How to prepare concrete: material requirements, proportions and composition calculation
Concrete is a building material consisting of a binder, sand and fillers, which, as a result of hardening, turns into stone. Not a single modern construction site can do without concrete, be it the construction of skyscrapers or the creation of garden paths. Due to its properties and durability, concrete has long been used by humans in order to obtain the design of the necessary shape and strength. However, there is one caveat: only properly made concrete will meet all the requirements. How to make concrete that is not only strong, but also durable? Let's dig into the essence of this issue, and find out all the details of making the right concrete mix.

Content:
The most important ingredient is cement.
In concrete of any brand, cement necessarily acts as a binder. There are many varieties of cements, such as Portland cement, slag Portland cement, quick-hardening cements and others. All of them differ in both the quality of binding and the conditions of use of the final product. Most often, Portland cement is used in construction. All cements used for construction are divided into grades, which indicate the maximum load on the finished product in megapascals. In domestic - the letter D and a figure indicating the percentage of impurities are still added. For example, Portland cement M400-D20 is a material, the finished product of which can withstand a load of 400 MPa, containing up to 20% of impurities.
Data on the grades of cements required to obtain a given grade of concrete under normal hardening conditions:
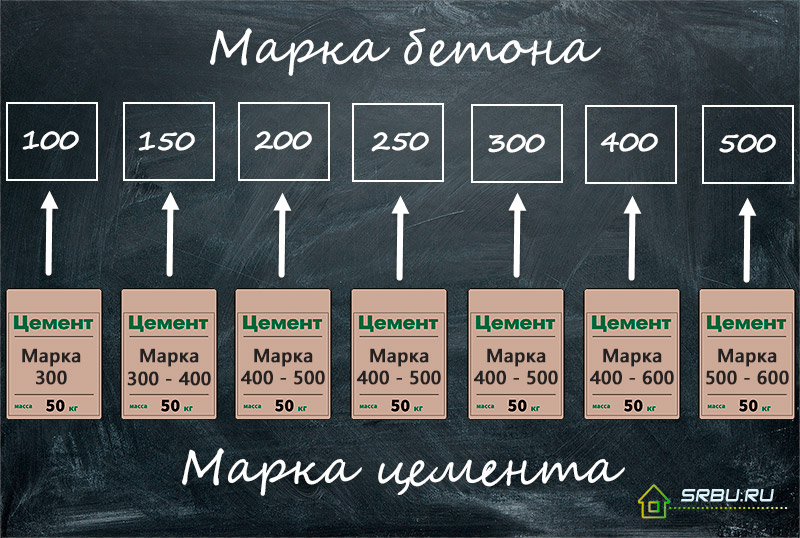
In the manufacture of concrete of high grades, 300 and above, for economic reasons, it is necessary to use a cement grade, which is 2 to 2.5 times higher than the concrete grade.
In household construction, Portland cement of brand 400 is often used - its strength is quite enough for these purposes. In industrial construction - 500 grade cements are most often used, and where high loads are expected - special cements of high grades. In order to correctly calculate the proportions of concrete, you must have accurate information about the brand and quality of the cement from which you are going to build.
Another important aspect is freshness - cement has an expiration date and loses its properties over time. Fresh cement is crumbly dust, without lumps and seals. If you see that there are dense pieces in the mass of cement, then you should not use such cement in your work - it has absorbed moisture and has already lost its binding properties.
Sand - what happens and what is needed
Sand can also be different. Moreover, the final result directly depends on the quality of this component.
According to particle size distribution, sands are divided into:
In the manufacture of concrete, all types of sand are used, however, if there is a lot of dust or clay particles in the sand, this can significantly degrade the characteristics of the mixture. This is especially true for thin sand, which contains a significant percentage of dust, it is unsuitable for concrete preparation and is used in the most extreme case.
How to prepare concrete of good quality, and at the same time not to lose money with sand? It's simple - you should use sea or river sand - these are the purest types of building material that do not carry dust particles or clay. Care must be taken to ensure that the sand is clean and free of organic contaminants.Career sand can be very dirty - it is often not used in a construction site without preliminary preparation, including washing and settling. It can also contain a lot of organic debris - the roots, leaves, branches and bark of trees. If such impurities get into concrete, voids in the thickness may appear, as a result of which, strength suffers.
Another important parameter to consider is sand moisture. Even dry-looking material may contain up to 2% water, and wet - all 10%. This can disrupt the proportions of concrete, and cause a decrease in strength in the future.
