How to choose heating radiators depending on the heating system and the main parameters
It seems that the days of the old clumsy cast-iron radiators of the Soviet model are passing. Today, people want to put in their place something more elegant and compact, but with good heat dissipation. About how to choose heating radiators that best meet these requirements, we will tell in this material.

Content:
And from what, in fact, is the choice
To begin with, we will provide a list of the main types of heating appliances offered by modern stores. Some of them can only be supplied in an autonomous heating system with its clean water and low pressure. And others can easily withstand a fierce battle with water hammer and chemically active water in centralized heating systems. Let's see what and how.
Cast Iron - Without It Even Today
Let's start with the cast iron radiators mentioned at the beginning of the article. Do not think bad of them - modern radiators made of this metal look pretty pretty. Budget models have flat neat surfaces and compact (compared to Soviet batteries) sizes. And exquisite retro models with beautiful moldings are at all the “highlight” of the interior. Standing on elegant legs near the window, they give the room a special charm and a touch of antiquity.
Storing heat for a long time and not suffering from corrosion, cast iron products can work for several decades. The disadvantages of these devices can be considered their weightiness and the associated complexity of installation, inertia and a large amount of coolant. In addition, the fragility of cast iron does not always allow it to withstand water hammer.
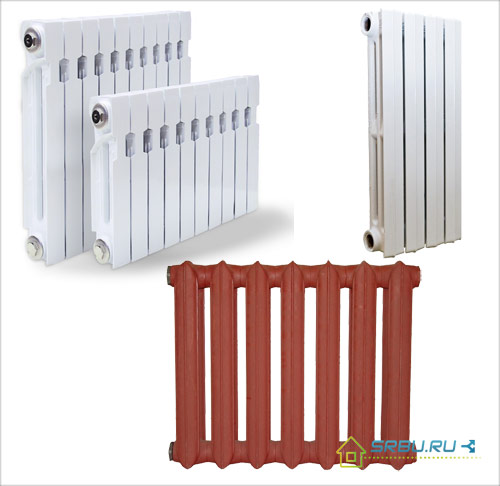

Cast iron radiators of domestic and foreign manufacturers.
Lightweight and beautiful aluminum radiators
For your own home, this is a wonderful solution - and they are not very expensive, and the design is varied and stylish. If the water in the heating system is clean and its acidity is normal, then aluminum radiators will last 15-20 years. After all, low pressure in CO will not test them for strength, and neutral water will not cause a violent chemical reaction with the release of hydrogen. Plus of these batteries - low inertia.

