What is better bimetallic radiators or cast iron - a comparison of technical specifications
To withstand the harsh everyday life of central heating, not every type of radiator is capable of. As it turned out, only bimetal and cast iron do not burst from high blood pressure and are not eaten by corrosion in a couple of seasons. But still, which radiators are better - bimetallic or cast iron - we will consider and compare their technical characteristics.

Content:
- Design differences and appearance
- Compare the heat dissipation of radiators
- Ability to hold pressure
- Resistance to poor coolant quality
- Maximum heat carrier temperature and its fluctuations
- Durability and Life
- Which radiators are easier to install
- Let's talk about the difference in the price of radiators
- We draw conclusions and determine the type of radiator
- Video: Replacing heating radiators in an apartment
Design differences and appearance
Cast iron
Let's start with cast iron radiators, which today have changed their design, but, as before, have wide water channels and are composed of several cast sections. Heat-resistant gaskets made of rubber or paronite, which are placed between sections, provide the necessary tightness. The length of the finished radiator is determined by the number of sections, the height varies from 0.35 to 1.5 meters, and the depth can be both 0.5 meters and several centimeters. In accordance with the volume of the room, you can select the desired size of the radiator, while it is possible to modify it (for example, remove the extra section or add a few new ones).
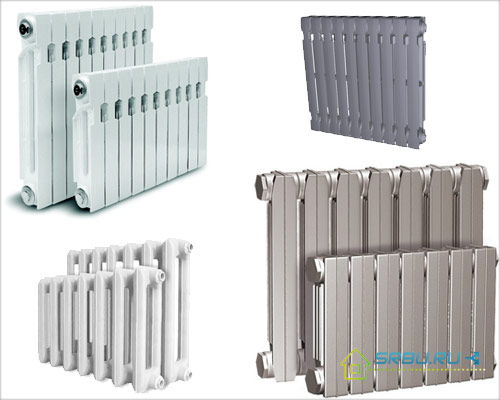

Varieties of cast-iron radiators.
It is worth mentioning the models of radiators, artistically cast from cast iron. They not only perfectly heat the room, but also are able to give it charm and charm. Such radiators with skillfully made molding patterns on their surface are produced mainly by foreign manufacturers. Like any piece of art, such devices are worth a lot of money.
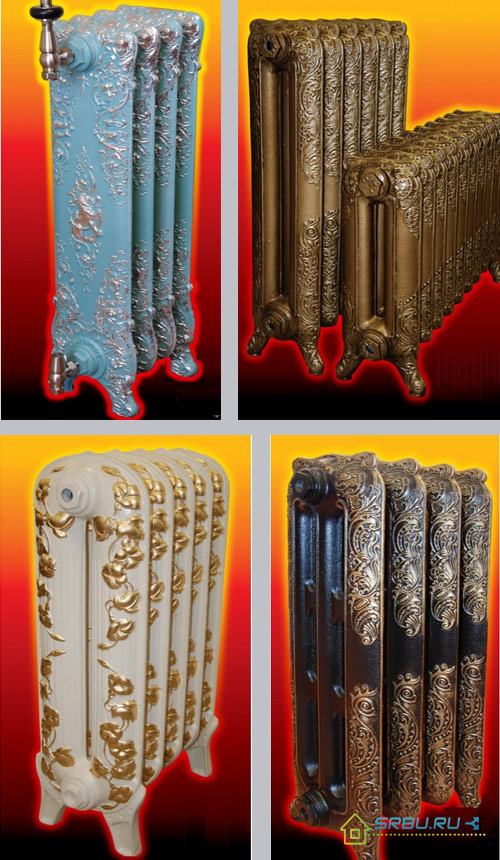

Several types of art cast-iron heating radiators.
Bimetal
The case of bimetallic radiators is aluminum, its shape is ribbed-shaped. So it is designed for better heat transfer. A solid steel core is hidden under the body - this refers to the “real” bimetal radiators. However, there are also semi-bimetallic (or pseudo-bimetallic) radiators - their difference is that only the vertical channels of the radiator are reinforced with steel. The rest of it is made of aluminum. Such a device costs about 20 percent cheaper than a completely bimetallic one, and gives more heat. But it is less reliable and durable, and it is extremely undesirable to use it in a centralized network.
