How to choose polycarbonate for a greenhouse, with maximum efficiency
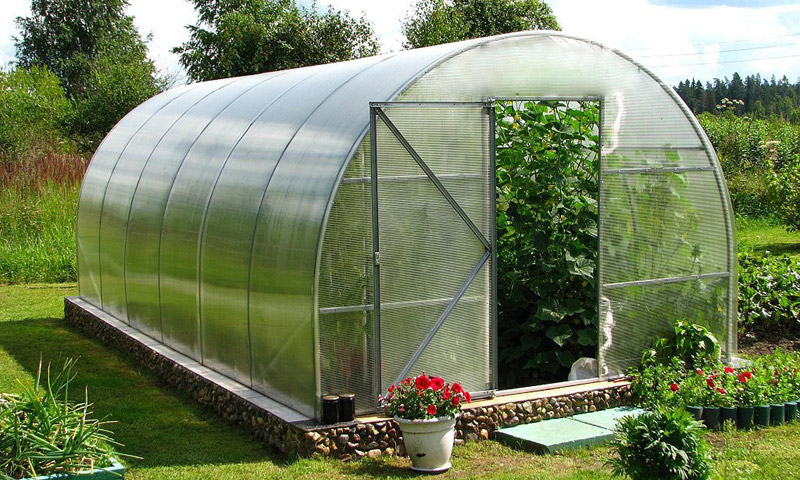
Sustainable crops in many regions of our country can only be obtained using protected farming technologies. Polycarbonate is the best material for greenhouses and greenhouses. Such constructions are often erected by the owners of personal plots and agricultural enterprises independently without the involvement of specialists. Under such conditions, a logical question arises, how to choose the best polycarbonate for the greenhouse in terms of price and quality. The assortment of panels on the market is large and not every one of them is suitable for the construction of such structures.

Content:
- What type of polycarbonate is best for greenhouses?
- The device and the main characteristics of cellular polycarbonate
- Optimal polycarbonate thickness for different types of greenhouses
- UV protective properties of polycarbonate
- The sheet size most suitable for the greenhouse
- Polycarbonate sheet color for greenhouses
- The procedure for choosing polycarbonate in the store
- Video: How to choose high-quality polycarbonate
What type of polycarbonate is best for greenhouses?
To make an informed decision on this issue, you need to understand the properties and technical characteristics of this material. The industry produces two varieties of polycarbonate: monolithic and cellular, the latter is just used for the construction of greenhouses. Such panels in their parameters best meet all the requirements that apply to roofing materials for such structures.
Before cellular polycarbonate appeared on the market, silicate glass and a plastic film were used for these purposes.
The use of cellular polycarbonate has several advantages over the above materials:

Depending on the type of panel, its mass is at least an order of magnitude lower than that of a glass sheet of the same size.

Cellular polycarbonate does not crumble into separate fragments like glass upon impact and is not prone to tearing like a plastic film.

High resistance to climatic influences: significant temperature fluctuations, rain and snow.
4. Low thermal conductivity.

Low thermal conductivity and, as a result, excellent insulating properties, which significantly reduces the cost of heating the greenhouse.
5. Light transmission and UV protection.

Excellent light transmission of panels in some species over 86% and reliable protection against hard ultraviolet radiation.
6. High ductility of the material.