Crushed stone and gravel are the most popular aggregates for concrete
The main filler for concrete of all grades is crushed stone or gravel - crushed rock. Most often used crushed stone. It is also divided into fractions, and has a rough, uneven surface. When choosing the composition of concrete, it should also be taken into account that sea or river pebbles cannot serve as a substitute for crushed stone, since a smooth, water-polished surface significantly worsens the adhesion of the stone to the rest of the mixture components.
Crushed stone is divided into the following fractions:
In order for your concrete to stand for many years and not collapse, it should be remembered that the maximum size of the stones in the gravel should not exceed 1/3 of the minimum thickness of the future product.
They also take into account such an indicator as the voidness of the filler - the amount of empty space between the stones of rubble. It is simple to calculate it - take a bucket of known volume, fill it with crushed stone to the edges, and pour water into it with a measured capacity. Knowing how much fluid has entered, we can calculate the voidness of the rubble. For example, if 4 liters of water got into a 10 liter bucket of gravel, then the emptiness of this gravel is 40%. The smaller the voidness of the filler, the lower the consumption of sand, and, importantly, cement.
To maximize the filling of voids, various fractions of crushed stone should be used: small, medium, large. It should be borne in mind that the fine fraction should be at least 1/3 of the total volume of crushed stone.
In addition to granite gravel and gravel, depending on the purpose of the concrete, claydite, blast furnace slag, as well as other fillers of artificial origin are used. For lightweight concrete, wood chips and ground polystyrene foam are used. For ultralight concrete - gases and air. However, the creation of light and ultralight concrete is fraught with a number of difficulties, and it is unlikely that it will be possible to correctly produce such a product outside the industrial workshop.
Depending on the density, all aggregates for concrete are divided into porous (<2000 kg / m3) and dense (> 2000 kg / m3) Also, do not forget that natural fillers have a small radiation background, which is inherent in all granite rocks. Of course, this is not a source of radiation pollution, but still it is worth remembering such a property of natural stone as a filler of concrete.
Water - requirements for concrete preparation
Water is no less important component than cement or sand. One simple truth can be taken as a rule - any water suitable for drinking is also suitable for mixing concrete. In no case can you use water from an unknown source, waste water after production, swamp and other water, of which you are not sure. The chemical composition and other indicators of water can greatly affect the strength characteristics of the finished concrete.
Table No. 1. Water consumption (l / m3) with different grains of filler:
| Concrete ductility level | Gravel | Crushed stone | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mm | 20 mm | 40 mm | 80 mm | 10 mm | 20 mm | 40 mm | 80 mm | |
| Very plastic | 215 | 200 | 185 | 170 | 230 | 215 | 200 | 185 |
| Medium plastic | 205 | 190 | 175 | 160 | 220 | 205 | 190 | 175 |
| Low ductility | 195 | 180 | 165 | 150 | 210 | 195 | 180 | 165 |
| Not plastic | 185 | 170 | 155 | 140 | 200 | 185 | 170 | 155 |
It is important to remember that calculating the composition of concrete includes all the moisture present in building materials before mixing them. If, for example, you have blast furnace slag planned as a filler, then its moisture content also matters - in fact, it is “excess” water, which is difficult to take into account, but it simply spoils the finished solution.
Another important indicator depends on the amount of water - the plasticity of the finished concrete.To obtain plastic concrete, water must be added strictly according to the norm. Exceeding the required norm is also harmful, as well as lack of water - concrete is stratified, and loses its quality. When mixing concrete mixture, the plasticity of concrete is determined by the "eye". If concrete spontaneously slides from a horizontally located bayonet spade, then it is considered very plastic. If it slides off a shovel only with a slight slope, then concrete is considered medium plastic. If concrete does not slip, even with an inclined shovel, it is considered slightly plastic. When concrete lies on a shovel with a tubercle, it is considered not plastic. It is impossible to make concrete too liquid as it loses its qualities.
Strength and concrete grade
Concrete brand is the ability of the finished product to withstand a load of 1 cm2 without damage. The brand of concrete is determined on the 28th day after its manufacture. The thing is that concrete gains its strength most quickly within 7 days. During this time, it can gain up to 40% strength. After 7 days, a good set of strength lasts up to 28 days. After 28 days, the set of strength decreases sharply, but continues for some time.
