Insulation for the exterior walls of the house: types, how to choose, the best brands
In this article you will learn which insulation is best used for the walls of the house outside. Here we have collected all the main types of modern materials for thermal insulation, popular brands and the main properties of insulation.

The selection of goods was carried out on the basis of reviews, opinions and ratings of users posted on various resources on the Internet. All information is taken from public sources. We do not cooperate with manufacturers and trademarks and do not call for the purchase of certain products. The article is for informational purposes only.
Than external insulation is better than internal
Warming of houses in most cases should be external. This recommendation is contained in the code of rules for design and construction (SP 23-101-2004).
The easiest way to explain this is that internal insulation takes away free space from the room, although this is not the main reason. Insulating the house from the inside is not prohibited, but it is recommended to resort to this only in exceptional situations. For example, if the special design of the building does not allow insulation from the outside.
Qualitatively insulate the house from the inside only when creating a vapor-tight layer - solid and durable. This is quite difficult to do. If warm humid air enters the insulation, condensation will inevitably form. The same thing will happen when the air comes in contact with a cold wall. With such insulation, the dew point moves inside the heat-insulating layer or between it and the wall.
Based on these reasons, recommendations for insulation are almost always consistent with the standards - conduct insulation from the outside.
Popular heaters used for exterior walls of a house
From a large assortment of thermal insulation it can be difficult to choose the right option. The most popular heaters for the exterior walls of the house are:
- expanded polystyrene foam;
- extruded polystyrene foam;
- stone wool.
Expanded polystyrene foam
Most often, this insulation is called polystyrene, but polystyrene is the common name for a large number of varieties of materials obtained by foaming. In the insulation of a house, solid plates are most often used. The material is of different densities, on which its thermal conductivity depends. The structure of the insulation is small balls filled with air and fastened together. Such a device provides good thermal insulation.
Expanded polystyrene is easy to use, moisture resistant and durable, while not at all expensive. All this makes it one of the most popular heaters. It is low combustible, and some species are self-extinguishing, they are marked PSB-S.
The disadvantage of expanded polystyrene foam is its low vapor permeability, therefore it cannot be used to insulate walls made of breathable material, as well as combustibility - during combustion it releases toxic substances in a large volume.
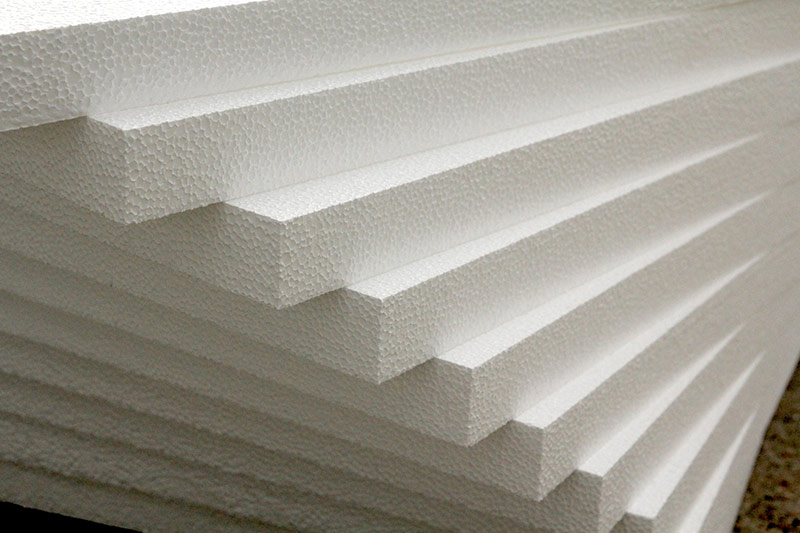

