Water heating convectors: device, principle of operation, varieties
All over the world, water heating convectors have been successfully competing with radiators for several decades. In our country, they are also used for quite some time, but in popularity they are still far inferior to cast-iron and bimetallic radiators. Low popularity is due not to the worst performance characteristics, but only to the lack of a significant part of the population's understanding of this type of heating equipment.

Content:
- Principle of operation
- The device of a water convector heating
- Wall and floor water heating convectors
- Underfloor heating water convectors
- Ability to control temperature
- Possibility of application for cooling the room
- Advantages and disadvantages of water convectors in front of conventional radiators
Principle of operation
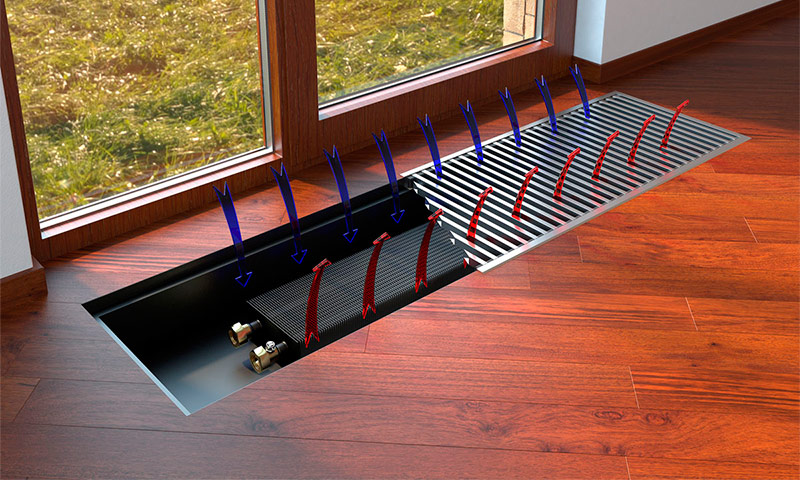
