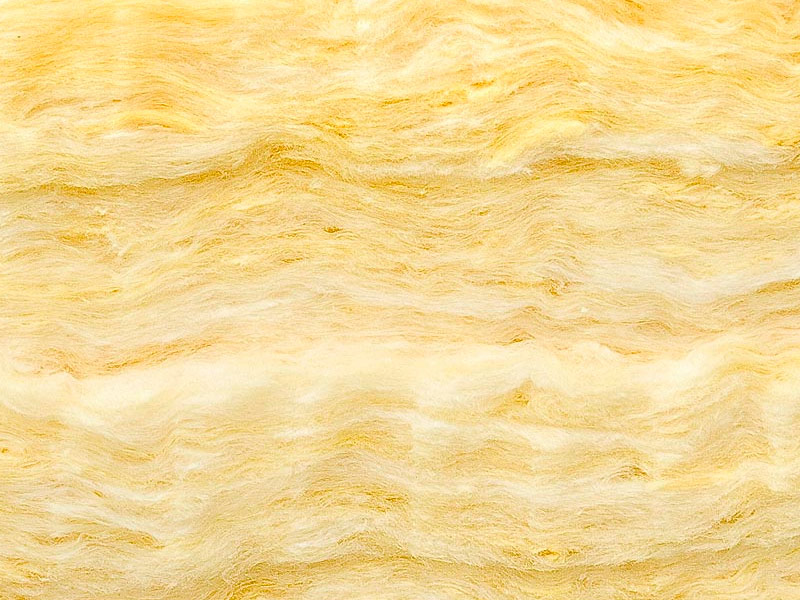

Glass wool fibers.
Glass wool gives greater shrinkage than stone wool, so from the point of view of form stability, the latter option is preferable for external insulation of the walls of a wooden building for siding. Glass wool is best used for thermal insulation of horizontal structures - ceiling ceilings, and not vertical walls.

Glass wool roll.
Slaggy
It is made from metallurgical industry waste - blast furnace slag - using old-style formaldehyde binders. Slag insulation absorbs moisture, since water-repellent additives are not added to it. The material is characterized by increased brittleness, fragility, shrinks, its shape after mechanical impact is not restored. Due to harmful vapors of formaldehyde, low consumer properties, they were slagged away from using it in modern housekeeping, although it is cheap and retains good heat.

A roll of slag.
Ecowool
Ecowool is an environmentally friendly product obtained as a result of pulp processing. 80% of its composition is cellulose fibers, and 20% is boric acid, antiseptics, flame retardants (borax). Ecowool is made from recycled materials - waste paper or waste from the pulp and paper industry - the marriage that occurs in the production of paper and cardboard. Today the share of this insulation on the market is growing, the demand for it is increasing.

Ecowool.
There are different technologies for applying ecowool:
- dry method;
- wet
- glue.
Dry application
The dry method of warming with ecowool involves filling or blowing with a loose mass of vertical or horizontal structures of the house: walls, roof slopes, ceiling or floor floors. For this, a cavity is preliminarily formed, into which a soft loose insulation is blown using a pump and a hose. Ecowool applied by this method is subject to shrinkage, and it is difficult to produce dry ecowool blowing in the case of finishing the house with siding, therefore it is better to refuse this method.
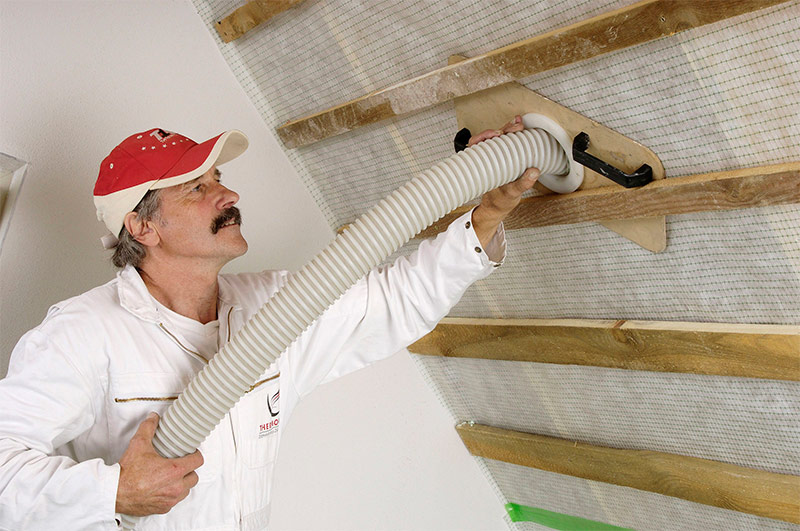

