Technical characteristics of ceramic bricks
Burnt clay bricks have been used in construction since ancient times, and buildings made of this material are distinguished by enviable strength and durability. Ceramic brick, whose technical characteristics are at a high level, is made from some types of clay. Its operational properties are determined by the quality of the raw materials and the exact observance of production technology.

Content:
- Composition, production and types of ceramic bricks
- Ceramic Brick Density
- Hollowness
- Thermal conductivity of ceramic bricks
- Moisture absorption
- Vapor permeability
- Frost resistance
- Fire resistance
- Soundproofing
- Green Ceramics
- Dimensions and geometry accuracy
- Special types of ceramic bricks
- Transportation and storage of ceramic bricks
- Video: Advantages and disadvantages of ceramic bricks
Composition, production and types of ceramic bricks
The manufacture of this type of building material is a complex process consisting of several stages. Currently, two ceramic brick production technologies are applied.
1. The plastic method involves molding a block of clay mass with a water content of about 17-30%. To implement this process, a belt press is used, then the brick is dried in a specially equipped chamber or under a canopy. At the last stage, it is fired in an oven or in tunnels, the cooled products are placed in a warehouse.
2. Semi-dry pressing technology. The initial mass in this case has a moisture content in the range of 8 -10%. The process of forming the block is carried out by pressing under high pressure up to 15 MPa.
Brick production is carried out in strict accordance with national standards GOST 7484-78 and GOST 530-95. In the process of preparing the mass, clay processing machines, rollers, runners, and clay mills are used. Brick molding in modern enterprises takes place on high-performance belt presses. The homogeneous structure of the blocks and the absence of voids is achieved through the use of vibration stands.
Dry brick is dried by chamber or tunnel method. In the first case, a batch of products is loaded into a specially equipped room, where the temperature and humidity are changed according to a given algorithm. In the second version, raw trolleys are sequentially conducted through zones with different microclimate parameters.
Brick firing occurs in special furnaces under certain conditions. The temperature regime is selected depending on the composition of the raw materials and its maximum values vary from 950 to 1050 ° C. The firing time is selected so that at the end of the process the mass part of the vitreous phase in the brick structure reaches 8 - 10%. This indicator provides maximum mechanical strength to the product.
The raw materials for the production of bricks are clay of a small fraction, which is mined in open pits using the single bucket or bucket wheel excavators. Ensuring proper product quality is possible only when using materials with a uniform composition of minerals. Factories for the manufacture of bricks are being built near deposits to reduce transportation costs and reliably supply the enterprise with mineral raw materials.
The main types of ceramic bricks differ in purpose and are divided into ordinary (other names: building or ordinary) and front.
Facial, depending on the technological design, can be of several types:
- front;
- glazed;
- shaped;
- figured;
- engobed.
Ceramic brick, in addition, can be monolithic or hollow, and its surfaces spoon and bonded are made smooth or corrugated. In this case, products of the same type often combine several features, so the ordinary block is made full-bodied or with cavities. The laying of stoves or fireplaces is carried out from a special fire-resistant (fireclay) brick, and for paving the tracks its special type is used - clinker.
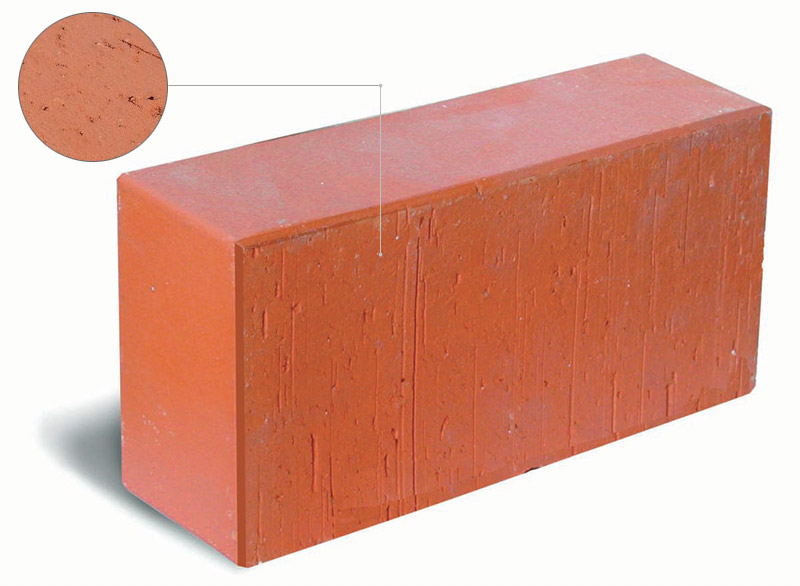
Ceramic brick and its structure.