Expanded polystyrene foam.
Extruded Styrofoam
This is a material similar in composition to foamed polystyrene foam, but is produced using a different technology, therefore it has a continuous cellular structure. As a heater, foam polystyrene is superior in properties. Its water absorption is the same - no more than 2%, but the thermal conductivity is 30% lower. It is a more durable material with a low vapor permeability index.
The properties of expanded polystyrene allow it to be used as a heater of the basement and basement. The disadvantages of the material are the same as conventional foam, but the price is higher.
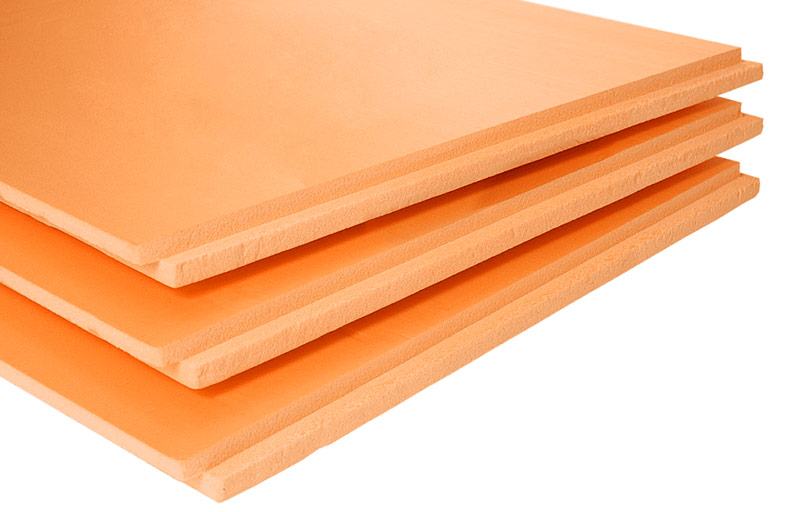

Extruded polystyrene foam.
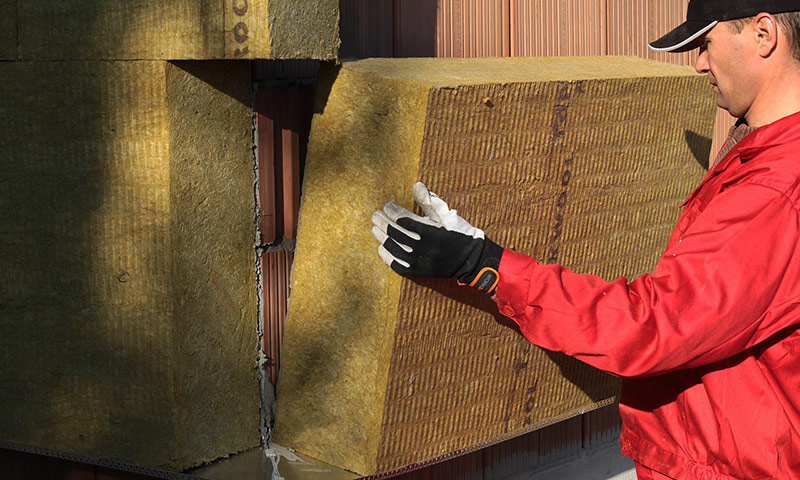
Stone (basalt) cotton wool
A type of mineral wool that is produced from rocks, mainly from basalt. The low thermal conductivity of the material is due to the fibrous structure with a low density. But cotton foam insulation is inferior in this indicator.
The advantage of stone wool is that it does not burn and is not subject to decay. It is considered a breathable material, that is, it has a low resistance before the passage of steam.
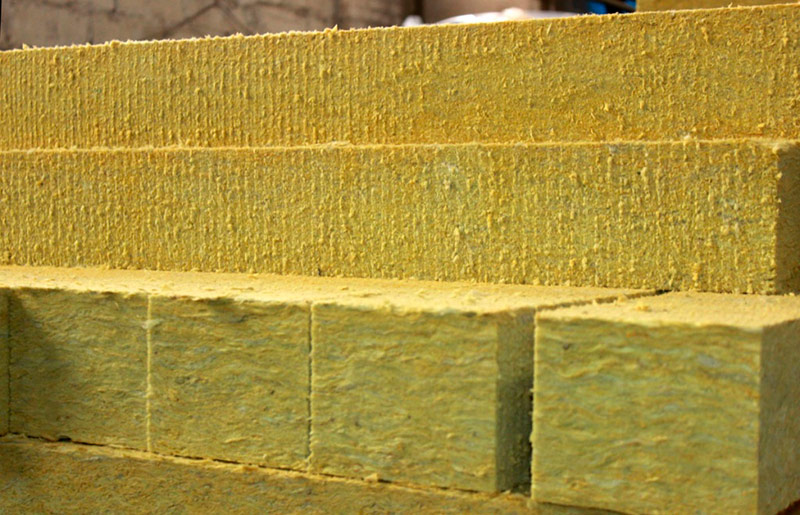