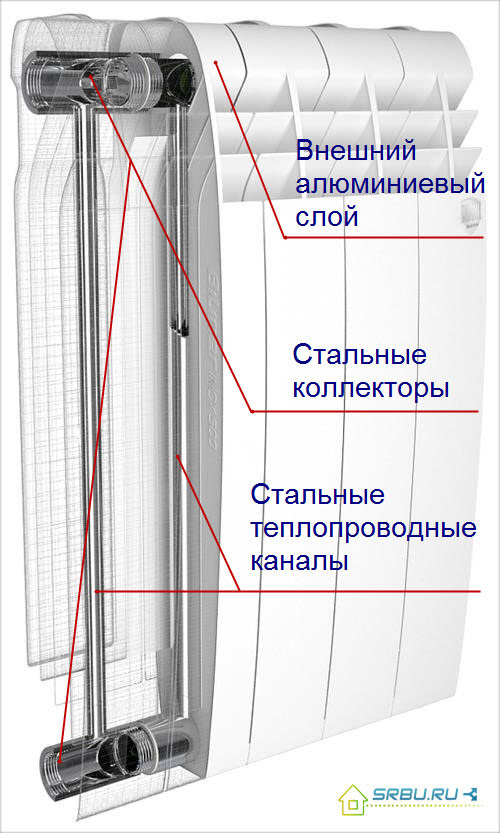
The device of a bimetal heating radiator.
Like cast iron radiators, their bimetallic colleagues are usually sectional, which allows them to be modified. Usually sold models with an even number of sections. A small segment of the market is occupied by monolithic models, which are not subject to disassembly, assembly and improvement. The design of all bimetal radiators is very attractive.
Appearance: Cast Iron + - | Bimetallic +
Compare the heat dissipation of radiators
Cast iron. And again, let's start with traditional cast-iron radiators. They are so slow that sometimes you can freeze, waiting for the cold room to warm up. But after all, such radiators cool down for a long time - and this is a completely different matter. After all, there are cases when the heating is turned on and off. Due to an accident or repair, for example. And next to the cast-iron battery, you can warm up for a long enough time.
A great advantage of cast iron products is that they heat the room not only by convection, but also by the radiation method. That is, when they are turned on, in addition to air, objects that are close to the batteries become warm.As for thermal power, it is usually given for one section and ranges from 100 to 160 watts. These are average values that may vary between models.
Bimetal. The good thing about these radiators is that they heat up just instantly. However, they cool just as quickly, alas. Heating in them is carried out mainly by the principle of convection - the radiation component is much less. This is some minus. The thermal power of sectional models is comparable to cast iron products. This figure is from 150 to 180 watts (on average). If we compare the rate of heating the room, then they certainly beat the cast-iron.
Heat dissipation: Cast iron + - | Bimetallic +
Ability to hold pressure
In a traditional central heating system, typical of multi-storey buildings, the pressure is by no means stable. Sometimes even water hammering occurs. After all, the cranes of circulation pumps according to the rules should turn on smoothly, but often the workers do not follow these rules. And with a sharp overlap of hot water, its pressure in the entire system jumps so that many batteries burst. Therefore, residents of apartments must definitely choose radiators with a good margin of pressure.
Cast iron radiators can withstand 9-12 atmospheres of pressure. This may be enough until a strong water hammer occurs. If it does happen, then brittle cast iron, unfortunately, can burst. Therefore, if you look from this point of view that cast-iron radiators or bimetallic radiators are better, then it is better to secure yourself and take bimetal.
After all, a bimetallic radiator is not afraid of any pressure surges - in the passport he has indicators for this parameter up to 20-50 atmospheres (depending on the model). So even powerful hydroblows are not capable of breaking a high-quality product from bimetal. And we also mention models with a monolithic steel core - they can easily withstand up to 100 atmospheres. An example of such radiators can be Russian-made radiators Rifar Monolit, its technical features you can see in the photo below.