Ceramic Brick Density
Physico-chemical properties and technical parameters of the product largely depend on the internal structure. One of the indicators that clearly characterize these qualities of ceramic bricks is density. It directly depends on the fractional composition of raw materials, the variety and porosity of building bricks.
Data on the density and some other indicators of ceramic bricks are given in the table:
| Kind of brick | Average density | Porosity | Strength grade | Frost durability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| kg / m3 | % | |||
| Private corpulent | 1600 - 1900 | 8 | 75 -300 | 15 - 50 |
| Private Hollow | 1000 - 1450 | 6 - 8 | 75 - 300 | 15 - 50 |
| Facial | 1300 - 1450 | 6 - 14 | 75 - 250 | 25 - 75 |
| Facial engobed | 1300 - 1450 | 6 - 14 | 75 - 250 | 25 - 75 |
| Clinker | 1900 - 2100 | 5 | 400 - 1000 | 50 -100 |
| Fireclay | 1700 - 1900 | 8 | 75 - 250 | 15 - 50 |
The density of a ceramic brick is determined by its class, which is indicated by a numerical code in the range from 0.8 to 2.4. The given indicator indicates the weight of one cubic meter of building material, expressed in tons. There are six classes of products, the introduction of this indicator greatly simplifies accounting and paperwork in the construction industry.
Knowledge of such an indicator as density is necessary for carrying out settlement and design work and determining the ultimate loads on the foundations and load-bearing elements of the building. The homogeneous structure of the brick provides it, on the one hand, with high mechanical strength, and on the other with low thermal insulation properties. If monolithic brick is used for the construction of a building, additional measures should be taken to warm the walls.
Hollowness
In order to reduce the mass of the product and its thermal conductivity, cavities of various shapes are left in it. Both ordinary and facing ceramic bricks can be hollow. The shape and depth of the holes is determined by the technology and can be very different: round, slit-like or rectangular. Voids in the body of the product are arranged vertically or horizontally, in some varieties they are made through in others, closed on one side.
The direction of the holes with respect to the load plane has a noticeable effect on the mechanical strength index. So, a brick with horizontal voids cannot be used when laying bearing walls; its destruction is possible under the influence of the mass of the building structure. In the manufacture of hollow blocks, up to 13% of raw materials are saved, which reduces their cost and makes them more affordable.
Improving the thermotechnical characteristics of bricks is possible by increasing its porosity. To do this, add a certain amount of the mixture to the raw mixture: finely chopped straw, peat or sawdust. Inclusions burn out during the firing process and pores filled with dry air form in the body. This fact has a significant effect on the thermal conductivity of the building material.
Thermal conductivity of ceramic bricks
The physical properties of ceramic bricks are largely dependent on its internal structure. The thermal insulation capabilities of the product are characterized by a coefficient of thermal conductivity. Its value shows how much heat is needed to change the air temperature by 1 ° C with a wall thickness of 1 m. The thermal conductivity coefficient is used in the design process of the building when calculating the thickness of the external walls.
There is a direct relationship between the density of ceramic bricks and its heat-insulating properties.