Stone wool.
There is another popular mineral wool insulation, which is called glass wool, but it is not recommended to use it as a heater for horizontal surfaces, since it sags heavily forming cold bridges. For this reason, this article is not considered.
New heaters used for exterior walls
Relatively new heaters used for external insulation are:
- polyurethane foam;
- ecowool.
Polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam is the same mounting foam used to close cracks in building structures.
The material is most often used for the manufacture of sandwich panels and thermal panels for facades. The sprayed option is convenient to use when it is necessary to create a seamless insulation surface. Previously, it was applied only using professional equipment. Now in the store you can buy such material in the form of an aerosol - this is a one-component variety for domestic use.
The disadvantage of this material is its low holding capacity. In wet facade systems, it cannot be used.
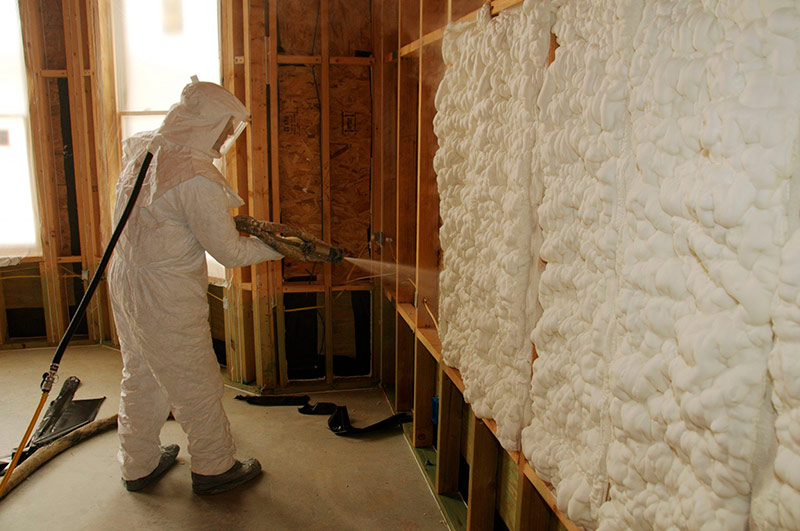

Application of polyurethane foam.
Ecowool
A new material for insulation, which is made from cellulose fiber. It is applied to the walls using a special machine. Warming is carried out in two ways:
- Filling the space between the wall and the facing material.
- Spraying together with an adhesive binder mass on a wall with a crate, followed by coating with facade panels.
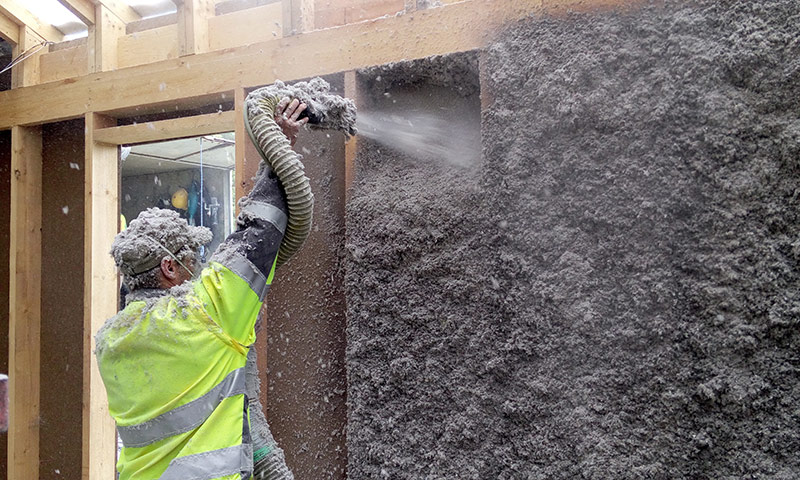