Plasticity of the material: during installation, it can bend to a certain diameter and is in this position for a long time.
Cellular polycarbonate is durable, provided that the panels are selected and installed correctly, the service life is 10 years or more without a significant change in properties.
An important factor in favor of choosing cellular polycarbonate as a material for greenhouses is the financial side of the matter. It is much cheaper than glass, and given its high durability, its use is more advantageous than using a plastic film. In addition to the direct effect of choosing cellular polycarbonate as a material for greenhouses, there are side effects.
The use of these panels allows the use of supporting frames with a lower margin of safety, which will save considerable money in the construction of such structures. Cellular polycarbonate due to its unique technical characteristics is becoming increasingly widespread in the construction of greenhouses.
The device and the main characteristics of cellular polycarbonate
The uniqueness of the properties of cellular polycarbonate is determined by two main factors: the honeycomb structure and the chemical composition of the material. This type of polycarbonate is a multilayer panel with transverse partitions, providing it with sufficient strength and rigidity. Honeycombs in the cross section of the sheet can have a rectangular and triangular shape in different combinations.
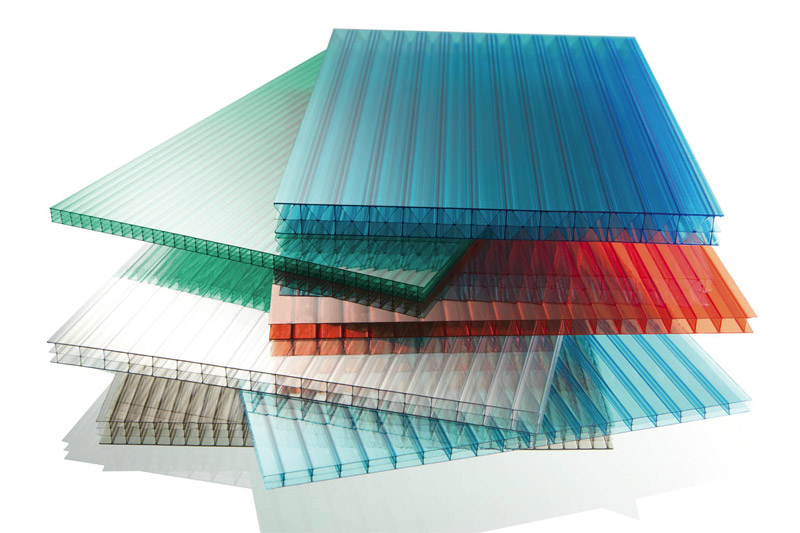
The total number of layers in a material can be from two to four, depending on its thickness and type.
The main technical characteristics of the most common varieties of cellular polycarbonate are presented in the table:
| Sheet thickness mm | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 16 | 20 | 25 |
| Panel length and width, mm | 6000 (12000)×2100 | ||||||
| The specific weight of the material, kg / m2 | 0,8 | 1,3 | 1,5 | 1,7 | 2,7 | 3,0 | 3,5 |
| Thermal conductivity of the sheet, m2× ° C / W | 0,24 | 0,27 | 0,28 | 0,29 | 0,42 | 0,56 | 0,68 |
| Light transmission,% | 83 | 82 | 82 | 80 | 76 | 51 | 58 |
| Minimum bending radius of the sheet, m | 0,7 | 1,05 | 1,5 | 1,75 | 2,8 | 3,5 | 4,4 |
| Change in properties during artificial aging of the material, conv. years | 10 | 20 | 30 | ||||
Analysis of the data given in the table allows us to draw some conclusions that facilitate the process of selecting material for greenhouses.
The most significant characteristics for cellular polycarbonates used in the construction of greenhouses are the following:
- light transmission;
- thermal resistance to heat transfer;
- specific gravity;
- mechanical strength;
- life time.
A simple comparison of parameters for different types of panels allows you to uniquely determine the direct dependence of the listed characteristics on the sheet thickness. Based on the results of this study, we can conclude that the operational characteristics of this material will directly depend on this parameter.
Optimal polycarbonate thickness for different types of greenhouses
The determining factor in which polycarbonate to choose for a greenhouse is the thickness of the panel, on which its technical characteristics directly depend. One of the most important indicators for the roofing material of a greenhouse is light transmission. Panels with a thickness of more than 10 mm absorb and scatter from a quarter to half of the light flux. This circumstance will adversely affect the illumination of greenhouses and will become a reason for reducing yields.
The second most important factor for greenhouses is the thermal resistance of the material to heat transfer, which increases with increasing thickness of the polycarbonate. This allows you to reduce the cost of heating the greenhouse and, accordingly, the cost of production. But, as was said above, an increase in thickness will negatively affect light transmission. The next characteristic of the panel taken into account when determining its optimal thickness is mechanical strength.
Often, in order to save money in the manufacture of greenhouses, 4 mm cellular polycarbonate is used. This is quite acceptable if the panels are really high-quality and their thickness corresponds to the nominal value. Some manufacturers, in order to reduce costs, allow this parameter to be reduced to 3.5 - 3.8 mm. This is invisible to the eye, but during operation, premature destruction of the material under wind load or due to the accumulation of snow mass is possible. It is better to refuse to use such cellular polycarbonate.
When determining the optimal thickness of cellular polycarbonate, the following factors are taken into account:
- Features of the frame structure (radius of curvature of the arcs and the distance between them, as well as between transverse profiles).
- The climatic zone of the region where the greenhouse is being built.
- The presence of a heating system and the period of use of the structure for its intended purpose.
As practice shows, for greenhouses cellular polycarbonate with a thickness of 4, 6 and 8 mm is used. In some cases, 10 mm panels are used for large enough permanent agricultural facilities. Thicker sheets reduce light transmission and greatly increase the load on the frame, which makes their use impractical.
UV protective properties of polycarbonate
Polycarbonate itself is susceptible to the destructive effects of ultraviolet rays, which under prolonged exposure destroy the polymer. To protect against such photochemical processes, a layer of a light-stabilizing substance is applied by coextrusion on one or both surfaces of the polycarbonate.
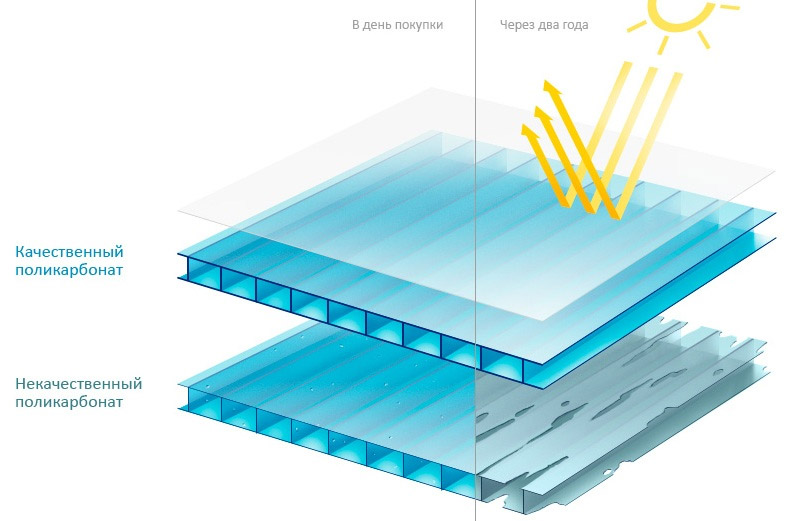
The thickness of this coating is from 0.0035 to 0.006 mm and this is quite enough to protect the sheet from destruction. The protective layer is applied during the production of the material and as a result, it partially diffuses into the substrate. The interpenetration of the light stabilizer and polycarbonate eliminates their delamination, which helps to increase the service life of the material.
1. Cellular polycarbonate provides reliable protection of plants from the effects of the most dangerous hard ultraviolet radiation. The radiation of this part of the spectrum is absorbed and scattered by the panels.
Ultraviolet rays are delayed by a layer of a photo of a stabilizing substance and this is quite enough for reliable protection of plants from harmful radiation.
2. Information on the presence of a light stabilizing layer is reflected in the documentation and on the packaging film. It is impossible to determine the presence of a protective coating by eye and should not be trusted by unscrupulous suppliers who approve of the introduction of such additives into the granulate melt in the manufacture of the panel.
Thus, they are trying to sell low-quality material suitable only for internal work.