Ecowool blowing in a dry way.
Wet application
With the wet method, water is added to the ecowool. After drying, a dense heat-insulating layer forms on the surface, which must be masked by the casing.With this method of applying ecowool is not subject to strong shrinkage, and during application does not create a lot of dust.
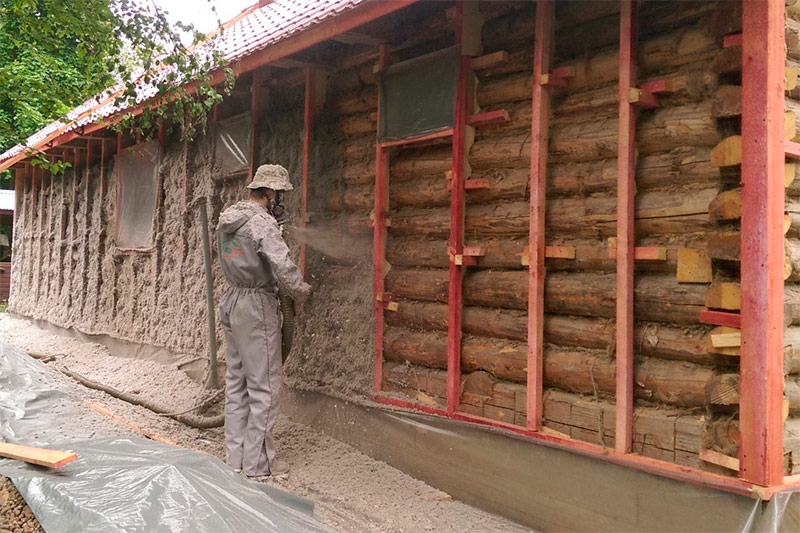