Note that there are two types of aluminum radiators:
- Extrusion radiators - have sections glued in three parts and pressed in. The central part is extruded on the extruder, and the upper and lower headers are injection molded.
- Injection radiators are more reliable and durable, each section is injection molded.
For the successful operation of aluminum devices, it is very important to monitor the pH value, which should not exceed 7-8. Otherwise, a chemical reaction of aluminum with the evolution of hydrogen will begin. This is fatal for radiators, and in a firefighting it is dangerous. To bleed air, it is necessary to put a Mayevsky crane (however, it is also necessary for other types of radiators).
Bimetal radiators, which have a lot of pressure on the shoulder
But this is already a good option for an apartment in a multi-storey building, where the pressure in the heating system is high. Not only that - there are also its jumps, called hydraulic shocks. Bimetal radiators, in which steel (or copper) durable pipes are hidden under an aluminum shell, can easily withstand pressure drops. In addition, they, unlike their aluminum counterparts, are not “gnawed” by corrosion. After all, steel and copper are not at all as chemically active as aluminum.
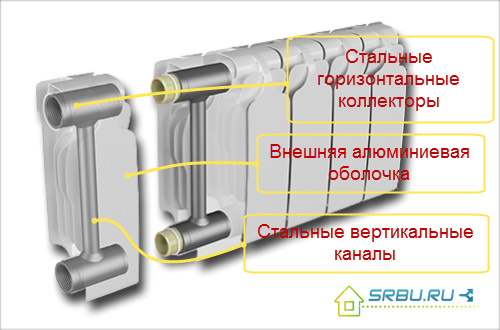
Bimetal radiators also exist in two varieties:
- Truly bimetallic radiators - have a core in which there are no aluminum parts.It is completely made of steel (or copper) and does not corrode, unlike an aluminum battery collector. A corrugated body, under pressure "worn" on a steel core, gives good heat dissipation.
- Pseudo-bimetallic (otherwise, semi-bimetallic) radiators have a core in which only vertical channels are reinforced with steel. The remaining parts are aluminum. This increases heat transfer, but reduces strength. Such appliances have a lower price than true bimetal heating appliances.
In addition, bimetallic heating devices can consist of either several sections, or represent an integral monolithic product:
- Sectional radiators are convenient in that they can be sorted out if necessary. For example, when one section fails, or if you need to increase or decrease the number of these sections, then all this can easily be done.
- The advantage of monolithic radiators is that they have a huge margin of pressure (about 100 atmospheres). Therefore, such devices are the best solution for "high-rise buildings" with central heating, where the pressure in the system is very solid, and sometimes you can not protect yourself from water shocks.
Steel radiators - inexpensive and tidy
Radiators made of steel have a modern design, low weight and good heat dissipation. There are heating devices made of steel of two types - panel and tubular.
1. Panel radiators consist of pairwise welded metal stamped sheets with oval recesses - channels for the coolant. These are the panels, the number of which can be from one to three. To increase thermal efficiency, convector ribs are welded from the inside of the panels. Ribbed models produce more heat but raise more dust due to convection. Smooth panels are easier to clean, due to the lack of dust they are great for children and medical facilities.
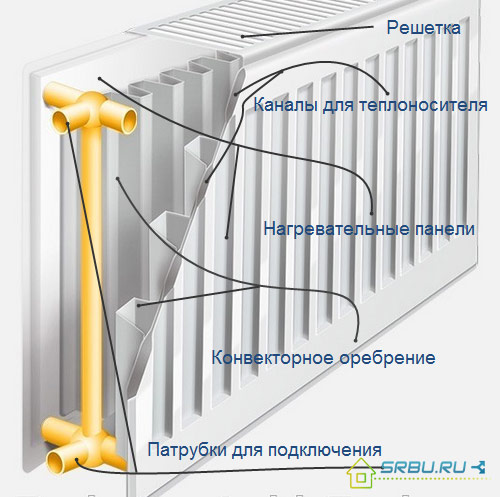
The device steel panel radiator.
2. Tubular radiators are a design in which the upper and lower manifold pipes are connected by a series of vertical steel pipes. These radiators have a slightly larger pressure margin than the previous type. Their cost is higher, and the design is more interesting and original than that of panel models.

Floor convectors - warm with warm air
A tube made of copper or steel equipped with fins for better heat transfer is the core of the convector. The shell of this heating element facilitates the movement of heated air from the lower to the upper zone. The convector is not afraid of high pressure and corrosion, has a small hydraulic resistance. It is never hot (its body heats up to no more than 43 degrees). It is convenient to adjust, since the device has low inertia.
But convection devices, unfortunately, often do not heat the room evenly (the floor is hotter than the ceiling), and they also raise dust. Such appliances are good where there are huge windows from floor to ceiling. The radiator creates a heat cable, and the room does not penetrate the cold. The disadvantages of these heating devices are inefficiency and not very high heat transfer.
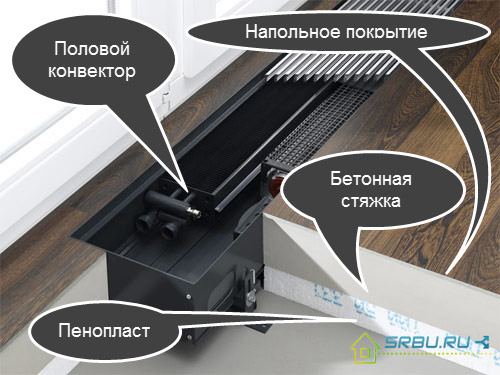
The device of the floor convector.
What are the main criteria for choosing radiators?
Type of heating system
Perhaps, it is precisely from this that we need to build on first of all. In our country there are two types of heating systems: centralized and autonomous. And both of them require the use of different radiators.
1. Domestic central heating is characterized by high working pressure, as well as its jumps. The fact is that we, unlike Europe, have a one-pipe system in which radiators are connected in series. In addition, no one is worried about smoothly turning on the centrifugal pump. And its sharp inclusion is fraught with water hammer. And the water in such a system does not shine with either purity or neutrality. It is tough, its acidity is high, and in the summer it is drained, which causes corrosion in many radiators. Therefore, such a system needs radiators that can withstand a working pressure of 6, and possibly 9 atmospheres (more will be said in the DEZ).Do not forget about the acidity of the water, choosing radiators that can work at high pH levels.
The best choice for a central heating system would be:
- Cast iron radiators, characterized by durability and lack of tendency to corrosion. Working pressure is 6-16 bar.
- Bimetallic radiators, also not subject to corrosion and withstanding pressure up to 35 bar (sectional models) or up to 100 bar (monolithic models).
2. Autonomous heating is fundamentally different from the central one. Water moves in a circle (two-pipe system), its pressure does not exceed 3-5 bar, and the acidity also complies with the standards. There are no extraneous impurities in this water. Therefore, almost all types of radiators are suitable for autonomous heating.
For an autonomous heating system, experts recommend:
- Aluminum radiators with the highest heat output.
- Steel radiators have a low price, characterized by a beautiful appearance and original design.
- In some cases, you can use the good old cast-iron radiators.
The use of bimetallic radiators in an autonomous heat supply system is not entirely justified due to their high cost and lower heat transfer compared to aluminum radiators.
Heat dissipation of different types of radiators
We give specific figures for thermal conductivity (the value for one section is indicated) Naturally, the average values are indicated. More precisely, you can find out the characteristics in the passport of a particular radiator.
Heat dissipation in one section:
- Cast iron radiators - from 100 to 160 watts.
- Aluminum radiators - from 82 to 212 watts.
- Bimetal radiators - from 150 to 180 watts.
Total heat transfer of non-sectional radiators:
- Steel radiators - from 1200 to 1600 watts.
- Convectors - from 130 to 10,000 watts.
To summarize. The leader in heat transfer is aluminum. Steel takes the second place. We give the third to cast iron, which also heats up for a very long time (that is, it has a large inertia). But it cools down for a long time, which sometimes comes to the rescue.

