The principle of operation of vacuum heating radiators and their true advantages
Radiators of a completely new type have now appeared on the market. Manufacturers and sellers claim that they are able to work just miracles. These are vacuum heating radiators, the principle of which we will analyze in detail in this material, and also consider whether they are really as effective as the manufacturers assure.

Content:
Vacuum radiator device
In general, there is nothing complicated in its design. The radiator consists of metal sections. Instead of water in the sections is a lithium bromide solution, boiling already at plus 35 degrees Celsius. The air from the sections is completely evacuated in order to reduce internal pressure. Hot water flowing from the heating system flows through the lower radiator header. It should not come into contact with the coolant, and contact occurs only through the metal surface of the pipe. This pipe (like the entire radiator) is made of one and a half millimeter carbon steel.
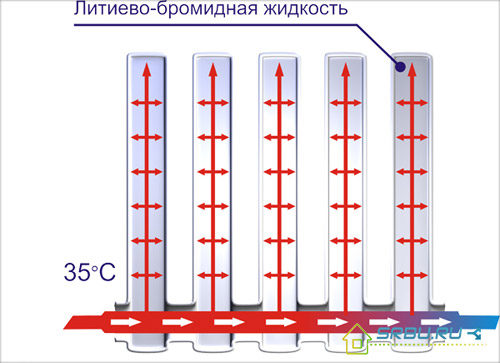
The device of a vacuum radiator.
Principle of operation of a vacuum heating device
Hot water coming from the heating system to the bottom of the radiator (connected to the heating system using standard couplings) transfers heat to the lithium bromide liquid. She quickly begins to evaporate, heating all sections of the radiator. The condensate flows down, then again turning into steam rises up. Thus, the outer wall of the pipe, bordering the coolant, is constantly cooled. And the temperature difference between its inner and outer surfaces contributes to an increase in heat flow.
Radiator sections heated in a couple of minutes with hot steam give off heat to the surrounding air. Moreover, according to manufacturers, this happens instantly. The heat transfer rate declared by them for one section of this device is 300 watts and a very small amount of water is used. These are serious numbers - then we’ll try to find out if this is so. And at the same time we’ll check how wonderful new heaters are.
Video: The principle of operation of vacuum radiators
Whether to advertise praising vacuum heating appliances
We will try to approach this issue as scrupulously and objectively as possible, taking as a basis only proven facts. In this case, we consider each of the advantages indicated by the manufacturer of these radiators. So, we started.
1. The lightning-fast warm-up time characteristic of vacuum radiators is constantly being advertised. Well, let's say. However, the whole house will not warm up so quickly. After all, it contains not only air, but also walls, internal partitions with furniture, a ceiling with a floor. To heat them, you need a certain time. And therefore it is not so important, the radiator itself will be heated for a minute or five.
2. Now about a small amount of coolant, which is supposedly very economical. The only question is where exactly is this savings. If the central heating system, then this is a real bluff - it is not so important here, more hot water will flow through the pipes or less. If you take a suburban country house, then the savings in it are in question, given the fact that the same modern panel radiators also do not require so much coolant
3. In vacuum-type radiators, air jams cannot occur. About this with enthusiasm broadcasts advertising. But radiators are not the whole heating system, but only a part of it. By the way, traffic jams appear only when this system is assembled illiterate. Otherwise, they will not be with any radiators.
4. Two more fat pluses that manufacturers trump. This is the impossibility of clogging radiators and the absence of corrosion.Perhaps, for autonomous heating systems, these advantages are unlikely to be so fat. If the hot water in the heating system is clean, its acidity level complies with the standards, and it does not drain from the system, then there will be no corrosion. And blockages come from nowhere.
5. As for the low hydraulic resistance, supposedly sharply reducing the item of heating costs, let's say. For central heating, it is not clear at all whose costs are in mind. Unless the owners of boiler houses distilling tons of hot water by hundreds of kilometers. It turns out that the benefit can only be when used in an autonomous heating system and this is still a question of whether it can be. And for an autonomous system in their home, many use the natural circulation of the coolant, so this issue is irrelevant.
6. The next point will be saving energy by half, or even four. There was a mistake with this, since the law of conservation of energy still applies. Radiators, even the most innovative ones, cannot generate energy. They only transmit it, and there is no need to talk about savings. How much heat is expended, so much must be replenished - that is the only way.
7. Now let's touch on the heat transfer of vacuum tubes, which, according to manufacturers' certificates, is not stable. This indicator may have deviations of up to 5 percent up and down. It turns out that this depends on the speed of water in the heating system, and on its temperature. So it’s hardly possible to adapt automation to such a radiator. And two radiators with an equal number of sections can have different parameters.
8. Separately, we will say about heating systems in private homes, where water circulates naturally. Here the hydraulic pressure is important, which is created due to the difference in the height of the hot water in the boiler and the radiator. So, for vacuum-type devices, this height is much less, therefore, in such a system they work with problems.
9. Now imagine that a crack appeared in the radiator case. Even if it is tiny, you can forget about the vacuum. He will leave irrevocably, and normal atmospheric pressure will be restored. And it, in turn, will lead to an increase in the boiling point of the coolant. The result will be disastrous - either the liquid will almost not evaporate, or steam will not appear at all. In short, the radiator will stop heating.
10. By the way, this wonderful (according to sellers and advertisers) lithium bromide liquid is also poisonous, it turns out. Therefore, the fact that radiators with a coolant leak will become cold is only half the trouble. Worse if the battery is worn out, for example, at night, poisoning the sleeping inhabitants of the apartment.
So, perhaps, it’s not always worth believing the advertising, so convincing at first glance.