The word "convector" itself serves as an indication that the basis of the principle of its operation is such a physical phenomenon as convection. Cold air, being more dense, is in the lower layers - near the floor of the room. Passing through the convector, the air warms up, its density decreases, as a result of which it rises.
Convection can be not only natural, but also forced. The built-in fan will help increase convection air flow and thereby increase the efficiency of the heater.
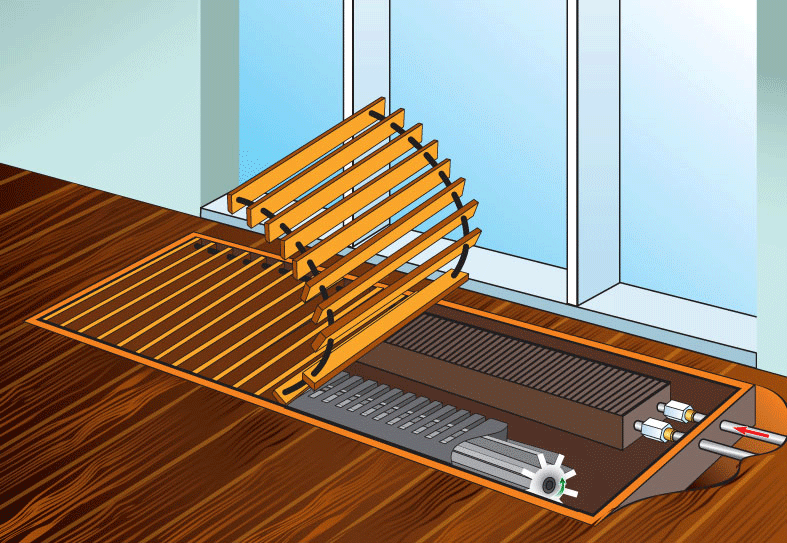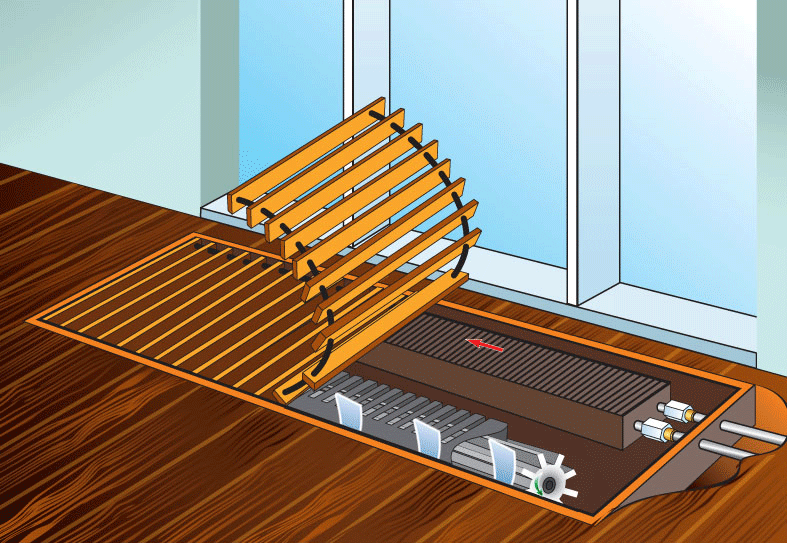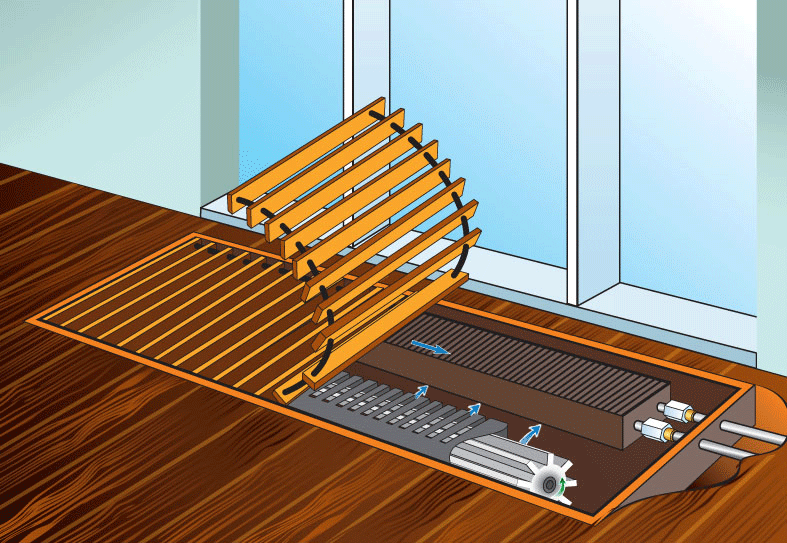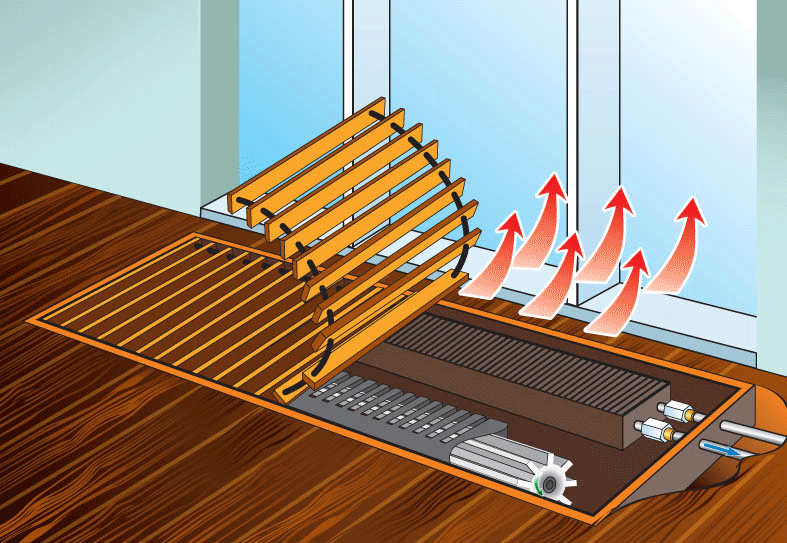
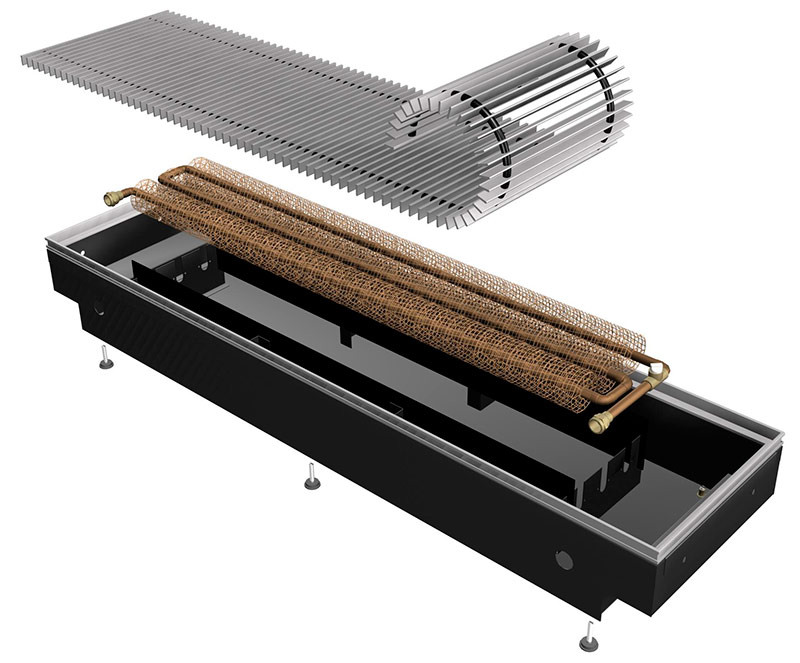
The device of a water convector heating
The main working element of the convector is a heat exchanger. It is with its help that heat is transferred from the coolant, the function of which is performed by hot water circulating in the heating system and the surrounding air. A heat exchanger is a pipe on which a plurality of metal plates (lamellas) are mounted, increasing the heat transfer area. Depending on the required power, the convector can be equipped with either one or two heat exchangers.