The sheet size most suitable for the greenhouse
The industry produces two main types of panels dimensions, which depend on the thickness of the sheets. The sheet size of cellular polycarbonate is 2100 mm wide and 6000 and 12000 mm long, with a permissible deviation from the nominal value in the transverse direction of not more than 3 mm in the longitudinal not more than 10 mm. This must be considered when choosing a roofing material for a greenhouse.
In order to rationally and fully utilize the material without scraps and residues, the following factors should be considered in the manufacture of greenhouse frames:
1. It is recommended to make the length of the arcs of the power structure equal to 3, 4, 6 and 12 m, which will allow avoiding transverse joints between individual sheets.


2. The distance between the bearing elements is selected so that the joints are on the profiles. This significantly increases the strength of the roof of the greenhouse.
3. In the manufacture or selection of finished arcs, the minimum allowable radius of curvature, which depends on the thickness of the sheet, is taken into account.


4. When constructing greenhouses with pitched roofs and vertical walls, their sizes should be calculated so that a sheet of 6 or 12 m is divided without residues.
Taking into account all the above recommendations will allow you to build a strong and durable greenhouse, which during operation does not require repair and any additional costs.
Please note that the installation of cellular polycarbonate on the frame of the greenhouse is carried out in such a way that the honeycomb goes along the slope. At the ends of the greenhouse, the sheet is fixed so that the honeycombs go vertically. This will ensure the removal of condensate from the cells and extend the life of the material.
Polycarbonate sheet color for greenhouses
Cellular polycarbonate manufacturers offer a wide range of panels in different colors. The choice of color of polycarbonate sheets for greenhouses is determined primarily by the purpose of this structure. It produces plants that need sunlight of a certain spectrum and intensity.
For greenhouses and hotbeds, transparent honeycomb polycarbonate is used with maximum light transmission. For panels with a thickness of 4 and 6 mm, this figure is up to 85%. The use of painted sheets is impractical, since this negatively affects the development of plants and, ultimately, crop yields.
The procedure for choosing polycarbonate in the store
Before you go to the store to buy this material, you should decide what polycarbonate is needed for the greenhouse.
The customer must know exactly the following characteristics of the panels he needs:
Sheet thickness. Usually, cellular polycarbonate with a thickness of 4 to 10 mm is used for the construction of greenhouses, and its value is determined by the project. When choosing a material, you can measure this parameter using a vernier caliper. A significant deviation from the declared value in a smaller direction, as a rule, indicates a low quality sheet.
Light stabilizing coating. Particular attention should be paid to the presence of a protective coating against ultraviolet radiation from the purchased cellular polycarbonate. It is possible to verify this only in documents and find this information in the certificate of conformity. In addition, the protective film indicates which side of the sheet should face the sun.
Material color. For the installation of greenhouses it is necessary to use exclusively transparent cellular polycarbonate.
The required number of panels of different sizes. Check with the seller for the size of the material you need.
The acquisition of high-quality cellular polycarbonate will allow the construction of a reliable greenhouse suitable for seasonal or year-round use. It should be remembered that cheap materials are usually made from recycled or low-quality raw materials and in violation of technology. Little-known manufacturers also often offer products of dubious quality. Experts recommend buying cell polycarbonate of those brands that have proven themselves on the positive side.