Wet ecowool application.
The choice of insulation, depending on the material of the walls and the method of finishing
Brick walls
For a brick house, any insulation for the exterior walls of the house is suitable. But for each type of finish there are recommendations on the technology of insulation.
Facing brick
If a facing brick is chosen as the external finishing layer, and the bearing walls of the house are also made of brick, then both insulated and extruded polystyrene foam and stone wool can be used as insulation. In the case of using stone wool, it is necessary to provide a ventilated air gap so that the water particles freely evaporate - this will help to avoid wetting the walls.
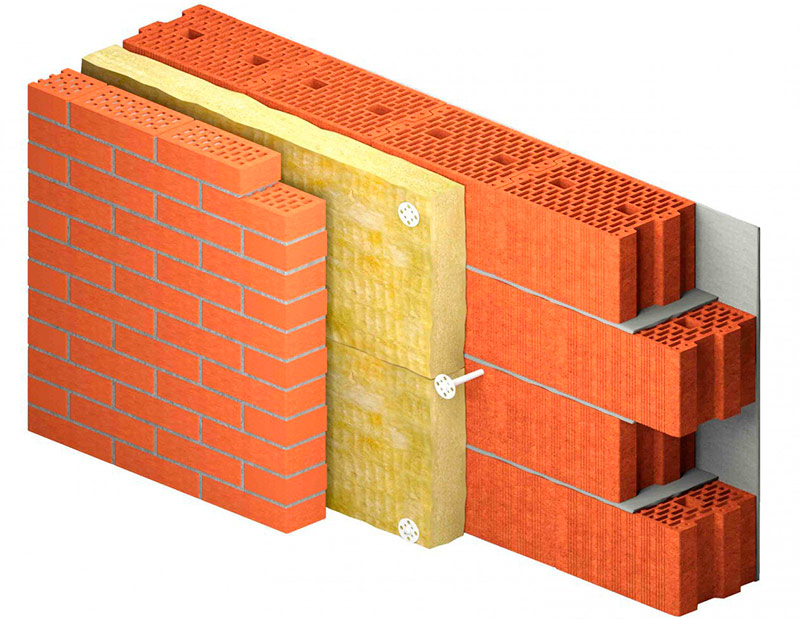
Brick house insulation pie with stone wool with brick lining.
Wet facade
According to the rules of construction and design (paragraph 8.5 of SP 23-101-2004), the layers should be arranged so that the vapor permeability of the inner layer is less than the outer. That is, the insulation should not interfere with the weathering of moisture from the walls of the room. If you adhere to this rule, mineral wool is best suited in this case because of its high vapor permeability.However, brick walls do not have high vapor permeability, therefore, for their insulation you can use polystyrene foam, followed by applying a plaster layer.
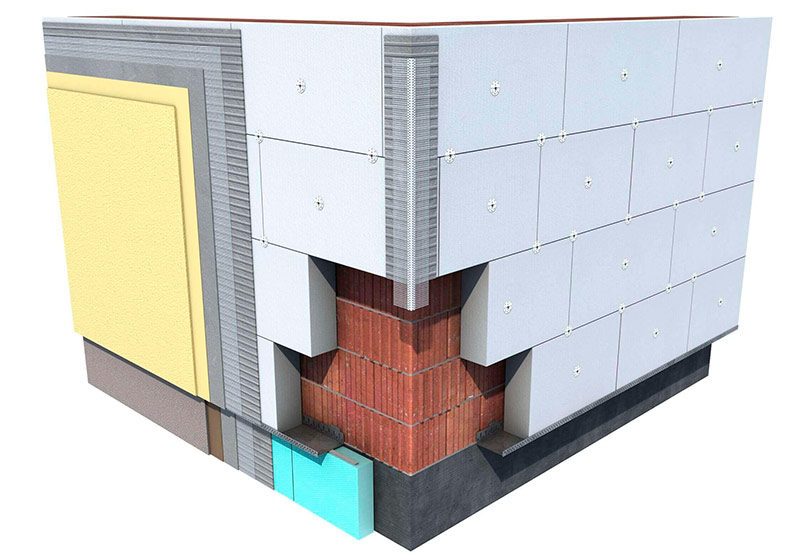
Pie for insulation of brick walls with expanded polystyrene followed by arrangement of the plaster layer.
Ventilated facade
If wall panels or large porcelain tiles that are mounted on a ventilated facade are selected as a brick wall cladding, it is recommended to use stone wool as a heater.
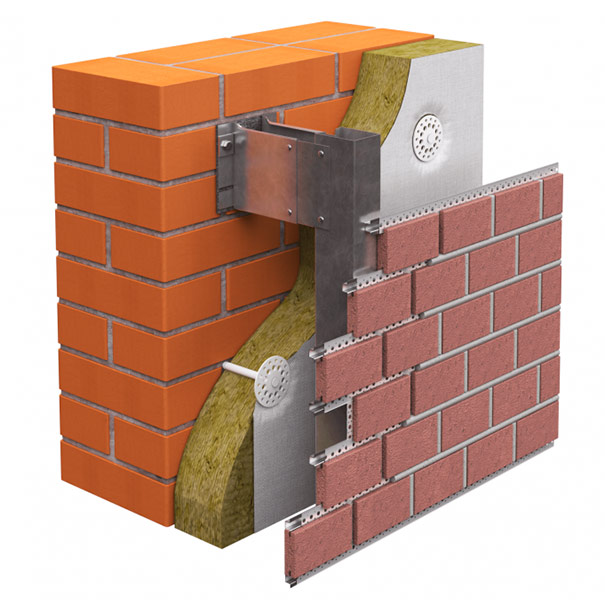
Pie of insulation of brick walls when arranging a hinged ventilated facade.
Wooden walls
Houses made of logs or beams are insulated both by the technology of a hinged ventilated facade and by the technology of a wet facade. In both cases, stone wool is recommended as a heater.
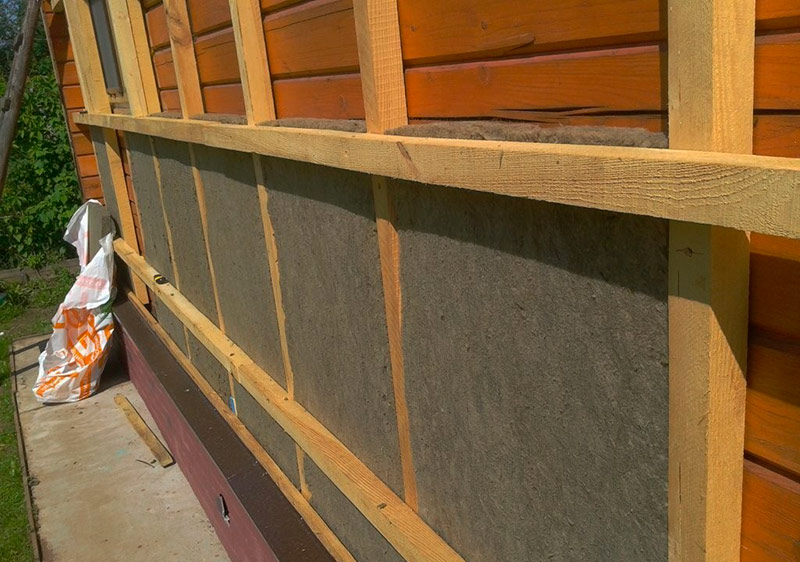