Which radiators are more reliable and durable
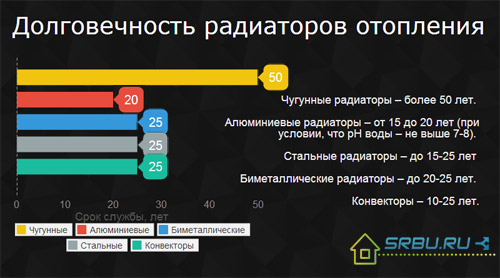
Once again, we provide in the form of a list the uptime guaranteed by the manufacturers.
- Cast iron radiators - more than 50 years.
- Aluminum radiators - from 15 to 20 years (provided that the pH of the water is not higher than 7-8).
- Steel radiators - up to 15-25 years
- Bimetal radiators - up to 20-25 years.
- Convectors - 10-25 years.
So, if, figuring out which heating radiator to choose, you put longevity as the main criterion, then you do not have to go far. Take cast iron - not a single new-fangled radiator will last longer. Only the manufacturer should choose a trusted one who makes really high-quality batteries using excellent raw materials and components. Behind him are bimetallic and steel radiators.
As for reliability, there are two aspects - the ability to withstand pressure and how one or another type of radiator is demanding on the coolant. If we talk about pressure, then bimetallic radiators will be the undisputed leader, followed by aluminum, cast-iron and steel radiators.
But radiators relate to the coolant differently. The most enduring in this regard are cast-iron radiators, then bimetallic ones. For steel radiators, it is important that water is not drained from the system for a long period, otherwise corrosion can occur if oxygen enters the system. Well, the most "tender" are aluminum radiators, which require Ph in the range of 7 - 8 units.
Appearance and finish
1. Cast iron radiators - models of domestic manufacturers, although they have become smaller in size, having undergone design changes (their facade has become flat), but cannot boast of decoration. They are coated only with an anti-corrosion primer, which involves subsequent staining. But the models of European manufacturers and the coating are beautiful and durable, and the design is quite modern.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the radiators in the "retro" style, they are expensive, but in their appearance they are simply amazing.
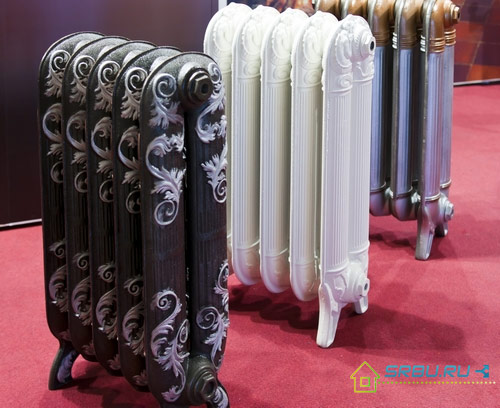

Retro cast iron radiators.
2. Aluminum radiators are distinguished by a variety of design. Many manufacturers produce multi-colored radiators that look very elegant and attractive. Models of aluminum radiators are characterized by a wide range of interaxal distances and sizes. This allows you to perfectly fit them in any corner of the house.

3. Steel panel-type radiators can fit into almost any apartment interior. Smooth panels are not very conspicuous, harmoniously blending with the decor.