The distance between the lamellas of the heat exchanger is not set arbitrarily, but is clearly calculated. It would seem that the more plates are mounted on the pipe, the better the heat transfer. However, their too high density will lead to the fact that air circulation through the device will be difficult. It is necessary to achieve a “golden mean” - so that the lamellas do not interfere with the movement of air, but at the same time provide the most efficient heat transfer.
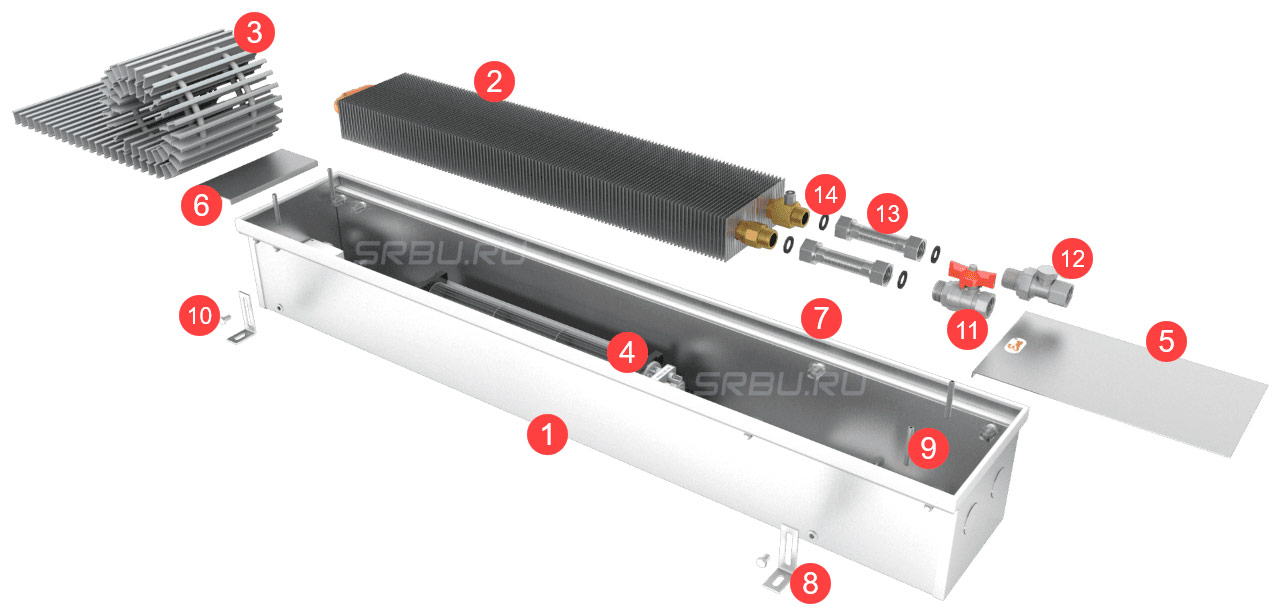
1. Conveyor body.
2. Heat exchanger.
3. Decorative grille.
4. Tangential fan.
5. Large decorative cover.
6. Small decorative cover.
7. Decorative edging.
8. Fixing foot.
9. Adjusting screws.
10. Fixing bolt.
11. Ball valve.
12. Shut-off and control valve.
13. Flexible eyeliner.
14. Gaskets.
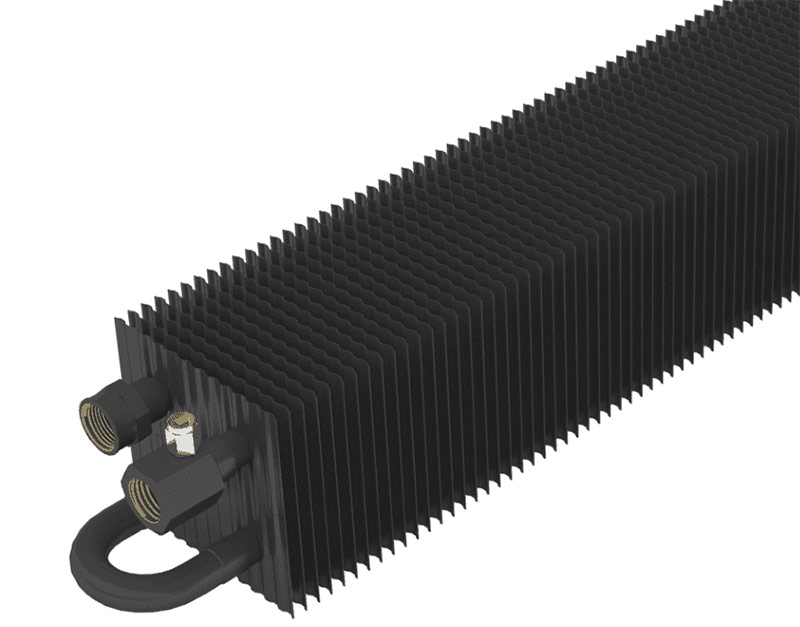
There is also an alternative from a structural point of view type of heat exchanger in which wire is used instead of lamellas. Wire convectors are somewhat more efficient, but at the same time much more expensive, and therefore less common than plate convectors, so we will not talk more about them.