Warming of wooden walls with stone wool.
Walls of aerated concrete blocks
Wet facade
If you follow the rule that the vapor permeability of building structures should increase in the direction from the inside to the outside, then for the insulation of load-bearing walls from aerated concrete blocks, it is best to use stone wool.
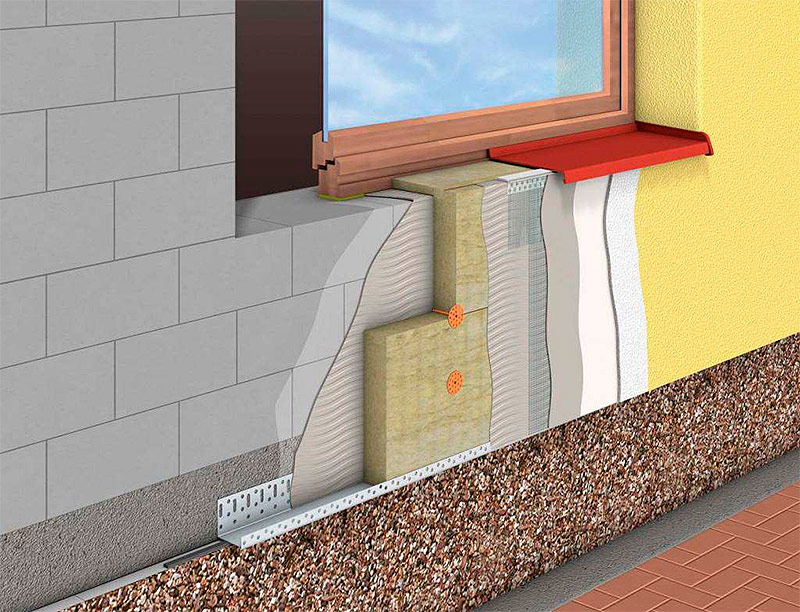