And tubular steel radiators are often distinguished by an unconventional form. For example, they can be angular or made in the form of a trapezoid. And they are surrounded by staircases, they are inscribed in niches and attics. And everywhere such radiators look fresh and modern, shining with multi-colored paints.
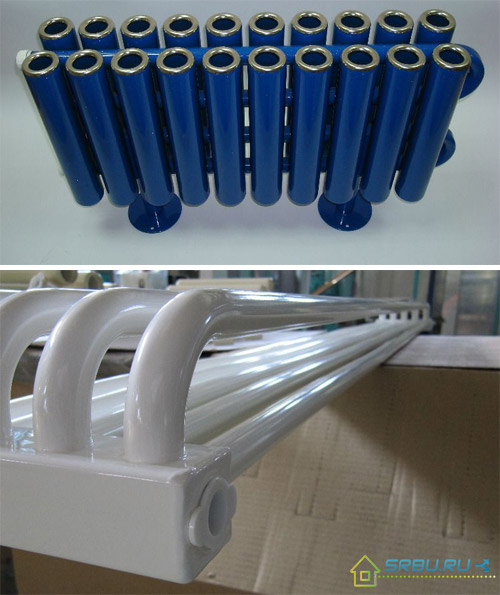

4. Bimetal radiators are very sophisticated in design. There are many models that have not straight, but curved surfaces. This allows them to fit perfectly into rooms with smooth corners. Such products are produced, in particular, by the RIFAR plant. SIRA RS Bimetal radiator also boasts smooth and beautiful bends of lines.
Model of bimetallic radiators RIFAR FLEX having a rounded shape.
5. Floor convectors in terms of appearance differ only in decorative grilles.
Price categories
- Cast-iron radiators (except for retro models) - from 300 rubles per section.
- Cast-iron radiators "retro" - from 2000 rubles per section.
- Aluminum radiators - from 300 rubles per section.
- Steel radiators (price for a whole radiator) - from 1,500 to 10,000 rubles.
- Bimetal radiators - from 500-600 rubles per section.
The cheapest radiators are steel panel and cast iron, especially domestic production. After them aluminum cast radiators will go, extrusion models will be a little cheaper. But the most expensive will be bimetallic radiators, cast-iron radiators in retro style and steel tubular models of radiators.
About the manufacturers - the most famous and reliable brands
Classical cast iron radiators are produced by such companies as the Czech manufacturer VIADRUS, Spanish - ROCA, Italian - FERROLI, Belarusian (MZOO), Turkish (DEMIR DÖKÜM). We make them in Cheboksary (ChAZ plant). Retro models are manufactured by ROCA (Epoca model), DEMIR DÖKÜM (Retro model).
Aluminum radiators are mainly made by Italians. So, these are the companies RAGALL, ROVALL, DECORAL, MECTHERM, FARAL, INDUSTRIE PASOTTI, GLOBAL, FONDITAL, RADIATORI 2000. We have the Stupinsky factory SMK, as well as a company from Mias MMZiK. Each company has its own “chips” for protecting radiators from corrosion. In particular, FARAL produces zirconium processing on its inside. A good anti-corrosion coating is also available on Calidor Super Aleternum radiators manufactured by FONDITAL, also Italian.
Steel tubular radiators are manufactured by German companies ZEHNDER, BEMM, ARBONIA, KERMI. Italian manufacturers are TET-A-TERM, and in Russia - KZTO from the city of Kimry, producing the Zavalinka model, where you can even lie down. However, models of the same plan (benches) are made by both ARBONIA and ZEHNDER. As for panel steel radiators, the following manufacturers produce them: German company KERMI, Czech - KORADO, Belgian - RADSON, Dutch - STELRAD, Turkish - DEMIR DÖKÜM, Polish-Finnish - PURMO), Italian - BIASI. Two enterprises can be named in Russia: MECHANICAL PLANT from St. Petersburg and the SVARTEPLOTECHNIKA plant from Tver.
Bimetal radiators are made by companies from Italy (GLOBAL, SIRA), Czech Republic (ARMATMETAL), Russia (Ryazan plant Tsvetlit-R, Moscow plant SANTEHPROM and an enterprise from the Orenburg region RIFAR). It is the products of the last manufacturer that are very in demand and popular.
Convectors are produced by Russian (KZTO, IZOTERM and SANTEHPROM), American (SLANT / FIN), and European firms. For example, Slovenian VTS CLIMA, Polish CONVECTOR, German KAMPMANNAN, English BISQUE RADIATORS, Belgian JAGA.
Choosing a specific radiator model
After you have decided on the type and type of heating radiators you need, it's time to calculate and select specific models of these radiators that will have the necessary technical parameters.
We calculate the thermal power
And how to choose heating radiators in order to achieve the proper level of heat and comfort? To do this, you need to calculate the thermal power of the radiators planned for purchase. For certain standard conditions, a heat output of 0.09 to 0.125 kilowatts per square meter of space is required. Such power should be enough to create optimal climatic conditions in the room.
Now about what is meant by standard terms. It's simple, this is a room in which there is a window with a wooden frame and three-meter (no higher) ceilings, as well as an entrance door. At the same time, hot water of seventy-degree temperature flows through the heating pipes. If you have the same conditions, multiplying 0.125 by the area of the room you will receive the power of the radiator or radiators (if several are needed) necessary for the room. Then it remains to look into the passport of specific radiators and, having learned there the thermal power of one section or the entire radiator, select the necessary model.
But this is a simple calculation, in fact, it is necessary to take into account some other factors that in this case will have an effect:
- You can reduce the power of radiators by 10 - 20% if you have plastic energy-saving double-glazed windows installed in your room, because they reduce the heat loss of the room by about so much.
- If there are not one, but two windows in the room, then you need to put a radiator under each of them. Their combined capacity should be 70% higher than the normative indicator. We will do the same in the case of a corner room.
- When increasing or decreasing the temperature of hot water for every 10 degrees, the power of the device also increases (or decreases) by 15-18%. The thing is that if the temperature of the coolant decreases, then the power of the heating radiators decreases.
- If the ceilings are higher than three meters, the heat output must again be increased. The increase must be made so many times how many times higher for 3 meters the ceilings in the room. If the ceilings are lower, then a reduction is necessary.
When calculating, we will take into account how our radiators will be connected. Here are some suggestions for this:
- If the coolant enters the radiator from below and exits from above, then the heat will be lost decently - from 7 to 10%.
- Lateral one-sided eyeliner makes it unreasonable to install radiators with a length of more than 10 sections. Otherwise, the last sections from the pipe will remain practically cold.
- Increases heat transfer from 10 to 15 percent gluing on the wall behind the radiator special reflective insulation material. For example, it could be material like Penofol.
Of course, not all indicators are indicated here, for example, you need to consider what material the house is built from, what its structure is, whether there is insulation, but in general they allow you to choose the necessary appliances for heating.
Determine the required dimensions
When buying a radiator, you need to know the following points exactly:
- What type of eyeliner do you have - hidden or open;
- How pipes are brought to the radiator, from the floor, from the wall, from above, from the side, etc.
- Diameter of heating pipes;
- The distance between the pipes (center distance).