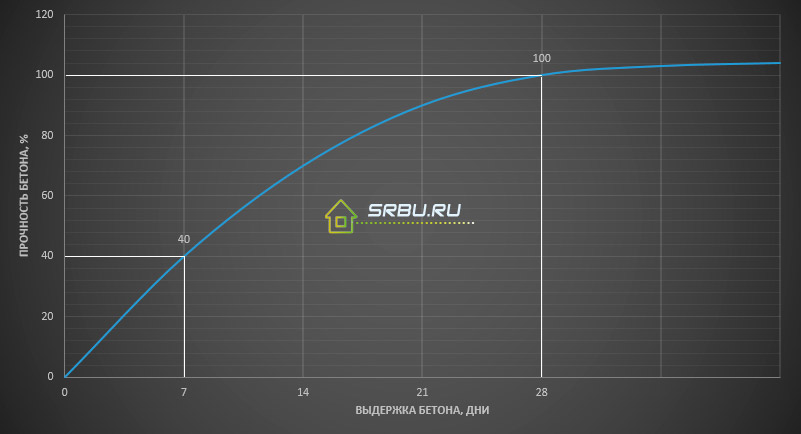
The graph of the set of concrete strength, under normal conditions.
How to calculate the composition of concrete
In order to correctly calculate the composition of concrete, it is important to have certain data.
These include:
- The required grade of concrete;
- The desired plasticity of the mixture;
- Brand of cement;
- Data on the particle size distribution of sand and gravel.
There are two ways to calculate the composition of concrete - by the weight ratio of cement, sand and gravel and the volume ratio of these materials. And in the first and second case, cement is always taken as a unit (for one part), and all other components of the concrete mix as a part of the weight or volume of cement.
Calculation of concrete composition by weight
We will calculate the composition to obtain concrete of medium ductility, the strength grade of which for 28 days will be M200.
Suppose we have:
- Portland cement M400;
- Crushed stone of the middle fraction;
To begin with, we need to determine the water-cement ratio (W / C). W / C is the proportion of the weight of water and cement, which is necessary for the preparation of concrete of a certain strength. This indicator is determined by formulas or empirically. We offer the already found H / C values, which are collected in a table.
Table No. 2. V / C values for various grades of concrete.
| Stamps cement | Concrete grades | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 400 | ||
| 300 | 0,75 | 0,65 | 0,55 | 0,50 | 0,40 | - | |
| 0,80 | 0.70 | 0.60 | 0.55 | 0.45 | - | ||
| 400 | 0,85 | 0,75 | 0,63 | 0,56 | 0,50 | 0,40 | |
| 0,90 | 0,80 | 0,68 | 0,61 | 0,55 | 0,45 | ||
| 500 | - | 0,85 | 0,71 | 0,64 | 0,60 | 0,46 | |
| - | 0,90 | 0,76 | 0,69 | 0,65 | 0,51 | ||
| 600 | - | 0,95 | 0,75 | 0,68 | 0,63 | 0,50 | |
| - | 1 | 0,80 | 0,73 | 0,68 | 0,55 | ||
Knowing the necessary brand of concrete and the brand of cement used, we find the value of V / C. In this case, it will be 0.63.
Now from table No. 1 we find the necessary amount of water to obtain concrete of medium ductility, with a crushed stone size of 40 mm. As a result, we get the value of 190 l / m3.
After that, we can calculate the amount of cement we need per 1m3 concrete. For this 190 l / m3 divide by 0.68 and get 279 kg. cement. From table No. 3 we find the proportions of the concrete mix for the required concrete grade M200 and cement grade M400.
Table No. 3. Weight ratios of cement, sand and gravel.
| Concrete grade | Portland cement brands | |
|---|---|---|
| 400 | 500 | |
| Proportions by weight, Cement: Sand: Rubble |
||
| 100 | 1 : 4,6 : 7,0 | 1 : 5,8 : 8,1 |
| 150 | 1 : 3,5 : 5,7 | 1 : 4,5 : 6,6 |
| 200 | 1 : 2,8 : 4,8 | 1 : 3,5 : 5,6 |
| 250 | 1 : 2,1 : 3,9 | 1 : 2,6 : 4,5 |
| 300 | 1 : 1,9 : 3,7 | 1 : 2,4 : 4,3 |
| 400 | 1 : 1,2 : 2,7 | 1 : 1,6 : 3,2 |
| 450 | 1 : 1,1 : 2,5 | 1 : 1,4 : 2,9 |
The ratio of C: P: U will be 1: 2.8: 4.8. If cement we need 279 kg, then 279 × 2.8 = 781 kg. sand and 279 × 4.8 = 1339 kg. crushed stone. Total it turns out that for the preparation of 1 m3 concrete of medium ductility and grade M200 from Portland cement M400 and crushed stone of medium fraction, it is necessary:
 279 kg cement.