Water convector with wire heat exchanger.
Many technical characteristics of a convector are determined by the material of which its heat exchanger is made. It can be steel, copper or a combination of copper and aluminum. The use of non-ferrous metals for the manufacture of a heat exchanger, due to their high thermal conductivity, leads to an increase in the efficiency of the device in comparison with the analogue of ferrous metal. By the way, aluminum lamellas are very thin, and if handled carelessly, they are easily jammed, which impairs aerodynamics.
Heat exchangers can differ not only in the material of manufacture, but also in the shape of the metal fins. Along with smooth lamellas, corrugated ones are also used: wave-shaped, U-shaped, meander, etc.Corrugated lamellas have a clear advantage: the relief increases the area of the plate, and hence the heat transfer.
Heat exchanger with wave-shaped lamellas.
The efficiency of heat transfer from the coolant to the lamellas largely depends on the tightness of the plates to the pipe: even a small gap can cause large heat losses. If the heat exchanger is made of steel, welding is usually used to connect the lamellas to the pipe, if soldering is made of copper. In the case of bimetallic heat exchangers, in which aluminum plates are in contact with copper pipes, neither welding nor brazing are applicable. However, here you can achieve a snug fit of the elements. In this case, they either use lamellas with special cuffs, or they use the burnishing method - they insert plates on the pipe, and then this pipe is expanded using a mandrel.
Some convectors are equipped with a fan that draws air into the heat exchanger and, thus, accelerates air exchange, and hence the process of heating the room. The fan can be tangential or axial. The first impeller extends along the entire length of the heat exchanger.
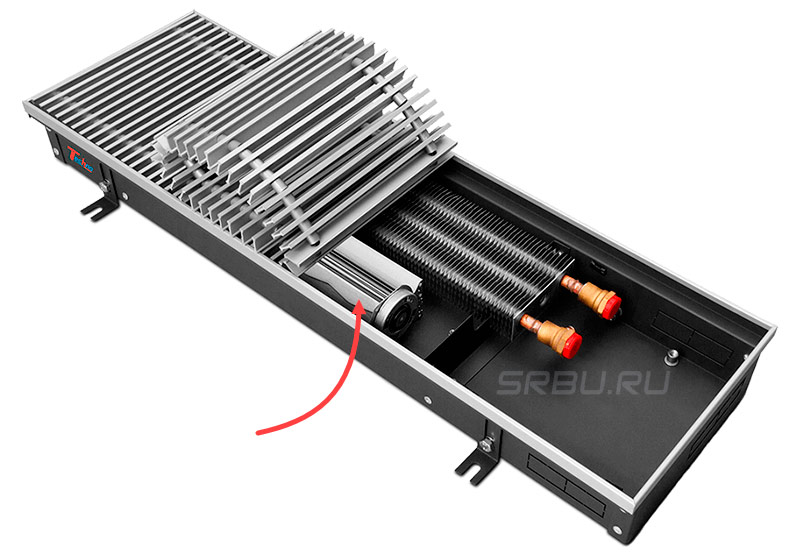
The axial fan propeller is located at the end of the heat exchanger and directs air along it.
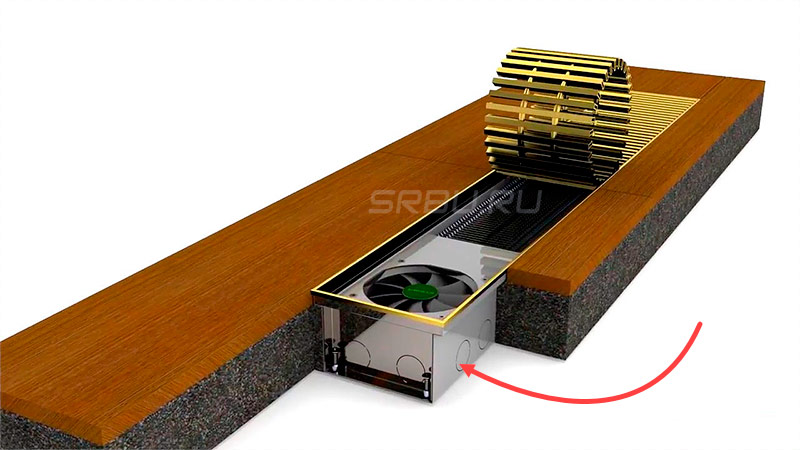
The advantage of a forced-convection heater is obvious - increased efficiency. But it also has obvious drawbacks: firstly, the need to connect to the mains, which may not always be easily feasible, and secondly, the noise that the fan emits during operation.