In accordance with this indicator, products can be assigned to one of five groups of thermal conductivity:
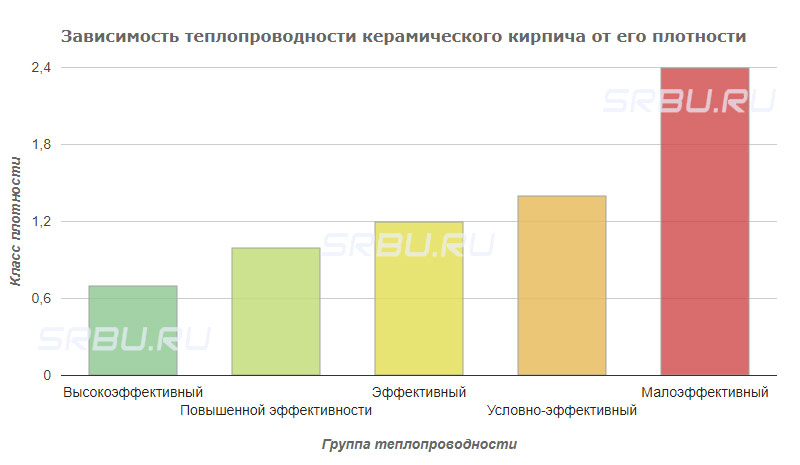
Full-bodied ceramic brick thermal insulation characteristics, which are relatively low is usually used for the construction of load-bearing structures. For walls made of such material, additional insulation is required. The use of hollow or slotted products can significantly reduce the thickness of the enclosing structures in low-rise buildings. The presence of dry air in the voids significantly reduces the loss of thermal energy through the walls.
Moisture absorption
The presence of pores in a ceramic brick can facilitate the penetration of water and vapors into its structure. The moisture absorption coefficient depends on many factors, and first of all on the density and some other characteristics of the material. For corpulent products, its value ranges from 6 to 14%, which is a rather low indicator. This has a positive effect on the strength and heat-insulating characteristics of the brick.
The safety of brick buildings and structures directly depends on the stability of heating. Lowering the temperature inside the room to the street level promotes the penetration of moisture into the pores and accumulation of water in them. Its crystallization during freezing causes the formation of stresses and microcracks, which gradually destroy the material of building structures. Directly with the ability to absorb moisture is associated with such an indicator as vapor permeability.
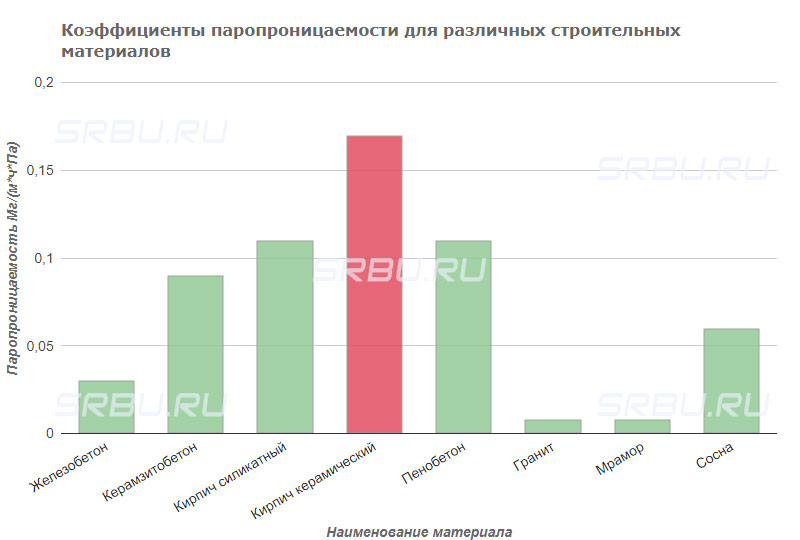
Vapor permeability
In any inhabited room, air humidity rises due to human activity. Brick walls are involved in the regulation of this parameter, which are able to actively absorb and give off vapors to the environment. This indicator for ceramic bricks is at the level of 0.14 - 0.17 Mg / (m * h * Pa) and this is enough to create a comfortable microclimate in an apartment, house or office.
The vapor permeability of the material is determined by a special coefficient. This indicator characterizes the density of the penetrating stream through the surface with an area of 1 square. m in one hour.
For comparison, the table shows the vapor permeability coefficients for different materials:
Frost resistance
Ceramic brick is widely used in the construction of buildings in various climatic zones of our country. The ability of a material to withstand low temperatures is called frost resistance. In accordance with the national standard, the quantitative expression of this indicator is determined by cycles. In fact, this is the number of years that a properly constructed wall can withstand.
The frost resistance of ceramic bricks is indicated in the form of an alphanumeric code from 50 F to 100 F. This means that with proper masonry and constant heating in the winter, the building will last from 50 to 100 years. Ceramic brick is highly resistant to external influences and extreme temperature fluctuations.