Pie of wall insulation from aerated concrete blocks with stone wool, with the arrangement of a plaster facade.
However, aerated concrete is not a tree, rotting cannot occur in it, and if the room is well ventilated, then polystyrene foam is allowed for external insulation of walls from aerated concrete.
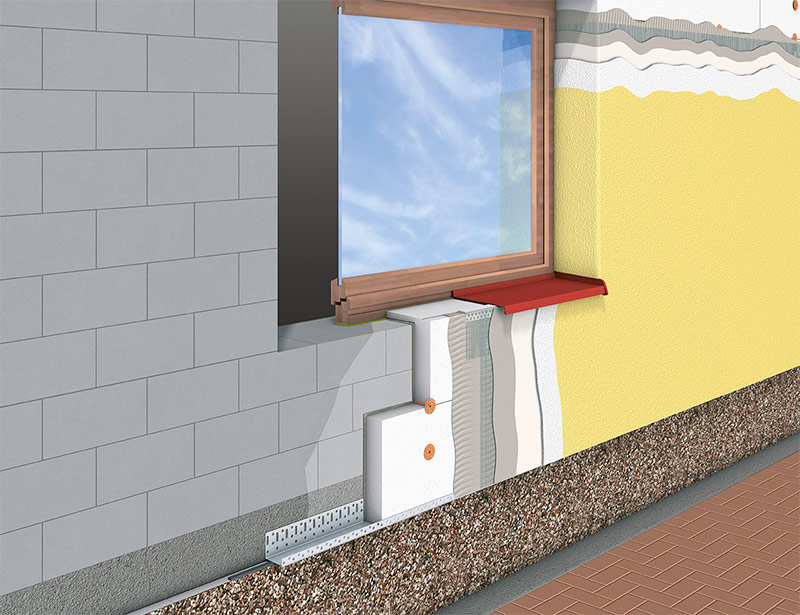