The heat exchanger, as well as the fan (if provided by the design), the points of connection to the heating system, the coolant supply regulator, and the air release valve are hidden behind the walls of the stainless steel casing. The upper end of the housing is closed by a grill, which does not impede the movement of air flows, but at the same time prevents foreign objects from getting inside. Some convectors have an air damper that allows you to control the intensity of the air flow.
Wall and floor water heating convectors
By the method of installation, all heating convectors are divided into wall, floor and floor. The first two types are very similar to each other, so we will consider them together.
The main difference between wall and floor convectors, very similar in appearance, is their dimensions. Wall mounted, as a rule, high enough, floor - low and compact. The latter, due to their modest size, are less conspicuous, they are easy to hide behind furniture.
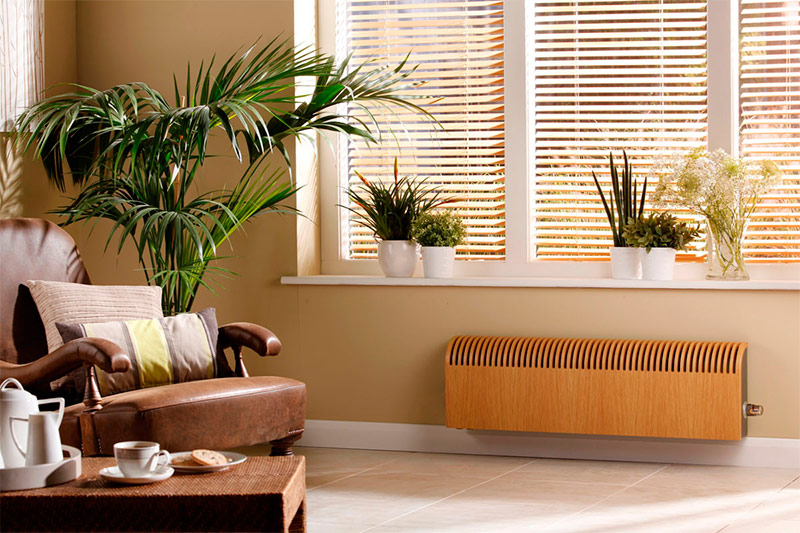

Wall mounted water convector.
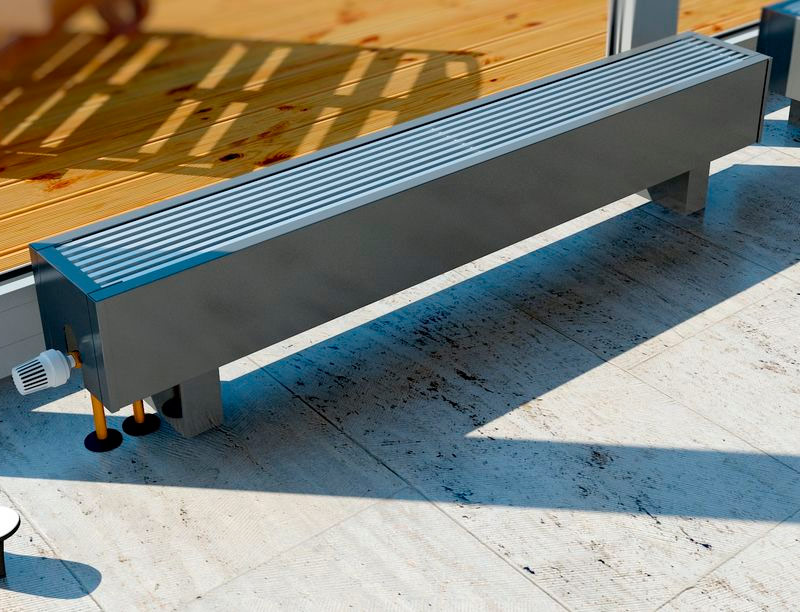

Floor convector.
There are even skirting models with a height of less than 200 mm, which can serve as a replacement for the skirting board and heat the room around the perimeter.