Fire resistance
Fire safety of buildings is determined by the ability of building materials to withstand the effects of high temperatures and open flame. Ceramic brick refers to non-combustible building materials, and its fire resistance depends on the type. This indicator is determined by the time that the wall of minimum thickness is able to withstand before its destruction.
Ceramic brick has a maximum fire resistance among other building materials over 5 hours. For comparison, reinforced concrete is able to withstand fire for no more than 2 hours, and metal structures for less than 30 minutes. An important parameter of the resistance of the material to fire is the maximum temperature that it can withstand. For ordinary brick, it is 1400 ° C, and for chamotte or clinker, it exceeds 1600 ° C.
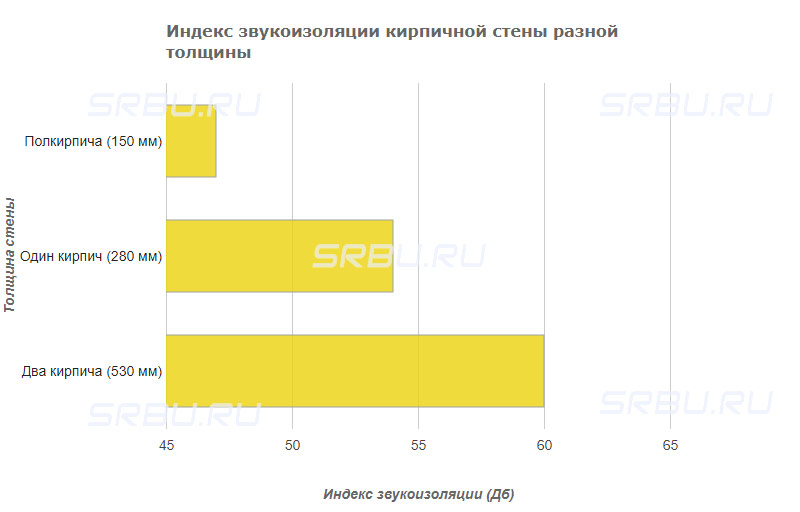
Soundproofing
This building material is characterized by the ability to damp acoustic vibrations in a wide frequency range. Soundproofing properties of ceramic bricks meet the requirements of SNiP 23-03-2003, as well as GOST 12.1.023-80, GOST 27296-87, GOST 30691-2001, GOST 31295.2-2005 and GOST R 53187-2008. Ceramic bricks perfectly damp out acoustic vibrations.
Ceramic brick is recommended by specialists for the construction of residential, public and industrial buildings. Products can be used for the construction of the following premises:
- soundproof partitions;
- special booths for monitoring and remote control of technological processes;
- acoustic screens (screens).
The sound insulation index of ceramic bricks is taken into account when conducting acoustic calculations of buildings and individual rooms. In this case, the level of sound power and the location of the radiation sources are taken into account. A wall made of hollow ceramic bricks has better characteristics in this parameter than a similar structure of blocks with a monolithic structure.
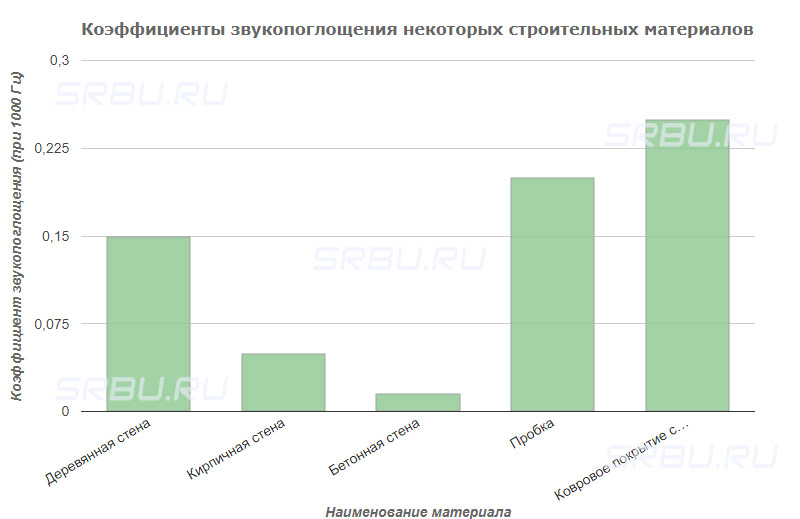
However, the construction of thick brick walls in order to increase sound insulation is not very effective. This is because when the wall thickness is doubled, the sound insulation level increases by only a few decibels.