We also provide for such a placement of the radiator so that air can flow freely around it - otherwise the room will not get from 10 to 15% of heat. Standards for the placement of radiators are as follows:
- The distance of the radiator from the floor is from 7 to 10 cm;
- distance from the wall - from 3 to 5 cm;
- the distance from the windowsill is from 10 to 15 cm.
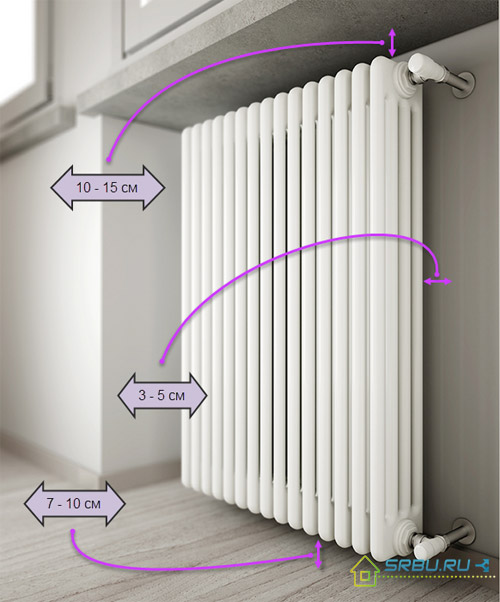

Basic standards for the placement of radiators.
The final stage of the purchase of radiators
Now, if you have autonomous heating, you can, taking these calculations with you, feel free to go to the store for heating appliances.But for residents of a high-rise building with centralized CO, it makes sense to first go to the DEZ, having learned what working pressure is in your heating system. We will build on this parameter, deciding which heating radiator is better to choose. The pressure specified in the instrument passport must be higher than that indicated by the employees of the DEZ, so that a certain reserve is obtained. After all, do not forget that in each new season, heating appliances experience pressure testing, which is 1.5 times more than the working one.