Wet ecowool application.
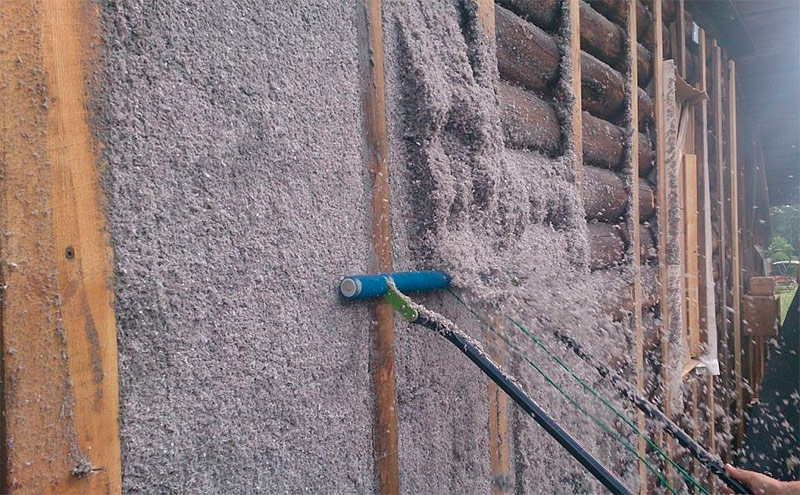

Removing excess ecowool.
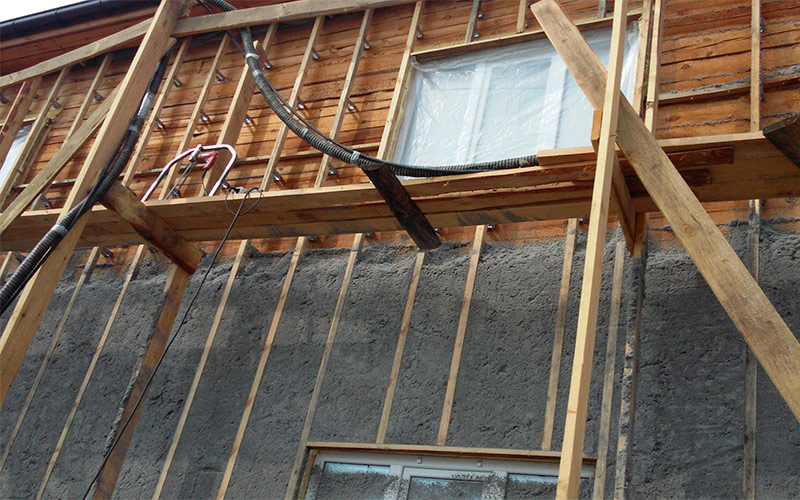

Ecowool with excess removed, ready for membrane installation and siding.
Glue application
When glue is added to ecowool instead of water, the adhesive properties of the insulation increase. The glue method is often used to isolate reinforced concrete and metal surfaces than wooden ones.
When insulating ecowool it is important to choose a good company that has modern equipment for applying ecowool. In this case, it is better to abandon dry blowing, since there is a high probability of subsidence of the insulation and the formation of cold bridges.
The key point in choosing a heater is if it is possible to entrust the insulation with ecowool to a contractor who can do this efficiently and prevent material shrinkage, then you should consider what to use - ecowool or basalt cotton wool. If there is no confidence in the quality of the ecowool insulation, then it is better to give the advantage of basalt cotton wool.
Ecowool is a new material, relative to stone wool, which has been used for a long time, and the insulation technology has long been run-in. Therefore, it is best to warm the house from wood with stone wool - this is a practical, simple and easy to install material.
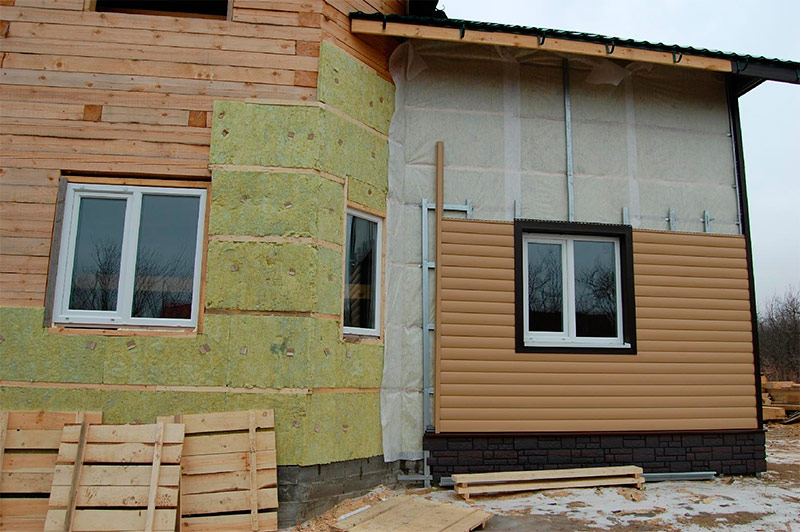