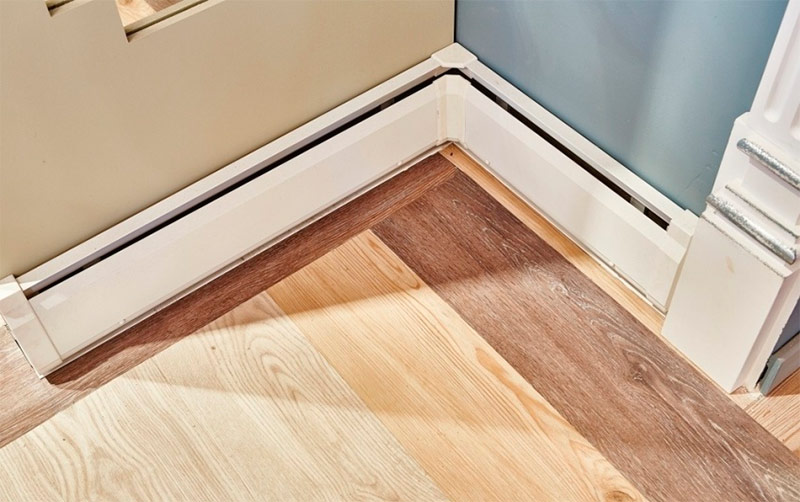

Plinth water convector.
All wall and floor convectors are divided into models with a casing and models without it. The casing does not play a decorative role, as one would expect: it contributes to the creation of additional traction to improve air circulation. Often, the height of the casing significantly exceeds the dimensions of the heat exchanger. Such a discrepancy is not a marriage of the manufacturer at all, it is done on purpose: the higher the casing, the stronger the traction. As for convectors without a casing, they also have a casing, but it only disguises the heat exchanger and protects it from mechanical damage.
It should be noted that the surface of the functional casing or the decorative case does not heat up too much. This distinguishes convectors from radiators - burn yourself by accidentally touching the surface of the body, in this case it is impossible.
Most often, convector bodies are made of steel, regardless of the material of the heat exchanger. The fact is that steel is easily painted, and this gives the buyer the opportunity to choose a heating device that fits perfectly into the interior of the room.However, steel - although the most common, but not the only option. If desired, you can find something more exotic, for example, a convector in a wooden case.
Underfloor heating water convectors
There is another kind of heating convectors, which is very different from the ones considered above and therefore stands apart. They are unusual in their place of installation - in a niche located below the floor. With a high degree of probability, you can find such heating devices in commercial or office premises with large panoramic windows, against which ordinary radiators or convectors will not look quite appropriate. In cottages and apartments, such convectors are also installed, but usually only in cases where the lower edge of the window is located no higher than 150-300 mm from the floor level. It is allowed to embed heating convectors in the windowsill.
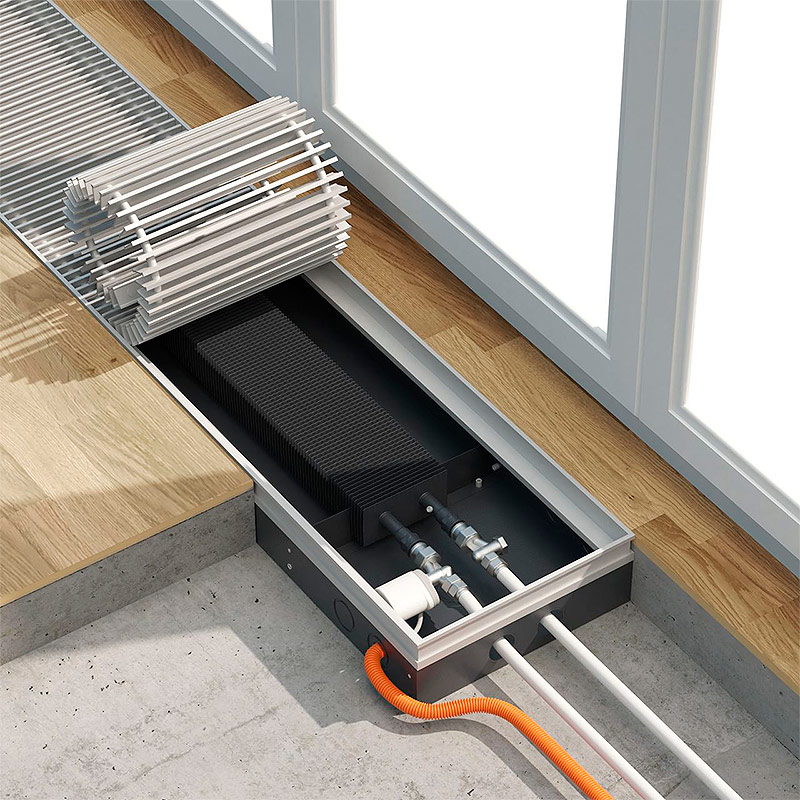

Convector of water heating built into the floor.
The height of the body of convectors embedded in the floor can vary from 50 to 130 mm, and the length can reach 3 m. But the user, if he himself was not involved in the design and installation, can only guess about the true dimensions of the heating device, because only the decorative grill will be visible to him at the level floor through which heated air rises.
