Monolithic polycarbonate - technical characteristics, properties and application of the material
In modern construction, transparent materials are widely used, often completely forming the appearance of buildings. Along with ordinary glass, monolithic polycarbonate properties are also widespread, and the use of which makes it possible to create unique building structures. This plastic has excellent technical characteristics, which makes it indispensable for the construction of structures for various purposes.

Content:
- What is monolithic polycarbonate?
- The ratio of monolithic polycarbonate to temperature
- Chemical resistance of the material
- Mechanical strength of polycarbonate ISO 527
- Sheet thickness and specific gravity
- UV resistant
- Fire performance
- Lifetime
- Environmental parameters
- Light transmission
- Thermal insulation
- Soundproofing
- Moisture resistant
- Panel colors
- Appointment and scopes of monolithic polycarbonate
- The complexity of mounting structures made of monolithic polycarbonate
What is monolithic polycarbonate?
This material was first obtained at the end of the 19th century as a by-product in the synthesis of drugs for pain relief. A quite natural question arises: what is monolithic polycarbonate, and what properties does it have? It is insoluble in water and many other liquids in terms of transparency and can compete with high-quality silicate glass.
Monolithic polycarbonate technical characteristics, which are at the highest level, belong to the group of thermoplastics. The most widely used aromatic compounds synthesized from bisphenol A. In turn, this substance is obtained by condensation of the relatively inexpensive components of acetone and phenol. This circumstance makes possible its widespread use in construction and other fields.
Monolithic polycarbonate is supplied to the consumer in the form of sheet material with a thickness of 1 to 12 mm in a standard size of 205 × 305 mm. By special order it is possible to manufacture panels with other geometric parameters while maintaining the width. This limitation is related to the standard dimensions of the extruder used to make the polymer.
The industrial production of monolithic polycarbonate is carried out in accordance with TU 6-19-113-87. This provides the material with the necessary characteristics in the following parameters: tensile strength, impact strength and resistance to low and high temperatures. Currently, the nomenclature of polycarbonates produced in our country and abroad consists of dozens of items.
In this list, the following grades of this material, different in some properties and characteristics:
- PC-005 and PC-003 refers to high viscosity polymers, until recently PK-1.
- PC-007 medium-viscosity thermoplastic replaced the polycarbonates PK-2 and PK-LT-10.
- RS-010 material with low viscosity previously designated PK-LT-12 and PK-3.
- PK-LT-18-m thermostabilized panels painted in black (until recently, PK-4).
- PK-5 - a material specially developed for medical purposes, is used along with imported monolithic polycarbonates.
- PK-6 - sheets for optical devices and lighting structures.
- PK-LST-30 - a material with a filler made of silicon or quartz glass (former designation PK-LSV-30 and PK-NKS).
- PK-M-1 - panels with a minimum coefficient of friction of the surface.
- PK-M-2 - high resistance to microcracking and excellent fire-fighting properties. Currently has no analogues in the world.
- PK-TS-16-OD - material belonging to the highest category in terms of resistance to open flame and high temperatures. Panels are specifically designed for structures with stringent fire protection requirements.
In addition to transparent monolithic polycarbonates, the industry offers the consumer panels with a low degree of light transmission of various colors.
The ratio of monolithic polycarbonate to temperature
Resistance indicators of polymer panels to climatic conditions are determined by the relevant Russian and international standards. Monolithic polycarbonate has significant frost resistance, it can be used for the manufacture of outdoor structures. The latter can be used at temperatures up to - 50 ° C provided that there are no mechanical loads, at - 40 ° C this material can withstand even shock.
The heat resistance of most grades of polycarbonates is up to + 120 ° C. For individual samples, this figure reaches +150 ° C. Like all materials, when the polymer is heated in size, the coefficient of thermal linear expansion is determined by a special technique. For monolithic polycarbonate, its value is 6.5 × 10-5 m / ° C, which allows it to be used for the manufacture of critical outdoor structures. They successfully operate in conditions with significant temperature differences.