Warming of a wooden house with stone wool.
Features of the ventilated facade
An important requirement for the insulation of a wooden house is the organization of ventilation of the insulation. You can’t just attach stone wool to a wall of timber, and attach a siding close to the insulation. It is necessary to provide a ventilated gap between the insulation and siding, about 40 - 50 mm.
This is necessary so that moisture entering the insulation from the inside of the room can be freely removed from the insulation. At the same time, it is necessary to protect the insulation from the outside with a vapor-permeable moisture and wind-proof membrane, which will not impede the exit of steam to the "street", but at the same time will prevent the penetration of atmospheric moisture from the outside into the insulation. This is achieved due to the fact that the molecules of water vapor and water have different sizes.
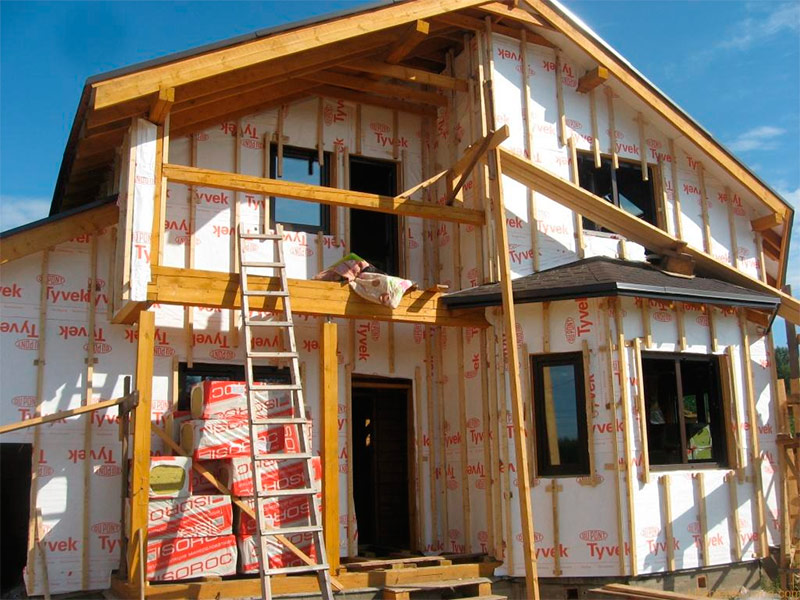

Insulation coated with vapor permeable membrane.
On top of the mineral wool with a waterproof membrane, decorative and protective casing is installed in the form of siding or wall panels, while the ventilation gap is observed.
Installation of a ventilated facade
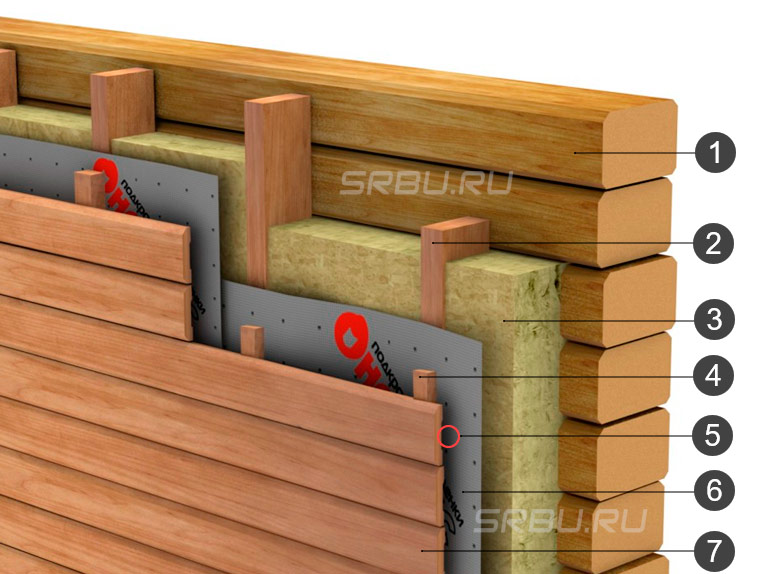
1. Wall of a house made of timber.
2. Crates racks.
3. Stone wool.
4. Counter grill.
5. Ventilation gap.
6. Vapor permeable membrane.
7. Exterior finish (siding, wall panels, etc.)
Knowing how different materials behave, what properties they possess, it will be easier for you to choose the right insulation for the exterior walls of a wooden house. Heat-efficient, vapor-permeable, non-combustible materials will allow to keep heat in the house, create a favorable microclimate, and ensure the safety of residents.