279 kg cement.
 781 kg. sand.
781 kg. sand.
 1339 kg. crushed stone.
1339 kg. crushed stone.
 190 l water.
190 l water.
At home, a 10 liter bucket is often used to measure various bulk materials. To make it easier for you to measure materials, we will provide data on the mass of a particular material contained in one 10 liter bucket:
- Cement - 13 - 15 kg, depending on the seal.
- Sand - 14 - 17 kg, depending on humidity.
- Crushed stone or gravel - 15 - 17 kg, depending on the size of the fraction.
It must be understood that the methodology of this calculation is slightly inferior to the methods used in the construction of large facilities, but this is much better than the principle - give more cement to get stronger.
In addition to applying proportions by weight, proportions of the composition of concrete by volume are also used. However, this method is less accurate.
Table No. 4. Volumetric ratios of cement, sand and crushed stone for concrete of different grades:
| Portland cement brand | Concrete grade | Proportions by volume, l | Concrete volume, l, at consumption of 10 liters. cement | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | Sand | Crushed stone | |||
| 400 | 100 | 1 | 4,1 | 6,1 | 78 |
| 150 | 1 | 3,2 | 5,0 | 64 | |
| 200 | 1 | 2,5 | 4,2 | 54 | |
| 250 | 1 | 1,9 | 3,4 | 43 | |
| 300 | 1 | 1,7 | 3,2 | 41 | |
| 400 | 1 | 1,1 | 2,4 | 31 | |
| 450 | 1 | 1,0 | 2,2 | 29 | |
| 500 | 100 | 1 | 5,3 | 7,1 | 90 |
| 150 | 1 | 4,0 | 5,8 | 73 | |
| 200 | 1 | 3,2 | 4,9 | 62 | |
| 250 | 1 | 2,4 | 3,9 | 50 | |
| 300 | 1 | 2,2 | 3,7 | 47 | |
| 400 | 1 | 1,4 | 2,8 | 36 | |
| 450 | 1 | 1,2 | 2,5 | 32 | |
| The amount of water is not indicated and depends on the required consistency and plasticity of concrete. | |||||
How to mix concrete
There is both a manual kneading method and a mechanized one - using concrete mixers and mixers.
Manual way of mixing concrete
Let's consider the manual method of kneading, as the most popular in home construction. For the correct mixing of the mixture, a container is needed in which all components will be mixed. This can be either an ordinary tin can or a specially assembled container. All the sand necessary for kneading is poured into it and cement is poured into the furrow in the middle. After carefully sand is mixed with cement, until a homogeneous gray mass is obtained. Then the resulting material is moistened with water, and again well mixed. Crushed stone is added later and the mixture is mixed until the solution covers each stone of the filler. At the same time, water is added little by little, the amount of which depends on the required plasticity. After the mixture becomes homogeneous, and all the stones of the filler are covered with a solution, the concrete is ready for laying.
With the manual method of kneading, there is one important point, namely, the speed of laying concrete. Even with a slight delay, the concrete in the trough may delaminate (it looks like water protruding from above), and lose some of its properties. Therefore, it is important to quickly lay concrete in the formwork.
The best option for how to prepare concrete would be a mechanical way of mixing using a concrete mixer. The advantages of this method will be to obtain a guaranteed homogeneous mixture and high quality concrete.

Mixing of concrete in a concrete mixer
For kneading in a concrete mixer, cement is first poured and a minimum of water is poured. Having obtained a homogeneous emulsion, sand is added to the mixer based on the proportion. Next, the solution intervenes with the addition of the required amount of water. After receiving the solution, the filler can be poured into the concrete mixer.
The advantage of the mechanical method of kneading is that the concrete does not delaminate, and can remain in a rotating mixer for up to one hour without losing its properties. However, the mixer should not be placed far from the place of installation - in order to avoid the loss of concrete properties during delivery.

Following these simple rules, you will get a reliable structural material, which will become stronger over the years!