Chemical resistance of the material
Monolithic polycarbonate is a polymer that can effectively withstand destructive environmental factors. The material is inert with respect to many aggressive media, and this ability depends on temperature and concentration of substances.
The panels are highly chemical resistant to the following compounds:
- Organic and inorganic acids and solutions of their salts.
- Reducers and oxidizing agents of various types.
- Alcohols and synthetic detergents.
- Organic fats and fuels and lubricants.
However, some chemical compounds are able to react with the polymer, which leads to the gradual destruction of the panels.
For the convenience of the reader, information about the resistance of polycarbonate to certain liquids is presented in table form:
| Acetic acid | + | Hexane | + |
| Salt | + | Hydrogen peroxide, concentration up to 30% | + |
| Butyl alcohol | + | Gasoline, diesel and mineral oils | + |
| Ethanol | + | Ammonia | – |
| Hydrochloric acid, up to 20% | + | Butyl acetate | – |
| Propane | + | Diethyl alcohol | – |
| Boric acid | + | Methyl alcohol | – |
| Potassium permanganate, max. conc. 10% | + | Alkaline solutions | – |
| The “+” sign in the table indicates the resistance of the material to prolonged exposure to the specified substance. | |||
Mechanical strength of polycarbonate ISO 527
The panels are characterized by their ability to withstand a wide variety of loads for a significant period of time. Polycarbonate certification in terms of mechanical strength is made in accordance with the requirements of Russian, American and international standards.
The advantages of this material include the following:
- The bending strength of the polymer is checked according to ISO 178 and amounts to 95 MPa, depending on the grade.
- The elastic modulus in this test is in the range of 2600 MPa.
- The tensile strength of the sheet when tested for tearing in accordance with ISO 527- up to 60 MPa.
- The elastic modulus at such loads is up to 2200 MPa with relative elongation of the sample in some cases reaches 100%.
- The viscosity of monolithic polycarbonate when tested using the Charlie method for products with an incision of a certain depth is not more than 30 - 40 kJ / m².
- A similar indicator for Izod is in the range from 600 to 800 J / m.
Polycarbonate sheet is highly resistant to impact. So, during the tests without preliminary incision of the material, it remained intact at maximum loads achievable in the laboratory.Particularly durable panels are used for the manufacture of protective products and means to ensure the safety of citizens and law enforcement officials.
Monolithic polycarbonate, unlike glass, can bend under normal environmental conditions. The indicated property of the material is widely used in the manufacture of various kinds of rounded structures: canopies, fences and the like. This quality is characterized by a limiting bending radius, which depends on the thickness of the sheet.
Detailed information on this issue is presented on the chart:
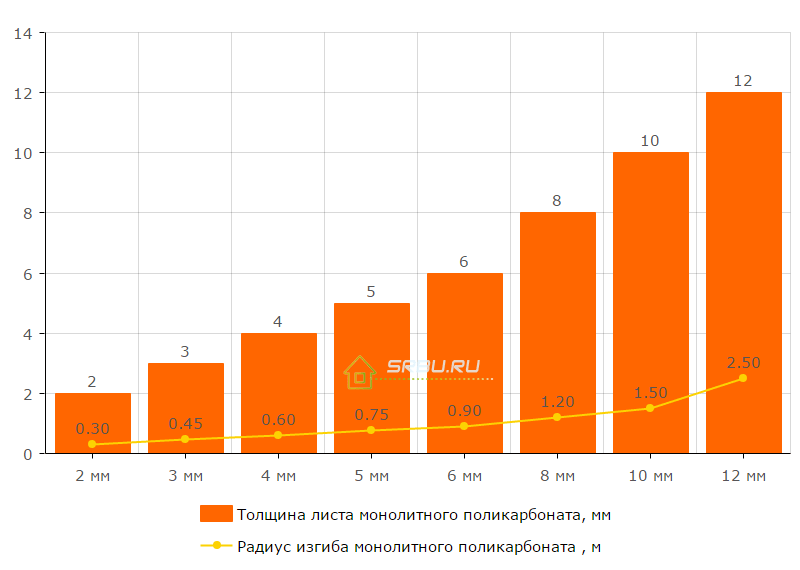
Dependence of the maximum possible bending radius on the thickness of a sheet of monolithic polycarbonate.