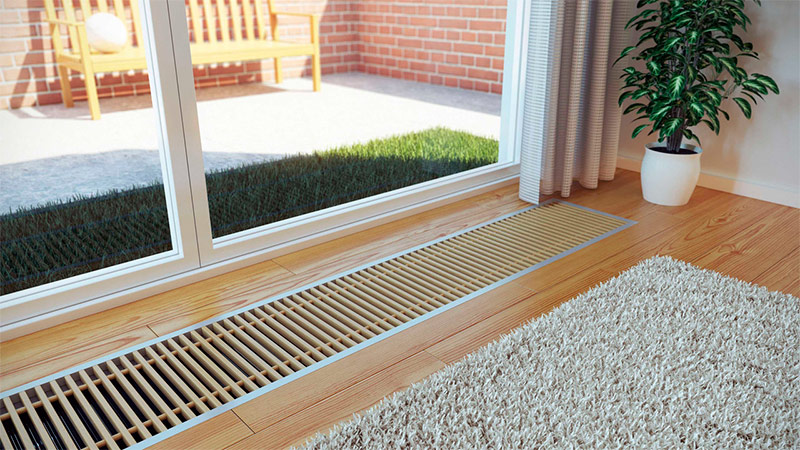

Most often, such grilles are made of steel, aluminum or plastic, but sometimes you can find cast iron, marble or, for example, wooden. Whatever material the lattice is made of, it must be strong enough so that you, passing by, are not afraid to step on it.
In the case of large French windows, floor convectors are an indispensable option for heating equipment. On the one hand, and we have already mentioned this, they, being located below the floor, do not interfere with the review. On the other hand, it is precisely such convectors that most efficiently heat a room with “floor” windows. Cold air from the window enters the convector through the grill, and from there it comes out already warm.
To install an underfloor convector, it is required to prepare in advance a niche in the floor with a depth of 100 to 300 mm. However, it is possible to carry out installation at the stage of performing the floor screed. It should be borne in mind that far from every convector you can use for floor installation.
The limiting factor in this case will be the height of the device. Powerful models several tens of centimeters high are not designed for installation in rooms located on the upper floors of the building. Of course, it is necessary to plan the installation of floor convectors in advance - even at the construction stage of the building. The exception is low-power low models, which allow mounting in a screed.
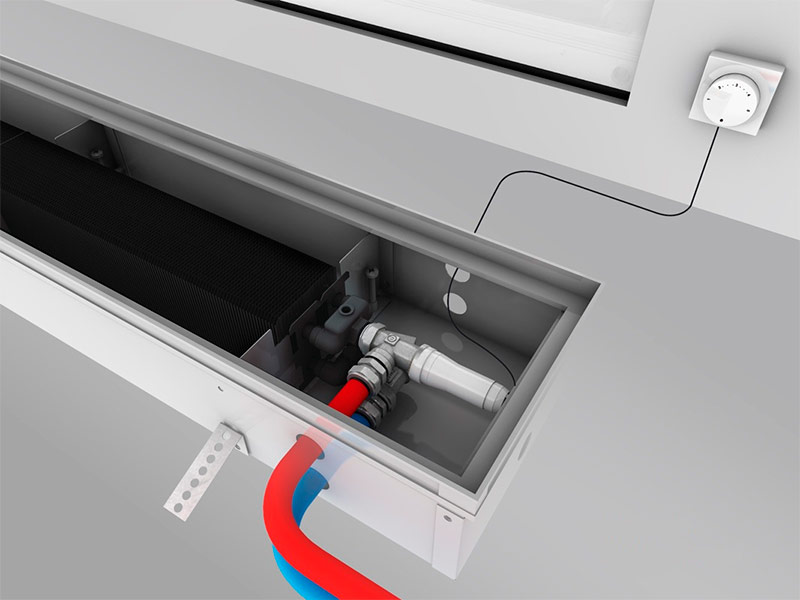
In-floor convectors for water heating, unlike wall-mounted or floor-mounted, often have in their design a fan for forced air supply to the heat exchanger, as well as a drainage system for collecting and draining condensate from the device body.
Ability to control temperature
Sometimes, especially in the spring, when it is still cold at night and the sun is already beginning to noticeably warm during the day, the desire periodically arises to reduce the heat coming from the heater. Water heating convectors are easily adjustable power. When the supply of coolant to the convector is blocked, it cools down quite quickly, which is due to the small volume of water inside it compared to the radiator. All you need to maintain the temperature in the room at a given level is a convector equipment with thermoregulating valves with mechanical or electronic control.

Mechanical temperature control valves.

Electronic thermostatic valves.
The thermostatic valve to be installed must have a high flow rate so that there is no significant hydraulic resistance at the inlet.Some manufacturers of convectors initially equip their products with thermostatic fittings. If the device you purchased is not equipped with a thermostatic valve, you can buy and install it yourself.