Ability to hold pressure: Cast iron - | Bimetallic +
Resistance to poor coolant quality
Another disadvantage of central heating is the dubious quality of the coolant. Hot water coming from pipes to radiators is neither different in purity nor in chemical neutrality. And it also contains a considerable fraction of the smallest grains of sand and pebbles that can act on the internal walls of the battery, like an abrasive.
Cast iron is chemically absolutely "calm", so a high level of alkalis or acids in hot water will not harm it. And in the summer, when there is a general discharge of water from the system, it does not rust. But she doesn’t like small pebbles-abrasives - they gradually wear out. However, if the walls of the radiator are quite thick, this is not so critical.
Bimetal is also resistant to reactive water during the heating season. However, in the summer, when water is drained from the system for repair and maintenance work, air appears in the radiators, the steel core may be attacked by corrosion. So the bimetal does not reach a little cast iron for endurance.
Not a good heat carrier: Cast iron + | Bimetallic + -
Maximum heat carrier temperature and its fluctuations
And the temperature of the coolant in our heating systems does not shine with stability. Sometimes the pipes are barely warm, then hot, like fire. It is important for us how the radiators behave in the latter case, whether they will withstand too hot water. The indicators for this parameter are as follows. For a cast-iron radiator - the coolant can heat up to 110 degrees. Hot water flowing through the pipes of the core of a bimetallic radiator can have a temperature of up to 130 degrees. But in general, both types of radiator tolerate temperature extremes. The only thing is that due to the difference in the extensions of steel and aluminum, with a sharp change in temperature, you can hear small crackles on the bimetal radiator.
Maximum heat carrier temperature: Cast iron + | Bimetallic +
Durability and Life
Cast iron products with proper care and periodic washing live very, very long - half a century or more. In some old houses there are even specimens whose age has exceeded one hundred years. Manufacturers release bimetallic radiators for years 15-20 (sectional) and years 25 (monolithic). Cast iron in this regard "steers", as you see.
Durability and Life: Cast Iron + | Bimetallic -
Which radiators are easier to install
There is nothing to argue about - naturally, there will be more problems with cast iron when installing and carrying. And one cannot afford to lift such a battery, and the brackets for it need special ones - especially durable, and the wall made of drywall will not stand it.
And one more thing: when buying cheap domestic radiators, you need to be prepared for the fact that they will additionally need their painting and broaching.
But it’s a pleasure to work with bimetallic radiators. They are so light and neat that hanging them (and on any surface) is not difficult. And if in the first place you have ease of installation, the answer to the question of which is better - bimetallic radiators or cast-iron radiators is unequivocal. Of course, bimetal.
Ease of installation: Cast Iron - | Bimetallic +
Let's talk about the difference in the price of radiators
Cast iron is undoubtedly cheaper, especially domestic production. So, the cheapest section of the MS model, for example, costs only about 300 rubles. However, such a "tasty" price will be only for classic models. But radiators in the "retro" style, made by the method of artistic casting, are several times more expensive. Similar models of the Konner brand cost from 2000 rubles (for one section).
Sectional models of bimetallic radiators will be somewhat more expensive than similar cast-iron radiators. For example, one section of a radiator from the company Rifar (Russia) will cost at least 500 rubles. The price of a section of the same Italian radiator starts from 600-700 rubles.
Price: Cast Iron + | Bimetallic -
We draw conclusions and determine the type of radiator
Now, after comparing cast-iron and bimetallic radiators, we can confidently say that cast iron radiators are a good option in old apartment buildings up to five floors high. The pressure supplied to the system, they can withstand. Naturally, if there are no powerful hydroblows. But here you have a choice, and if finances allow, then of course you can put a more stylish bimetal.
If the apartment is located in a high-rise building, then the working pressure of the coolant will be significantly higher. Therefore, in this case, it is more reasonable to supply bimetal heating devices, which have a greater pressure resource.
Well, and one more nuance. If earlier in your apartment there were cast-iron radiators, you can exchange them for more modern cast-iron radiators and for bimetallic products. But after steel or aluminum, it is definitely better to put bimetal.
Having an autonomous heating system, you can install any of the radiators, but as a rule in such systems it is most advisable to use steel or aluminum radiators.
Video: Replacing heating radiators in an apartment