Sheet thickness and specific gravity
The industry offers an extensive range of transparent and opaque panels in a wide variety of colors. Monolithic polycarbonate characteristics, which are unique in many respects, have a density of 1200 kg / m3. This is significantly lower than that of window glass, which has more than twice the specific gravity. This circumstance makes it possible to greatly facilitate many building structures, provided that their mechanical strength is maintained at an appropriate level.
Knowledge of such an indicator as the weight of one square meter of monolithic polycarbonate is necessary to determine the mass of roofing material during the design and construction work.
The mass value of the monolithic polycarbonate will depend on the thickness of the sheet of material:
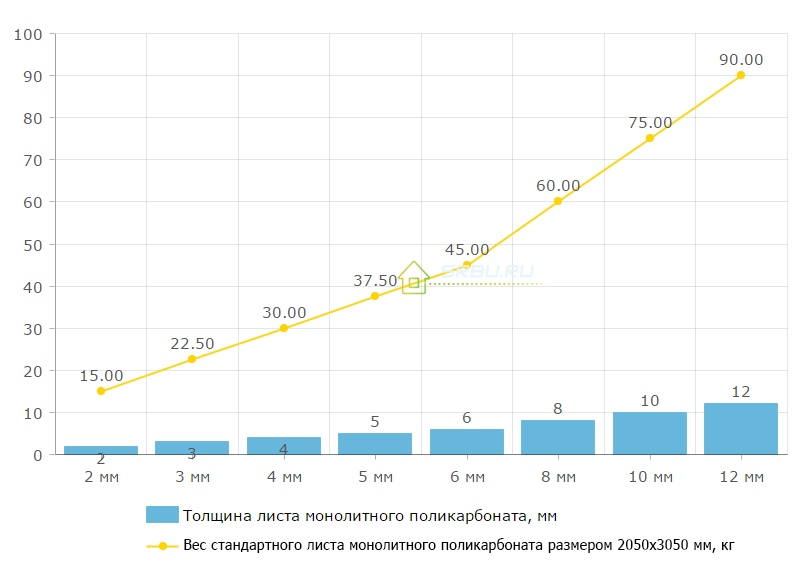
Dependence of the weight of a standard sheet of monolithic polycarbonate, size 2050x3050 mm, on its thickness.
UV resistant
Monolithic polycarbonate panels have selective light transmission. To achieve this effect, a protective coating is applied to the sheet surface by extrusion. The thickness of this layer is sufficient to delay and absorb radiation from the ultraviolet part of the spectrum, while visible and soft infrared light freely penetrates through the barrier. Depending on the brand of the board, a protective coating is applied on one or both sides.
The extrusion technology used eliminates the possibility of delamination from the base due to the interpenetration of materials. Another technology to protect the panel from exposure to UF radiation is to use special additives of stabilizers in the volume of plastic. This method of polymer protection is more expensive, but its effectiveness is much higher.
To protect monolithic polycarbonate from damage during storage and transportation, it is glued with a plastic film. It indicates the brand of the panel and the side on which the protective coating is applied. The film is removed directly during installation or immediately after it, otherwise it will be difficult to remove it from the surface of the panel.
Fire performance
Polycarbonate under the influence of an open flame and when a certain temperature is exceeded, begins to melt and it ignites. Upon termination of external exposure, this process spontaneously fades. Panels made of polymer material have the following features in terms of ensuring fire safety:
- resistance to high temperatures and open flame;
- during combustion, smoke formation is minimal;
- combustion products are not toxic;
- the oxygen index of the material is 28-30%.