Green Ceramics
Currently, much attention is paid to the impact of materials on human health and the environment. Ceramic brick is a product that is made from natural raw materials: clay by high-temperature firing. This material does not emit harmful and toxic substances during the operation of residential and industrial buildings and structures.
Ceramic brick is recommended for the construction of almost all types of structures:
- preschool, educational and medical institutions;
- low-rise and apartment buildings for year-round use;
- catering facilities;
- production facilities and much more.
In terms of environmental friendliness, this material is able to compete with natural wood and natural stone. In rooms built of ceramic bricks, a healthy environment is formed, safe for living, health of both children and adults.
Dimensions and geometry accuracy
Manufacturers of building materials offer an extensive range of blocks of various types. In total, the industry produces almost five sizes of ceramic bricks in the following formats:
- normal or single;
- "Euro";
- thickened;
- single modular;
- thickened with horizontal holes.
The dimensions of ceramic bricks are determined by the requirements of national GOST 530-2007, which corresponds to the European standard EN 771-1: 2003. Data for ease of use are summarized in the table:
| Product Names | Designation | Length mm | Width mm | Thickness mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Private or single | KO | 250 | 120 | 65 |
| Euro | KE | 250 | 85 | 65 |
| Thickened | KU | 250 | 120 | 88 |
| Single modular | KM | 288 | 138 | 65 |
| Thickened with horizontal voids | KUG | 250 | 120 | 88 |
The standard rigidly sets the maximum deviations from the nominal dimensions of the product. In length, the ceramic brick should not differ from the reference value by more than 4 mm, in width - 3 mm and in thickness - 2 mm. The permissible manufacturing error in the angle between perpendicular faces is not more than 3 mm. Such requirements for the accuracy of products make it possible to lay large building structures with minor deviations.
The standard allows the manufacture of ceramic bricks with other nominal sizes, which are not indicated in the table. Such products are available on special order and upon agreement between the client and the manufacturer. At the same time, the requirements for the accuracy of linear dimensions and block geometry are preserved in full.
Special types of ceramic bricks
The described building material is widely used for the construction of structures for a wide variety of purposes. Special types of ceramic bricks are used for laying combustion chambers and furnaces of stoves and fireplaces.Another type of product is indispensable in paving footpaths in the yards of individual houses and landscape gardens. These products meet certain requirements.
Refractory brick
Refractory or fireclay bricks are highly resistant to high temperature influences ranging from 1400 to 1800 ° C and open fire. Up to 70% of refractory clay, which prevents the destruction of the product during cooling, is introduced into the composition of the molding material.
There are different types of refractory ceramic bricks, which are determined by the operating temperature and resistance to various environmental factors:
- Quartz. Designed for laying arches of furnaces that perform the functions of a reflector.
- Fireclay. Used for laying household stoves and fireplaces, the most common type of refractory brick.
- Main. It is made from magnesia-lime masses and is used in metallurgy for the construction of smelting furnaces.
- Carbonaceous. It is used in some industries for the construction of a domain; it includes pressed graphite.
Brick brick
Clinker brick is intended for facing facades and basement parts of buildings, paving floors in industrial premises and walkways on the street. The product is characterized by high mechanical strength, wear and frost resistance, is able to withstand up to 50 cooling cycles to extreme temperatures with subsequent heating. The strength grade of a product of at least M400 is ensured by high density and special requirements for the composition of raw materials.
Transportation and storage of ceramic bricks
Ceramic bricks can be transported by all types of land, water and air transport in compliance with the relevant rules. For convenience of transportation and ensuring safety, the product is packaged on standard pallets of a fixed size. Transportation of this building material in bulk with subsequent discharge to the ground is not allowed, such actions lead to damage up to 20% of products.
Long-term storage of ceramic bricks is carried out under a canopy in paved areas. Products can be placed on pallets in one or more tiers or in stacks directly on the surface. Loading and unloading operations are carried out mechanically or manually in compliance with safety rules and measures.