Pie for wall insulation from aerated concrete blocks with expanded polystyrene, with the arrangement of a plaster facade.
Facing brick
If a facing brick is chosen as the external finish of aerated concrete walls, it is possible to use both stone wool and expanded polystyrene as a heater. In the case when the insulation is made with stone wool, it is necessary to provide a ventilation gap between the insulation and the brickwork. This will allow moisture to evaporate from the insulation.
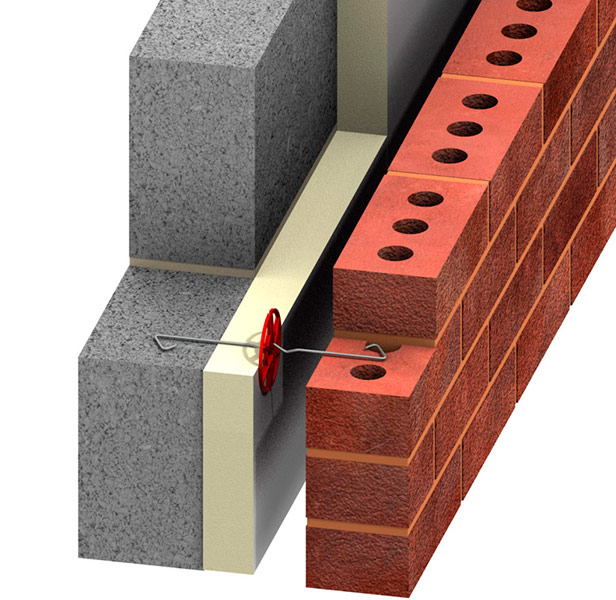
Wall insulation cake made of aerated concrete blocks followed by finishing with facing bricks.
The best heaters for the walls of the house outside
Next, we will review the most successful brands of insulation used to warm the exterior walls of the house.
The best brands of stone wool for exterior walls
Rockwool Light Batts Scandic basalt cotton wool
This is a modern type of stone wool, created from basalt rocks. Available in the form of plates, the main advantages of which are lightness and moisture resistance.
The product is unique in the new technology for producing stone fibers. Thanks to it, the finished plates are compressed up to 70%. The material is easily restored and retains its properties. Vata adheres tightly to the surface, leaving no cracks.
The plates are made according to Flexi technology - one end side of them can spring. This feature facilitates the installation process. In order not to check each plate, the springy edge is marked on the inside, this further adds to the convenience of installation.

Application. Light Butts Skandik boards are recommended for use as a non-load insulating layer in lightweight coatings. It can be attics, partitions, floors between floors, as well as the walls of low buildings. Used in vertical and inclined walls. Plates cannot be subjected to heavy loads.
Main characteristics:
- density - 37 kg / m3
- water absorption - 1 kg / m2
- combustibility group - NG
- vapor permeability coefficient - 0.3 mg / m * h * Pa
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.036 W / (m * C)
Rockwool Basalt Cotton Wool Facade Butts
Insulation is intended for use in plaster facades. These plates are rigid and dense, they are resistant to deformation. Made from basalt rocks.
To install Rockwool Facade Butts insulation, a special adhesive should be used. For more reliable fixation, additional mechanical fastening with dowels is required.

Application. Plates Facade Butts are suitable for facade insulation with a thin layer of plaster.The material provides reliable thermal insulation, and is also used as the basis for the finish layer.
Main characteristics:
- density - 130 kg / m3
- water absorption - 1 kg / m2
- combustibility group - NG
- vapor permeability coefficient - 0.3 mg / m * h * Pa
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.037 W / (m * C)
Thermal insulation Tekhnonikol Tekhnofas Cottage
This insulation is available in the form of plates. Belongs to the group of non-combustible materials, protects against moisture. The product is made from basalt fibers on a low phenolic binder.
Application. TechnoFas Cottage is designed for thermal insulation in facade composite systems with external plaster layers. It is used only for insulation of facades of low-rise buildings, with a height of not more than 10 m.
Main parameters:
- density - 115 kg / m3
- combustibility group - NG
- vapor permeability coefficient - 0.3 mg / m * h * Pa
- heat conductivity coefficient - 0.038 W / (m * C)
Basalt cotton wool Technonikol Technovent Optima
This material provides thermal and sound insulation. It is non-combustible and hydrophobized - it repels water due to its special composition. It has good vapor permeability and does not retain moisture that leaves the room, which creates the right microclimate in the house.

Application. Technovent Optima is designed for residential buildings and industrial construction. Used in ventilated facade systems.
The main properties of the material:
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.036 W / (m * C)
- vapor permeability coefficient - 0.3 mg / m * h * Pa
- combustibility group - NG
- density - 81-99 kg / m3
Universal heat-insulating material Paroc Extra
This material is suitable not only for heat and sound insulation, but also for fire protection - it is completely non-combustible. Available in flexible, resilient slabs that are easy to install. The heat-insulating design does not shrink and does not lose its qualities during use. Protects even in the coldest winters, while maintaining high resistance to heat loss.
The material retains its properties in a wide temperature range. Binding components begin to evaporate at a temperature of 200 degrees, and fusion occurs at 1000 degrees.