Monolithic polycarbonate belongs to the category of self-extinguishing materials. This allows it to be classified as fire safety category V-1 (B1) in accordance with the requirements of UL-94 and DIN 4102 standards. Moreover, no flame retardants and other additives are used in the production process.
Lifetime
Monolithic polycarbonate panels are made of granules by extrusion or injection molding.
The life of this material is determined by the following factors:
- quality of raw materials and compliance with the technical conditions of manufacture;
- correct installation;
- climatic conditions and exposure to adverse environmental factors.
Different manufacturers declare their terms of use of the material, while the minimum figure exceeds 10 years. Studies conducted in a specialized laboratory showed long-term exposure (more than 2000 hours) causes a decrease in panel permeability of less than 10%. This corresponds to approximately 20 years of polycarbonate exploitation in the desert regions of Arizona or Israel.
Environmental parameters
As mentioned above, monolithic polycarbonate is produced from raw granulate on special equipment with a closed technological cycle. This method of manufacturing panels allows you to minimize negative environmental impacts. The material itself is characterized by chemical inertness and does not emit any harmful and dangerous substances for humans and animals.
Monolithic polycarbonate according to its environmental characteristics is recommended for indoor use. Special brands of panels are made specifically for use in medicine and the pharmaceutical industry. Allow the use of this material in construction to perform exterior and interior decoration.
Light transmission
The industry produces several types of polycarbonate with different indicators of permeability to sunlight and artificial lighting. In terms of light transmission, transparent panels have the following indicators from 86 to 89%. In this case, the introduction of special additives into the material allows one to change the optical properties of the material and achieve maximum absorption of the ultraviolet rays of the spectrum.
Other optical indicators of polycarbonate characterize the degree of its transparency. Thus, the yellowness index for colorless samples is not more than one unit, and the degree of turbidity does not exceed 0.5%. Panels made of this polymer are in no way inferior to silicon glass, and along with other advantages, they retain their characteristics throughout the entire life cycle.
Thermal insulation
Monolithic polycarbonate does not belong to the category of materials designed to reduce energy losses through building envelopes. However, these panels have lower thermal conductivity than ordinary window glass. For polycarbonate, this characteristic has a value of 0.2 W / mK, the measurements were carried out according to the method approved by the DIN 52612 standard. Window glass also has a large thermal conductivity.
It should be borne in mind that the insulating properties of the material increase with increasing thickness. So, ceteris paribus, a sheet of monolithic polycarbonate of 8 mm is almost 20% more effective than similar glass. An even greater difference is observed when installing two or more panels with an air gap between them. In recent years, this polymer is increasingly used in double-glazed windows instead of traditional glass.
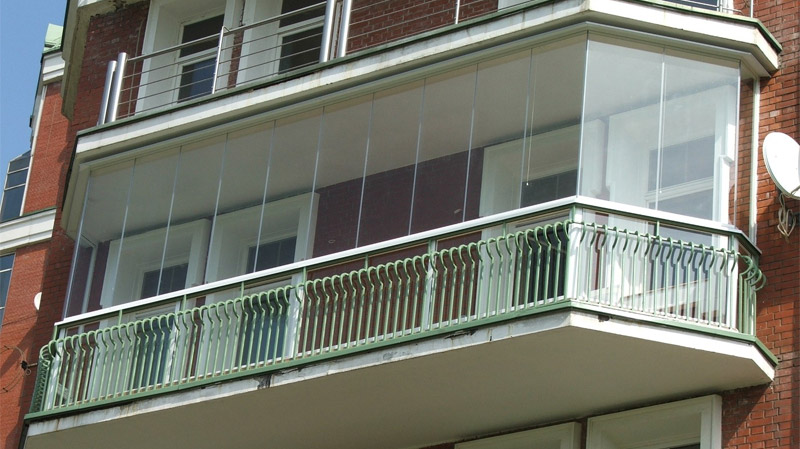

The balcony is glazed with monolithic polycarbonate.