You can adjust the room temperature manually. Some convector models have a damper that the user, if desired, can turn and block the way for heated air.
Possibility of application for cooling the room
The convector can be called universal climatic equipment, because in different seasons it can perform different tasks: in winter - to warm, in summer - to cool. True, not every device is adapted for cooling, manufacturers usually indicate the availability of this feature in one or another of their models. It should be borne in mind that convectors generate cold significantly worse than heat, so when calculating the power of the device, you need to rely on your needs for cold, because it is not difficult to reduce the heating power, as you now already know.
So that your convector does not start to warm, but to cool the air in the room, you need to empty it, fill it with special liquid and connect it to the chiller. However, there are models in which the transition from one mode to another is much simpler and faster. In them there are immediately two unconnected circuits: one for the coolant, the other for the refrigerant. To change the operating mode, it will be enough for you to turn off the fluid circulation in one circuit and turn it on in another.
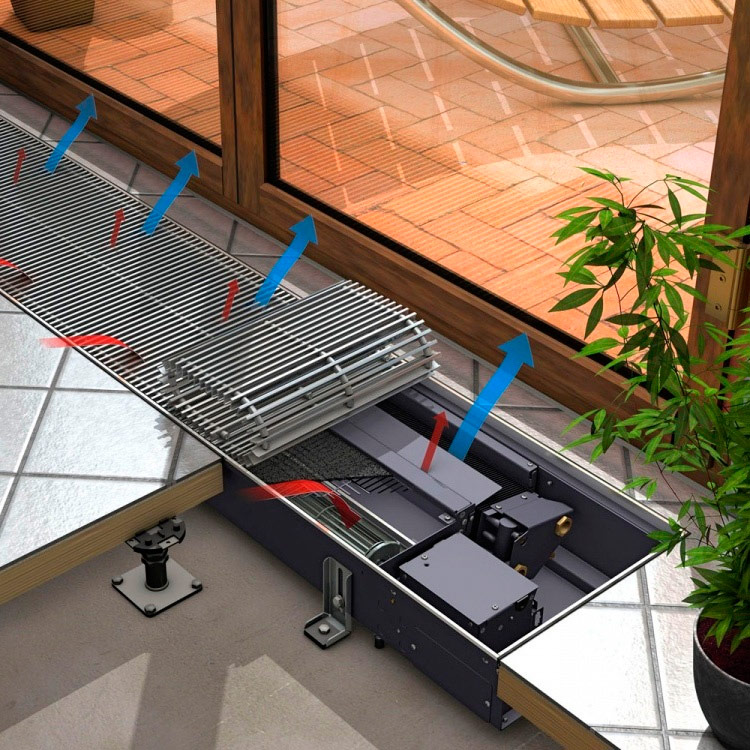

And a couple of comments regarding the possibility of using this type of climatic equipment for cooling the room. Recalling the principle of operation of the convector, you will understand that in the natural mode it is not able to work on cooling. That is why all models designed to work in two modes are equipped with fans. In addition, the fan helps to reduce the amount of condensate formed on the heat exchanger during convector cooling operation.
Advantages and disadvantages of water convectors in front of conventional radiators
You have learned a lot for yourself about water convectors, but most likely, this will not be enough for you to understand whether you personally need such a heating device. To help you make a choice (no matter whether it is positive or negative), we compare water convectors with conventional radiators, familiar and familiar.

+ Pros of water heating convectors
- Convectors warm up faster to rated power. The reason for this is quite simple: the internal volume of the convector pipes is rather small, due to which the circulation rate of the coolant in the system is higher. Convectors not only heat themselves faster, but also warm the room faster, which is greatly facilitated by the high thermal conductivity of the rib plates.
- Convectors do not require a high coolant temperature: for efficient heating of the room it is enough that the water in the system is heated to 50-60 ° C. From this it follows that the energy consumption for heating the coolant in a heating system with convectors is less than in a system with radiators.
- Convectors, unlike radiators, are able to create an effective thermal curtain, cutting off the cold air flows entering the room from the windows. Windows do not fog or freeze.
- Air congestion in water heating convectors is a rarity.
- Due to the low weight of the convectors, it is possible to install them even on light partitions made, for example, of drywall. In the case of radiators, especially cast iron, this can not even be thought of.
- Convectors do not constitute a danger to young children: the surface of the body practically does not heat up, which means that the probability of getting burned is zero.
- The hidden installation of floor convectors, in which neither the pipes nor the heating devices are visible, is a long-standing dream of many room designers, which finally came true.

- Cons of water heating convectors
- Convectors can only be used in rooms with natural ventilation. Air intake from a room with forced ventilation, as a rule, is carried out near the ceiling. This means that all the warm air created by the convector will be pulled out, that is, the heater will work idle.
- As a result of the uneven distribution of air flows coming from the convector, draft is possible.
- This heater facilitates the circulation of dust in the room, moved by convection air flows.