Application. Paroc Extra basalt wool should not be exposed to external stress. It is advisable to use it on the exterior walls, floors, attics, internal partitions, pitched roof.
The main properties of the material:
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.036 W / (m * C)
- combustibility group - NG
- water absorption - 1 kg / m2
- density - 30-34 kg / m3
Top brands of extruded polystyrene foam for exterior walls
Thermal insulation Penopleks Wall
The material is extruded polystyrene foam. It is characterized by zero water absorption, high strength and low heat conductivity. Plates are available with a milled surface for better bonding with adhesives and plasters. This feature makes the design more durable and durable, and also facilitates and accelerates the installation of thermal insulation systems.

Application. Penoplex Wall is intended for building envelopes as internal and external thermal insulation. Used in wet facade systems.
Main characteristics:
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.032 W / (m * K)
- vapor permeability coefficient - 0.005 mg / m * h * Pa
- combustibility group - G4
- water absorption - not more than 0.5% by volume
- density - from 20 kg / m3
Thermal insulation Tekhnonikol Tekhnopleks
The insulation is an extruded polystyrene foam in the production of which nanosized particles of graphite are used. Nanographite reduces the thermal conductivity of the material and increases the strength of the plates. Due to these additives, Technonikol Technoplex boards have a grayish tint.

Application.The insulation has a wide range of applications and is designed specifically for thermal insulation of private houses and repair of residential premises. It can be used both for insulation of vertical and horizontal structures.
The main properties of the insulation:
- heat conductivity coefficient - 0,034 W / (m * K)
- vapor permeability coefficient - 0,010 mg / (m * h * Pa)
- combustibility group - G4
- water absorption - 0.2%
Thermal insulation of Ursa XPS-N-III-L G4
This is extruded polystyrene foam produced in the form of rigid plates. In the manufacture of insulation, freons are not used. Ursa insulation is durable, not subject to moisture, reliably protects from the cold and has high strength. It is convenient both for domestic use and for industrial facilities.
The plates are available in different thicknesses, you can choose the most suitable option depending on the required insulation layer. They are lightweight, do not break or crumble when sliced, tolerate transportation well. Installation does not require special knowledge and special tools. The edge of the plate is made in the form of steps, the edges are interconnected tightly, without gaps.

Application. Ursa XPS-N-III-L G4 is recommended for thermal insulation of balconies, foundations and socles, basements inside and outside, pitched roofs, walls, followed by plastering.
Basic properties:
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.032 W / (m * K)
- vapor permeability coefficient - 0.004 mg / m * h * Pa
- combustibility group - G4
- water absorption - not more than 0.3% by volume
TechnoNicol Carbon Eco TB
Insulation boards are manufactured using ThermoBonding thermal bonding technology, which increases its thermal insulation properties and strength, in comparison with other manufacturing methods. The composition includes carbon nano-particles, which further reduces thermal conductivity and makes the structure stronger.

Application. Scope - low-rise construction (cottages, summer residences). It is used for walls and floors, facades, roofs, foundations.
Basic properties:
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.033 W / (m * K)
- vapor permeability coefficient - 0.014 mg / m * h * Pa
- combustibility group - G4
- water absorption - not more than 0.4% by volume
The best brands of expanded polystyrene foam
Polyfoam Knauf Therm Facade RRO
Insulation is made in the form of rectangular plates. Special production technology eliminates shrinkage of plates after installation and during operation. High moisture resistance allows the use of the material in humid climates. The low weight of the insulation does not create a load on the foundation. The material does not emit harmful substances.
Application. Knauf Therm is used to insulate the walls of a house, cottage, office and industrial premises.
Basic properties:
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.038 W / (m * K)
- vapor permeability coefficient - 0.026 mg / m * h * Pa
- combustibility group - G3
Styrofoam Knauf Wall
The advantages of this insulation - it does not sag, does not change shape when used. Knauf Wall is an environmentally friendly material with no toxic or flammable additives. Plates are high strength, do not absorb moisture.
Application. Suitable for three-layer brickwork (well). Slabs can be laid as a middle layer in the construction of brick walls, as well as in the production of reinforced concrete panels.
Specifications:
- heat conductivity coefficient - 0,044 W / (m * K)
- combustibility group - G3