Soundproofing
Monolithic polycarbonate has a viscous internal structure of the plate and, due to this feature, is able to effectively absorb sounds. According to the measurement results, the sound insulation level for plates with a thickness of 4 to 12 mm ranges from a minimum value of 18 dB and a maximum value of 23 dB.
Monolithic polycarbonate has a lower density than window glass and, as a result, can significantly attenuate sound waves, especially in the low-frequency range. This property of the material allows it to be used for the manufacture and installation of sound-absorbing screens along busy roads.
Moisture resistant
Monolithic polycarbonate is non-hygroscopic, in other words, the polymer does not absorb water. This property makes it possible to use it in rooms with high humidity in greenhouses, hotbeds, pools and other structures of this kind.To prevent condensation on the inner surface of the plate during the production process, a special polymer film can be applied. Special grades of material are marked on the protective film and are installed inside the coating during installation.
Panel colors
Manufacturers of monolithic polycarbonate offer their customers, in addition to transparent sheets, also painted ones. In different companies, the color gamut of plates may differ significantly from the products of competing enterprises.
The most common are the following plate colors:
Panel coloring is carried out by introducing pigment into the mass of material immediately before molding. This technology provides high color uniformity and significant durability. The coloring composition is evenly distributed throughout the panel, which prevents it from burning out. Individual companies producing this material also offer other custom color solutions.
Appointment and scopes of monolithic polycarbonate
Transparent and painted plastic panels are becoming increasingly popular among consumers and are increasingly becoming a replacement for silicate and quartz glass. Monolithic polycarbonate, whose use in construction is constantly expanding, is in demand in other industries.
The main areas of use for transparent and painted panels are as follows:
1. The manufacture of light domes in buildings and on the street.
2. Glazing of vertical surfaces in the construction of residential buildings and public buildings.
3. The device of canopies, peaks above the entrance doors and bus stops.
4. Glazing of terraces and other structures of complex shape with bending panels.
5. The device of domes over outdoor pools.
6. Production of sound-absorbing barriers along the highways, which can significantly reduce the noise level.
7. Production of greenhouses, hotbeds and conservatories.
8. Installation of partitions in offices, trade, museum and exhibition halls, as well as in industrial enterprises.
9. Production of outdoor advertising media and displays in stadiums, train stations and other public places.
10. The device of transparent floors with backlight.
11. Protections for stairs and balconies.
12. Installation of protective barriers over the sides of hockey pitches.
In recent years, the scope of application of monolithic polycarbonate panels has been expanding more and more. The material is also used in medical institutions for the installation of boxes with sterile conditions and the production of other special equipment.
The complexity of mounting structures made of monolithic polycarbonate
This material is simple and convenient in the manufacture, molding and fastening of parts. To work with monolithic polycarbonate, manual or electric tools with a steel cutting surface can be used. It is important that circular or band saws have the correct sharpening. For professional use, carbide tipped or carbide tipped tools are recommended with cooling of the cutting site or drilling with compressed air.
In the manufacture of structures from monolithic polycarbonate, the following methods of processing the material are allowed:
- Milling.
- Cutting with a circular saw, band saw or scissors.
- Drilling or punching holes with a special device.
- Laser cutting of material.
Monolithic polycarbonate sheets can be cold and hot formed. In this case, the minimum permissible bending radius should be 150 times the thickness of the panel. Sheet rounding should be done exclusively along the extrusion line. The correct bending direction must be indicated on the protective film, which is removed during installation.
Fastening sheets to building structures can be carried out using self-tapping screws with a press washer and polymer or rubber gaskets.Separate panels are interconnected using special solvents, welding and other methods. Correct installation of monolithic polycarbonate provides the possibility of its use throughout the entire life cycle.